Mastering the art of cooking as a chef involves understanding diverse cuisines, perfecting knife skills, and managing kitchen operations efficiently. Your ability to balance flavors, presentation, and timing can transform simple ingredients into unforgettable meals. Discover expert tips and techniques in the full article to elevate your culinary skills.
Table of Comparison
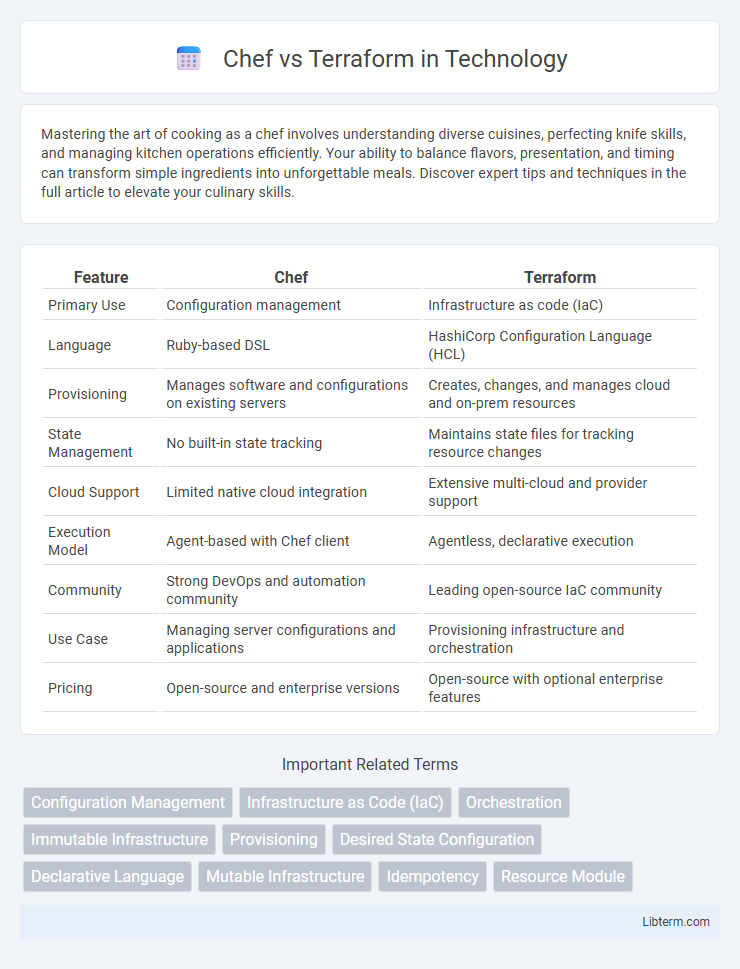
| Feature | Chef | Terraform |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Configuration management | Infrastructure as code (IaC) |
| Language | Ruby-based DSL | HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) |
| Provisioning | Manages software and configurations on existing servers | Creates, changes, and manages cloud and on-prem resources |
| State Management | No built-in state tracking | Maintains state files for tracking resource changes |
| Cloud Support | Limited native cloud integration | Extensive multi-cloud and provider support |
| Execution Model | Agent-based with Chef client | Agentless, declarative execution |
| Community | Strong DevOps and automation community | Leading open-source IaC community |
| Use Case | Managing server configurations and applications | Provisioning infrastructure and orchestration |
| Pricing | Open-source and enterprise versions | Open-source with optional enterprise features |
Introduction to Chef and Terraform
Chef is a powerful configuration management tool designed to automate infrastructure provisioning by defining system configurations as code, enabling consistent and repeatable deployments. Terraform, an open-source infrastructure as code software, allows users to safely and predictably create, change, and improve infrastructure across multiple cloud providers using declarative configuration files. Both tools streamline infrastructure automation but differ in their primary focus: Chef emphasizes ongoing configuration management, while Terraform specializes in infrastructure provisioning and lifecycle management.
