Protocols establish standardized rules and procedures that enable effective communication and data exchange across networks or systems. Understanding the specific protocol relevant to your technology can enhance security, efficiency, and compatibility. Explore the detailed insights in this article to master how protocols impact your digital interactions.
Table of Comparison
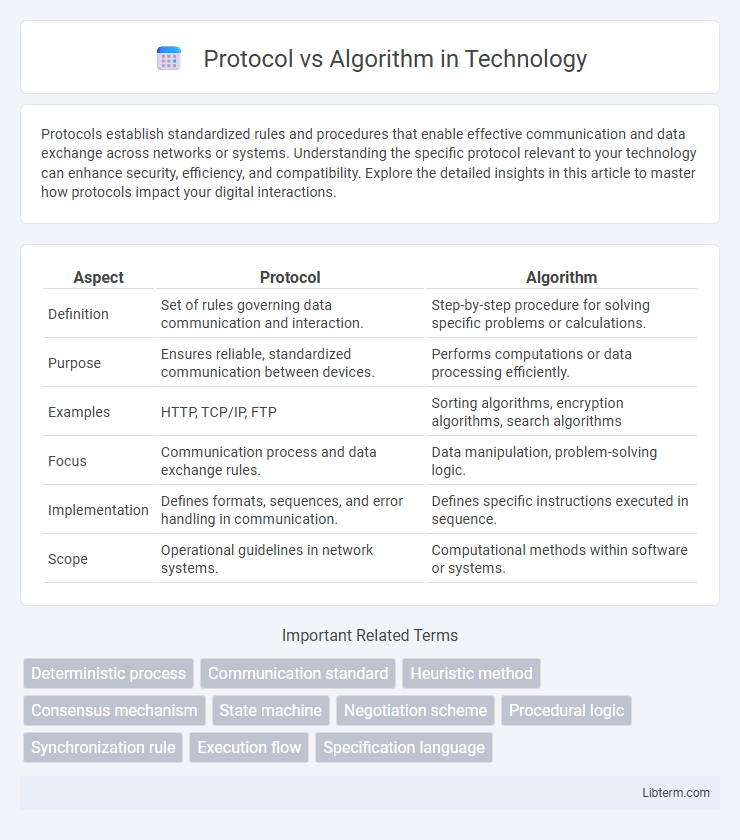
| Aspect | Protocol | Algorithm |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Set of rules governing data communication and interaction. | Step-by-step procedure for solving specific problems or calculations. |
| Purpose | Ensures reliable, standardized communication between devices. | Performs computations or data processing efficiently. |
| Examples | HTTP, TCP/IP, FTP | Sorting algorithms, encryption algorithms, search algorithms |
| Focus | Communication process and data exchange rules. | Data manipulation, problem-solving logic. |
| Implementation | Defines formats, sequences, and error handling in communication. | Defines specific instructions executed in sequence. |
| Scope | Operational guidelines in network systems. | Computational methods within software or systems. |
Understanding the Basics: What is a Protocol?
A protocol defines a set of rules and conventions for communication between network devices, ensuring data is transmitted accurately and efficiently. It establishes guidelines for data formatting, error detection, and synchronization, enabling interoperability across diverse systems. Unlike an algorithm, which is a step-by-step procedure to perform a specific task, a protocol governs the overall communication process in network environments.
Defining an Algorithm: Core Concepts
An algorithm is a finite sequence of well-defined, step-by-step instructions designed to perform a specific task or solve a problem efficiently. Core concepts of algorithms include input, output, definiteness, finiteness, and effectiveness, ensuring each step is clear and executable without ambiguity. Algorithms form the foundational blueprint for computational processes, enabling systematic data manipulation and problem-solving in computer science.
Key Differences Between Protocol and Algorithm
Protocols define a set of rules and conventions for communication between devices in a network, ensuring data is transmitted accurately and securely. Algorithms are step-by-step procedures or formulas used to solve specific problems or perform tasks, focusing on computational logic and efficiency. Protocols govern interaction and data exchange, while algorithms provide the method to process and manipulate data within those interactions.
Real-World Examples of Protocols
Protocols like HTTP and FTP govern how data is transmitted over the internet, ensuring reliable communication between devices. Algorithms such as Dijkstra's algorithm focus on solving specific problems, like finding the shortest path in a network. Real-world protocols, including TCP/IP, HTTPS, and SMTP, establish standardized rules that enable seamless data exchange and secure online transactions.
Notable Algorithms in Technology
Notable algorithms in technology, such as Google's PageRank, RSA encryption, and the A* search algorithm, play critical roles in data retrieval, secure communication, and pathfinding respectively. Protocols, unlike algorithms, define rules for data exchange and communication between devices, exemplified by HTTP, FTP, and TCP/IP. Understanding the distinction is vital as algorithms solve specific computational problems while protocols ensure standardized interactions across networks.
Protocols in Network Communication
Protocols in network communication define a set of rules and conventions for data exchange between devices, ensuring successful transmission and reception. They specify syntax, semantics, and synchronization, enabling interoperability across heterogeneous systems. Key examples include TCP/IP, HTTP, and FTP, which manage error handling, data formatting, and connection establishment in various layers of the network stack.
Role of Algorithms in Data Processing
Algorithms play a critical role in data processing by providing step-by-step procedures to analyze, transform, and interpret raw data efficiently. They enable tasks such as sorting, filtering, and pattern recognition essential for converting data into actionable insights. Unlike protocols that define communication rules between systems, algorithms focus on the methods used to manipulate and process data internally.
Interdependence: When Protocols Use Algorithms
Protocols define the rules and procedures for communication in networks, while algorithms provide step-by-step methods to perform specific tasks within these protocols. Protocols rely on algorithms to ensure efficient data transmission, error detection, and security measures, making their functions interdependent. This synergy enables robust and reliable network operations, where algorithms optimize protocol performance and protocols structure algorithm implementation.
Security Implications: Protocol vs Algorithm
Protocols define the rules and procedures for secure communication between systems, ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and authentication across networks. Algorithms, such as cryptographic algorithms, provide the mathematical foundation for encryption and decryption processes within these protocols, directly impacting the strength of security measures. The interplay between protocols and algorithms determines the overall effectiveness of security implementations, where robust protocols manage key exchanges and authentication steps, while strong algorithms prevent data breaches and resist cryptographic attacks.
Choosing the Right Approach: Protocol or Algorithm?
Choosing the right approach between a protocol and an algorithm depends on the context and requirements of the task. Protocols define a set of rules for communication and interaction in network systems like TCP/IP or HTTP, ensuring standardized data exchange and interoperability. Algorithms provide step-by-step computational procedures for problem-solving, such as sorting or encryption techniques, making them ideal for tasks requiring precise, repeatable operations.
Protocol Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com