Data warehousing involves collecting, storing, and managing large volumes of data from diverse sources to support business intelligence and decision-making processes. Efficient data warehousing enhances data quality, accessibility, and analysis speed, empowering your organization to gain valuable insights and achieve competitive advantages. Explore the rest of this article to understand key concepts, benefits, and best practices in data warehousing.
Table of Comparison
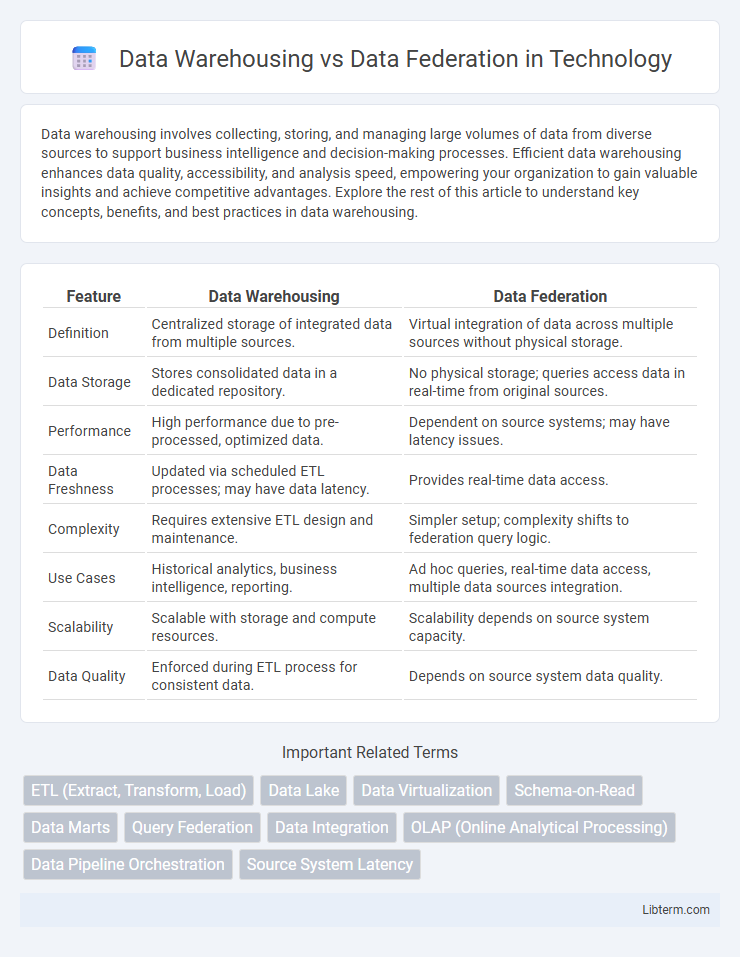
| Feature | Data Warehousing | Data Federation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized storage of integrated data from multiple sources. | Virtual integration of data across multiple sources without physical storage. |
| Data Storage | Stores consolidated data in a dedicated repository. | No physical storage; queries access data in real-time from original sources. |
| Performance | High performance due to pre-processed, optimized data. | Dependent on source systems; may have latency issues. |
| Data Freshness | Updated via scheduled ETL processes; may have data latency. | Provides real-time data access. |
| Complexity | Requires extensive ETL design and maintenance. | Simpler setup; complexity shifts to federation query logic. |
| Use Cases | Historical analytics, business intelligence, reporting. | Ad hoc queries, real-time data access, multiple data sources integration. |
| Scalability | Scalable with storage and compute resources. | Scalability depends on source system capacity. |
| Data Quality | Enforced during ETL process for consistent data. | Depends on source system data quality. |
Introduction to Data Warehousing and Data Federation
Data warehousing consolidates large volumes of structured data into a centralized repository optimized for query performance, analytics, and historical reporting. Data federation integrates data from multiple distributed sources in real-time without physical storage, providing a unified virtual view for faster access and operational agility. Understanding the differences between data warehousing and data federation helps organizations choose the best strategy for efficient data management and decision-making.
