Glass-box testing focuses on examining the internal structures or workings of an application, ensuring that every function and logic path operates correctly based on code analysis. This method helps detect hidden errors, optimize code quality, and improve overall software reliability by scrutinizing source code, branches, and conditions. Discover how glass-box testing can enhance your development process by exploring the comprehensive insights detailed in this article.
Table of Comparison
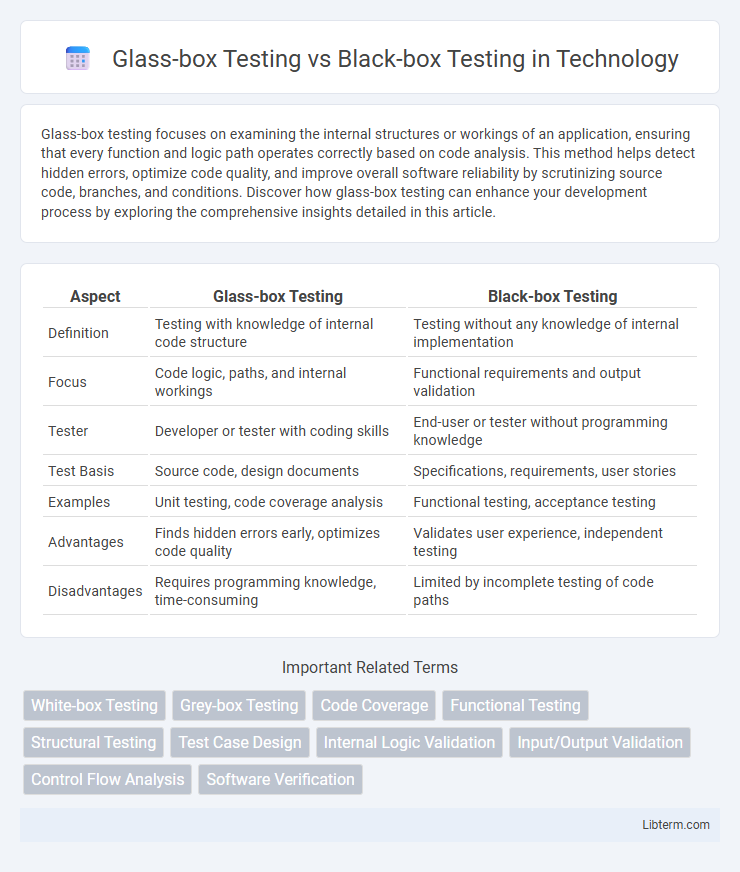
| Aspect | Glass-box Testing | Black-box Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Testing with knowledge of internal code structure | Testing without any knowledge of internal implementation |
| Focus | Code logic, paths, and internal workings | Functional requirements and output validation |
| Tester | Developer or tester with coding skills | End-user or tester without programming knowledge |
| Test Basis | Source code, design documents | Specifications, requirements, user stories |
| Examples | Unit testing, code coverage analysis | Functional testing, acceptance testing |
| Advantages | Finds hidden errors early, optimizes code quality | Validates user experience, independent testing |
| Disadvantages | Requires programming knowledge, time-consuming | Limited by incomplete testing of code paths |
Introduction to Software Testing
Glass-box testing involves examining the internal structure and logic of the code to design test cases, ensuring comprehensive coverage of all pathways and statements. Black-box testing evaluates software functionality without knowledge of the internal code, focusing on input-output behavior to validate requirements and user expectations. These testing approaches complement each other by addressing different aspects of software quality assurance in the development lifecycle.
Definition of Glass-box Testing
Glass-box testing, also known as white-box testing, is a software testing method that involves examining the internal structure, design, and coding of an application to verify its functionality and security. This approach requires detailed knowledge of the codebase, enabling testers to create test cases that assess specific paths, conditions, and branches within the software. Glass-box testing contrasts with black-box testing, which evaluates the application solely from an external perspective without insight into the internal workings.
Definition of Black-box Testing
Black-box testing is a software testing method where the internal structure, design, and implementation of the item being tested are not known to the tester. The testing process focuses on inputs and expected outputs without considering how the software's internal code operates. This approach is essential for validating the functionality of software applications from an end-user perspective and detecting discrepancies between expected and actual behavior.
Key Differences Between Glass-box and Black-box Testing
Glass-box testing involves examining the internal code structure, logic, and implementation details, providing testers full visibility into the source code, whereas black-box testing evaluates software functionality solely based on input-output behavior without knowledge of internal workings. Key differences include the test design approach: glass-box testing requires programming skills and focuses on code coverage, such as path, branch, and condition coverage, while black-box testing emphasizes requirements validation and user experience through functional and non-functional testing. Glass-box testing is generally performed during unit and integration testing phases, whereas black-box testing is commonly applied in system, acceptance, and regression testing stages.
Advantages of Glass-box Testing
Glass-box testing offers the advantage of full visibility into the internal code structure, enabling testers to identify hidden errors and optimize code efficiency. It supports thorough coverage of all code paths, which reduces the risk of overlooking critical vulnerabilities. This approach also facilitates early detection of logical errors, improving software reliability and maintainability.
Advantages of Black-box Testing
Black-box testing offers the advantage of evaluating software functionality without requiring knowledge of the internal code structure, allowing testers to focus purely on input-output behavior and user experience. This method enhances defect detection related to system integration and interface issues, making it well-suited for validating compliance with specifications and requirements. Its independence from programming expertise makes it accessible to a broader range of testers, streamlining the testing process and improving efficiency.
Limitations of Glass-box Testing
Glass-box testing is limited by its reliance on the tester's knowledge of the internal code structure, which can result in overlooked behavioral errors that occur outside the tested code paths. It struggles to identify system-level issues, such as performance bottlenecks and integration flaws, because it does not test the software from an end-user perspective. The approach can be time-consuming and complex for large systems due to the need for detailed source code analysis and coverage for all possible execution paths.
Limitations of Black-box Testing
Black-box testing often struggles with limited coverage of internal code structures, leaving potential hidden defects undetected in complex algorithms or logic paths. It heavily depends on well-defined requirements and specifications, so ambiguous or incomplete documentation can lead to inadequate test cases and missed errors. This approach also tends to be less effective in identifying performance bottlenecks and security vulnerabilities that require in-depth code analysis.
When to Use Glass-box vs Black-box Testing
Use Glass-box Testing when detailed knowledge of the internal code structure, logic, and implementation is available, enabling thorough examination of program flow, branches, and conditions to identify hidden errors. Opt for Black-box Testing in scenarios where the focus is on validating software functionality against requirements without access to internal code, ideal for usability, input validation, and system-level testing. Choose Glass-box Testing during unit and integration testing phases, while Black-box Testing fits best for acceptance and system testing stages to ensure comprehensive quality assurance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Testing Approach
Glass-box testing offers deep insight into internal code structure and logic, making it ideal for identifying security vulnerabilities and optimizing performance. Black-box testing evaluates software functionality from the user's perspective without needing code knowledge, ensuring comprehensive validation of input-output behavior and usability. Selecting the right approach depends on project goals, with glass-box preferred for detailed defect detection and black-box suited for functional and acceptance testing.
Glass-box Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com