Key Differences Between Chef and Terraform
Chef primarily automates configuration management by defining infrastructure as code for consistent server setups, while Terraform specializes in provisioning and managing cloud infrastructure through declarative templates. Chef uses Ruby-based scripts to manage application and system configurations, whereas Terraform employs HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL) for orchestrating infrastructure resources across multiple cloud providers. The key difference lies in Chef's focus on configuration management and state enforcement, contrasting with Terraform's emphasis on infrastructure provisioning and lifecycle management.
Overview of Configuration Management with Chef
Chef is a powerful configuration management tool designed to automate infrastructure provisioning and application deployment by defining infrastructure as code. It uses a domain-specific language based on Ruby to write reusable and testable configuration recipes, enabling efficient management of system states across large-scale environments. Chef's architecture follows a client-server model, where the Chef server stores cookbooks and policies, and Chef clients converge system configurations to the desired state specified in those cookbooks.
Infrastructure as Code: Terraform’s Approach
Terraform utilizes a declarative Infrastructure as Code (IaC) approach, enabling automated provisioning and management of cloud resources through configuration files written in HashiCorp Configuration Language (HCL). Unlike Chef, which primarily focuses on configuration management with imperative scripts, Terraform emphasizes immutable infrastructure and dependency graphing to create, update, and version infrastructure consistently. Its strong integration with major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform empowers teams to automate infrastructure changes reliably across multi-cloud environments.
Use Cases: When to Choose Chef or Terraform
Chef excels in configuration management and automating complex application deployments across multiple servers, making it ideal for maintaining consistent environments and enforcing compliance policies. Terraform specializes in infrastructure as code, provisioning and managing cloud resources across various providers with a declarative approach, which suits dynamic infrastructure scaling and multi-cloud management. Choose Chef for detailed system-level configuration and state management, and opt for Terraform when orchestrating infrastructure provisioning and cloud resource lifecycle automation.
Integration and Ecosystem Compatibility
Chef offers deep integration with various cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud through its robust cookbook ecosystem, facilitating seamless configuration management across hybrid environments. Terraform excels in provisioning infrastructure using a wide range of providers, including Kubernetes, VMware, and major cloud services, enabling infrastructure as code with declarative configuration files. Both tools complement each other in the DevOps pipeline, with Terraform handling infrastructure provisioning and Chef managing application deployment and configuration, ensuring comprehensive ecosystem compatibility.
Learning Curve and Community Support
Chef presents a steeper learning curve due to its Ruby-based DSL and complex configuration structure, requiring users to have programming skills and deeper system knowledge. Terraform offers a gentler learning curve with its declarative HCL (HashiCorp Configuration Language), making infrastructure provisioning more accessible to beginners. Both tools benefit from robust community support; however, Terraform boasts a rapidly growing community with extensive modules and provider plugins, while Chef maintains a mature ecosystem backed by strong enterprise backing and comprehensive documentation.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Chef and Terraform serve different purposes in infrastructure management, with Chef specializing in configuration management and Terraform focusing on infrastructure provisioning. Terraform demonstrates superior scalability through its declarative approach and state management, enabling efficient handling of large-scale cloud resources across multiple providers. Chef's performance is optimized for complex application deployments and configuration drift correction but may require additional orchestration for extensive, rapidly changing environments.
Security Practices in Chef vs Terraform
Chef enforces security through policy-based configurations and role-based access control (RBAC), ensuring consistent compliance across infrastructure by automating security patches and updates. Terraform integrates with external security tools but relies heavily on secure state management and access controls to prevent unauthorized resource changes, emphasizing infrastructure as code (IaC) best practices. Both tools support secret management integrations, but Chef offers more granular node-level configuration security while Terraform focuses on secure provisioning workflows.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Tool
Chef excels in configuration management with its robust automation and policy-driven approach, ideal for complex infrastructure requiring detailed control. Terraform specializes in infrastructure as code with a declarative model, enabling efficient provisioning, scaling, and management across diverse cloud platforms. Choosing the right tool depends on whether the priority is detailed configuration management (Chef) or scalable infrastructure provisioning (Terraform).
Chef Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com