Core Concepts: What is Data Warehousing?
Data warehousing involves collecting, storing, and managing large volumes of structured data from multiple sources into a centralized repository designed for query and analysis. It uses ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes to ensure data consistency, quality, and integration, supporting complex reporting and business intelligence tasks. Unlike data federation, which provides real-time access without physically consolidating data, data warehousing physically stores integrated data optimized for performance and historical analysis.
Core Concepts: What is Data Federation?
Data federation is a data integration technique that provides a unified virtual view of data from multiple disparate sources without physically moving or consolidating the data. It enables real-time querying and analysis by dynamically aggregating data from different databases, applications, or platforms through a middleware layer. Unlike data warehousing, which stores data in a centralized repository optimized for reporting and analytics, data federation focuses on on-demand data access and integration across heterogeneous systems.
Architecture Differences: Data Warehousing vs Data Federation
Data warehousing architecture centralizes data storage by extracting, transforming, and loading (ETL) information into a single repository optimized for fast querying and analysis. In contrast, data federation architecture provides a virtualized data access layer that integrates multiple heterogeneous data sources in real time without physical data movement. Data warehousing supports complex analytics through consolidated datasets, while data federation emphasizes agility and real-time access across distributed systems.
Data Integration Approaches
Data warehousing consolidates data from multiple sources into a centralized repository optimized for query performance and long-term storage, enabling complex analytics and historical reporting. Data federation provides a virtual integration layer that queries disparate data sources in real-time without physically moving data, supporting agile access to up-to-date information across heterogeneous systems. Choosing between data warehousing and data federation depends on factors like latency requirements, data volume, query complexity, and the need for a single source of truth versus real-time data access.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Data warehousing centralizes data into a single repository, enabling optimized query performance through indexing, partitioning, and pre-aggregation, which enhances scalability by handling large volumes of historical data efficiently. Data federation queries multiple heterogeneous data sources in real-time without data movement, offering flexible access but often suffering from latency and limited scalability due to network bottlenecks and source system constraints. While data warehousing supports complex analytical workloads with consistent high performance, data federation favors agility and real-time integration at the potential cost of slower response times and scalability challenges under heavy query loads.
Use Cases for Data Warehousing
Data warehousing excels in use cases requiring centralized data storage for complex analytics, historical reporting, and data consolidation from multiple sources into a single repository. It supports enterprise-wide business intelligence, batch processing, and enhances data quality through structured integration and transformation processes. Ideal for scenarios demanding high query performance and consistent, governed datasets, data warehousing enables strategic decision-making across finance, sales, and operations.
Use Cases for Data Federation
Data Federation excels in use cases requiring real-time data integration from multiple heterogeneous sources without physical data movement, such as operational analytics and unified data access for agile decision-making. It is ideal for scenarios demanding on-the-fly data aggregation across distributed databases, enabling seamless querying across cloud platforms, enterprise applications, and legacy systems. Organizations leverage Data Federation to support dynamic reporting and ad-hoc analysis where latency and data duplication must be minimized.
Key Advantages and Limitations
Data Warehousing offers centralized data storage that ensures data consistency, improved query performance, and historical data analysis but requires significant storage resources and complex ETL processes. Data Federation provides real-time data access across multiple systems without data duplication, facilitating agile decision-making while facing challenges in query performance and data consistency due to distributed sources. The choice depends on the need for centralized data control versus real-time integration across heterogeneous systems.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Choosing between data warehousing and data federation depends on the business's data integration needs and query performance requirements. Data warehousing offers centralized storage for structured data, enabling complex analytics and historical reporting with high query speed. Data federation provides real-time access to distributed data sources without physical consolidation, ideal for businesses needing up-to-date data with lower latency and simpler implementation.
Data Warehousing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com