A hard start occurs when an engine ignites abruptly with excessive fuel or improper timing, causing rough operation and potential damage. This issue often results from cold conditions, faulty spark plugs, or carburetor problems that disrupt fuel-air mixture balance. Discover effective solutions to prevent hard starts and keep Your engine running smoothly in the full article.
Table of Comparison
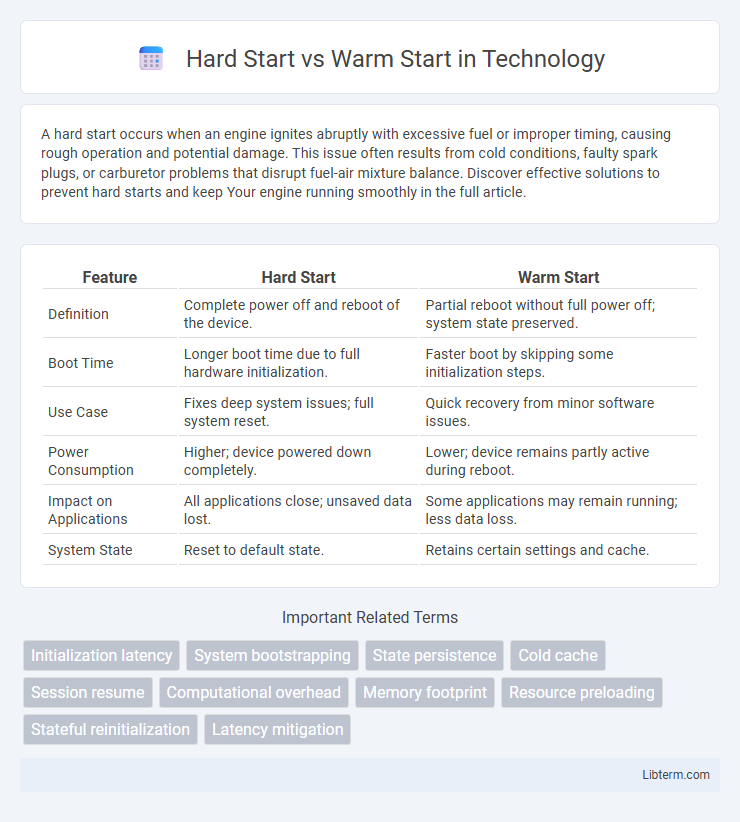
| Feature | Hard Start | Warm Start |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete power off and reboot of the device. | Partial reboot without full power off; system state preserved. |
| Boot Time | Longer boot time due to full hardware initialization. | Faster boot by skipping some initialization steps. |
| Use Case | Fixes deep system issues; full system reset. | Quick recovery from minor software issues. |
| Power Consumption | Higher; device powered down completely. | Lower; device remains partly active during reboot. |
| Impact on Applications | All applications close; unsaved data lost. | Some applications may remain running; less data loss. |
| System State | Reset to default state. | Retains certain settings and cache. |
Introduction to Hard Start and Warm Start
Hard start and warm start refer to different methods of initiating compressor systems. Hard start involves applying full power to a compressor motor from a complete stop, resulting in a high inrush current that can cause mechanical stress and electrical surges. Warm start, on the other hand, restarts the compressor when its components are still at partial operating temperature, reducing startup load and minimizing energy spikes.
Defining Hard Start
A hard start refers to the process of powering on a device or system from a completely powered-off state, where all components initialize from zero. This type of start involves a full boot sequence, including hardware checks, firmware loading, and system diagnostics, ensuring the system reaches a stable operational state. Hard starts typically take longer than warm starts because they reset all volatile memory and hardware settings.
Understanding Warm Start
Warm start in machine learning refers to initializing a model's training process using previously learned parameters, which accelerates convergence and improves performance by building on prior knowledge. This technique is advantageous in scenarios involving iterative training, fine-tuning pre-trained models, or adapting models to new but related datasets. Understanding warm start helps optimize resource usage and reduce training time compared to hard start, where training begins from random initialization without leveraging existing information.
Key Differences Between Hard Start and Warm Start
Hard start compressors deliver high starting torque and establish operational pressure rapidly, making them suitable for applications requiring immediate full power. Warm start compressors, conversely, initiate operation at reduced voltage and pressure, minimizing mechanical stress and energy consumption during startup. The key difference lies in startup behavior: hard start ensures quick and powerful engagement, while warm start focuses on gradual acceleration to enhance system longevity and efficiency.
Applications of Hard Start
Hard start methods are essential in applications requiring rapid motor acceleration, such as industrial machinery and heavy-duty compressors, where immediate torque is critical to overcome initial inertia. This approach is commonly used in HVAC systems and large pumps to minimize stalls and ensure reliable startup under load. Employing hard start capacitors enhances motor efficiency and reduces the risk of overheating in demanding operational environments.
Applications of Warm Start
Warm start techniques are widely applied in machine learning and optimization to accelerate convergence by initializing algorithms with prior solution information. This approach is particularly useful in real-time systems such as model predictive control, where time-sensitive decision-making benefits from reduced computation times. In large-scale data analysis and iterative solvers for complex problems, warm starting improves efficiency by leveraging previous iterations, enhancing overall performance in dynamic environments.
Pros and Cons of Hard Start
Hard start motors provide a high starting torque, making them ideal for heavy load applications such as compressors and pumps. However, they draw a large inrush current during startup, which can lead to voltage drops and increased mechanical stress on the motor components. Their robust construction ensures reliable performance under frequent starts, but this can result in higher energy consumption and increased wear compared to warm start motors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Warm Start
Warm start provides faster initialization by utilizing previously stored data to speed up convergence in optimization problems. It reduces computational cost and improves efficiency, especially in iterative algorithms, but may risk suboptimal solutions if prior information is inaccurate or poorly chosen. Warm starts are advantageous for large-scale or real-time systems but rely heavily on the quality of the initial guess, potentially limiting robustness compared to hard starts.
Choosing Between Hard Start and Warm Start
Choosing between hard start and warm start depends largely on application requirements and power availability. Hard start systems provide reliable ignition from a complete power-off state, ideal for environments needing full resets or encountering frequent interruptions, while warm start systems enable faster restarts by retaining some operational parameters, optimizing efficiency and reducing downtime in continuous-use scenarios. Evaluating factors such as cycle frequency, energy consumption, and system complexity guides the optimal choice for startup strategy in industrial or commercial settings.
Conclusion: Which Start Method is Right for You?
Choosing between hard start and warm start methods depends on your specific appliance type, usage frequency, and energy efficiency goals. Hard start devices provide a powerful surge to kickstart heavy motors quickly, ideal for older HVAC systems or units with high starting torque. Warm start methods offer smoother, energy-saving operation suited for newer, energy-efficient compressors, making them the preferred choice for reducing electrical strain and extending equipment lifespan.
Hard Start Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com