VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) segment a physical network into multiple logical networks, improving security and traffic management by isolating broadcast domains. They optimize network performance and simplify administration by grouping devices based on function or department rather than physical location. Explore the rest of the article to discover how VLANs can enhance your network's efficiency and security.
Table of Comparison
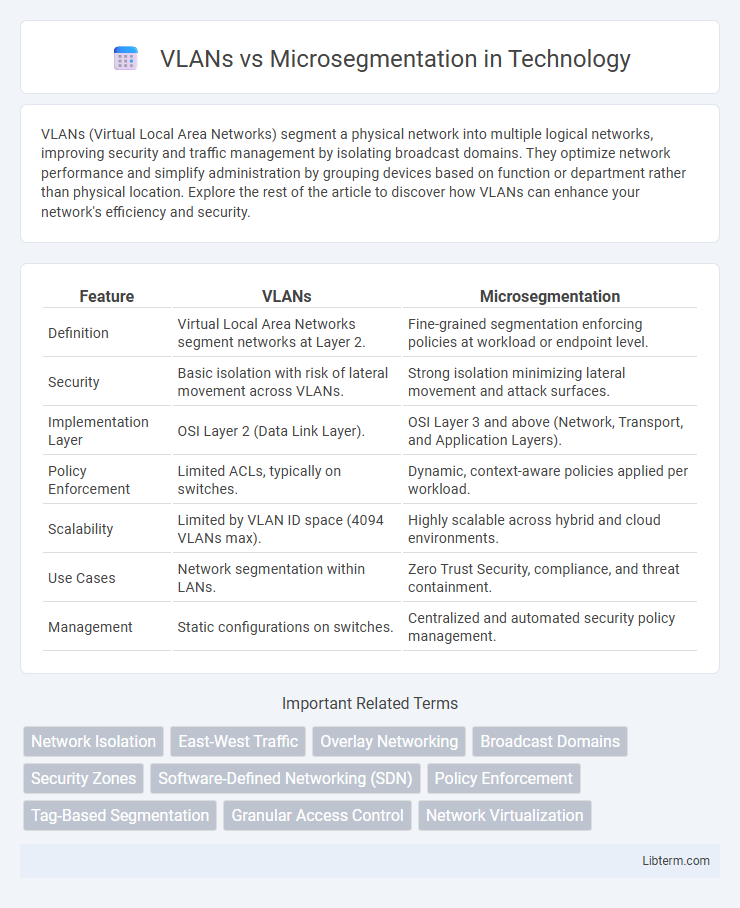
| Feature | VLANs | Microsegmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Virtual Local Area Networks segment networks at Layer 2. | Fine-grained segmentation enforcing policies at workload or endpoint level. |
| Security | Basic isolation with risk of lateral movement across VLANs. | Strong isolation minimizing lateral movement and attack surfaces. |
| Implementation Layer | OSI Layer 2 (Data Link Layer). | OSI Layer 3 and above (Network, Transport, and Application Layers). |
| Policy Enforcement | Limited ACLs, typically on switches. | Dynamic, context-aware policies applied per workload. |
| Scalability | Limited by VLAN ID space (4094 VLANs max). | Highly scalable across hybrid and cloud environments. |
| Use Cases | Network segmentation within LANs. | Zero Trust Security, compliance, and threat containment. |
| Management | Static configurations on switches. | Centralized and automated security policy management. |
Introduction to Network Segmentation
Network segmentation enhances security by dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to control traffic flow and minimize attack surfaces. VLANs achieve segmentation by logically separating devices within switches based on broadcast domains, improving network efficiency and limiting broadcast traffic. Microsegmentation extends this concept by using software-defined policies to enforce granular security controls down to the workload level, enabling precise isolation regardless of physical location.
What Are VLANs?
VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks) segment a physical network into multiple logical networks, enhancing security and reducing broadcast traffic within an enterprise environment. Each VLAN isolates devices at the data link layer (Layer 2), allowing administrators to group users and resources based on function or department without changing physical cabling. VLANs improve network efficiency by limiting broadcast domains and enabling flexible network policy enforcement across switches.
How Microsegmentation Works
Microsegmentation works by creating secure zones within a data center or cloud network, enabling granular control over east-west traffic at the workload level, rather than relying on broad VLAN-based segmentation. It utilizes software-defined networking (SDN) and network virtualization techniques to enforce security policies directly on individual workloads or virtual machines, isolating them and reducing attack surfaces effectively. This approach allows dynamic, automated policy enforcement, ensuring that only authorized communications occur between specific microsegments, enhancing overall network security beyond traditional VLAN limitations.
Key Differences Between VLANs and Microsegmentation
VLANs segment networks by dividing broadcast domains at the data link layer using switch configurations, limiting local traffic within predefined groups. Microsegmentation operates at the software or hypervisor level, enforcing granular security policies and isolating workloads individually regardless of their physical location. Unlike VLANs, microsegmentation offers dynamic, context-aware controls that minimize lateral movement of threats within data centers or cloud environments.
Security Benefits of VLANs
VLANs enhance network security by isolating broadcast domains at the data link layer, reducing unnecessary traffic and limiting attack surfaces within a physical network. They enable segmentation of devices into distinct groups based on function or department, thereby controlling access and preventing unauthorized lateral movement. This logical separation supports policy enforcement and improves containment of potential threats compared to flat network architectures.
Security Advantages of Microsegmentation
Microsegmentation offers superior security advantages over traditional VLANs by enabling granular, policy-driven controls at the workload or application level, effectively isolating traffic within the same network segment. Unlike VLANs, which primarily rely on broad network segmentation and are vulnerable to lateral movement attacks, microsegmentation drastically reduces attack surfaces by enforcing strict, identity-based access policies, preventing unauthorized access even within a segmented network. This advanced approach enhances threat detection and containment by limiting east-west traffic exposure and providing detailed visibility into inter-workload communications.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
VLANs segment networks by dividing broadcast domains, offering moderate performance improvements but limited scalability due to static configurations and reliance on physical infrastructure. Microsegmentation utilizes software-defined policies to enforce granular security and traffic control at the workload level, substantially enhancing performance through optimized traffic flows and reducing lateral movement risks. Scalability in microsegmentation is superior, as it dynamically adapts to virtualized and cloud environments without dependence on physical hardware constraints.
Use Cases: When to Choose VLANs
VLANs are ideal for segmenting large enterprise networks by department or function, offering simple traffic isolation and reducing broadcast domains without physical separation. They work well in scenarios requiring basic network segmentation to improve performance and security with minimal management complexity. Choose VLANs when cost-efficiency, ease of implementation, and compatibility with existing Layer 2 devices are primary considerations.
Use Cases: When to Opt for Microsegmentation
Microsegmentation is ideal for environments requiring granular security controls, such as data centers hosting sensitive applications or multi-tenant clouds where isolation between workloads is critical. Unlike VLANs, which segment network traffic at Layer 2, microsegmentation operates at the workload level, enabling policy enforcement based on user identity, application type, and threat intelligence. Enterprises aiming to reduce lateral movement in cyberattacks and achieve compliance with strict regulatory standards benefit most from implementing microsegmentation.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Segmentation Solution
Choosing between VLANs and microsegmentation depends on network complexity and security requirements; VLANs offer basic traffic separation suitable for smaller, less dynamic environments. Microsegmentation provides granular, software-defined security controls ideal for cloud-native and zero-trust architectures. Evaluating factors such as scalability, regulatory compliance, and threat landscape ensures the optimal segmentation strategy aligns with organizational goals and risk mitigation.
VLANs Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com