Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a framework that enables secure electronic communication through digital certificates and cryptographic key pairs, ensuring data integrity and authentication. It supports various applications such as secure email, VPNs, and online transactions, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. Explore the rest of the article to understand how PKI can enhance your organization's cybersecurity.
Table of Comparison
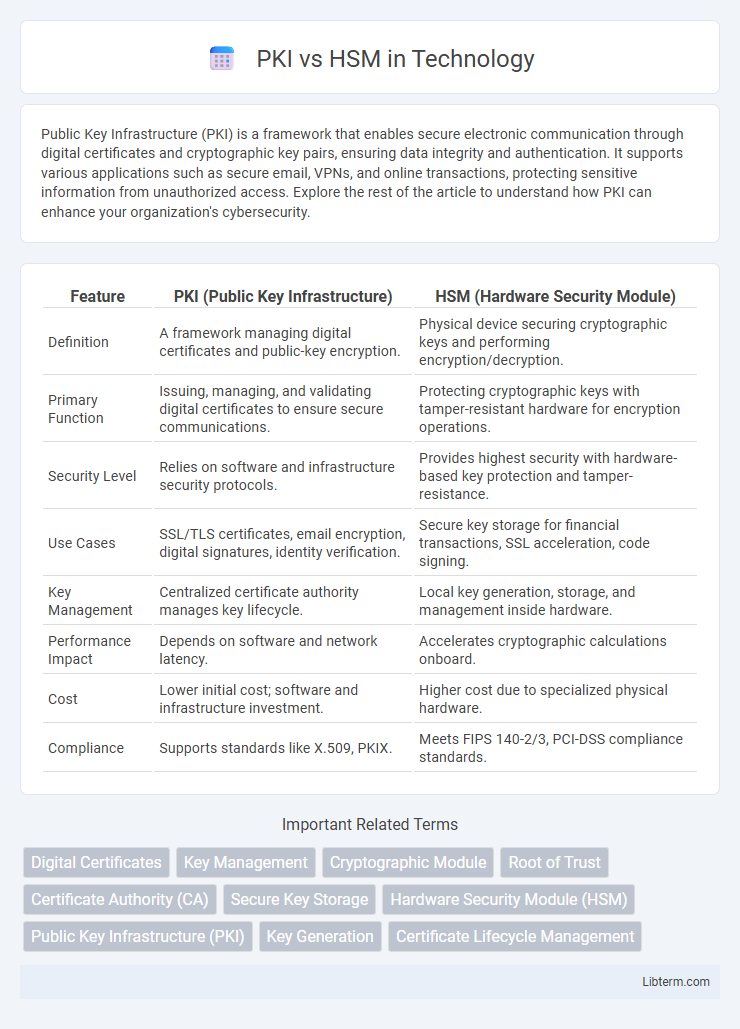
| Feature | PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) | HSM (Hardware Security Module) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A framework managing digital certificates and public-key encryption. | Physical device securing cryptographic keys and performing encryption/decryption. |
| Primary Function | Issuing, managing, and validating digital certificates to ensure secure communications. | Protecting cryptographic keys with tamper-resistant hardware for encryption operations. |
| Security Level | Relies on software and infrastructure security protocols. | Provides highest security with hardware-based key protection and tamper-resistance. |
| Use Cases | SSL/TLS certificates, email encryption, digital signatures, identity verification. | Secure key storage for financial transactions, SSL acceleration, code signing. |
| Key Management | Centralized certificate authority manages key lifecycle. | Local key generation, storage, and management inside hardware. |
| Performance Impact | Depends on software and network latency. | Accelerates cryptographic calculations onboard. |
| Cost | Lower initial cost; software and infrastructure investment. | Higher cost due to specialized physical hardware. |
| Compliance | Supports standards like X.509, PKIX. | Meets FIPS 140-2/3, PCI-DSS compliance standards. |
Introduction to PKI and HSM
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) establishes a framework for secure electronic communications through digital certificates, cryptographic key pairs, and trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) are dedicated physical devices designed to generate, store, and manage cryptographic keys securely, providing tamper-resistant protection against unauthorized access. While PKI manages the overall trust and identity verification process, HSMs enhance security by safeguarding private keys and performing cryptographic operations within a hardened environment.
Core Concepts of Public Key Infrastructure (PKI)
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is a framework that uses cryptographic keys and digital certificates to establish secure electronic communications and verify identities. It involves components such as Certificate Authorities (CAs), Registration Authorities (RAs), and public and private key pairs to enable encryption, digital signatures, and authentication. Unlike Hardware Security Modules (HSMs), which are physical devices designed to securely generate and store cryptographic keys, PKI provides the overall architecture for managing keys and certificates across a network.
Fundamentals of Hardware Security Modules (HSM)
Hardware Security Modules (HSM) are dedicated physical devices designed to manage digital keys and perform cryptographic operations securely, providing a tamper-resistant environment that safeguards sensitive data from unauthorized access. Unlike Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), which is a framework for managing digital certificates and public-key encryption, HSMs enhance security by generating, storing, and managing cryptographic keys in isolated hardware to prevent extraction or misuse. These modules ensure high-performance cryptographic processing, compliance with regulatory standards, and hardened protection against physical and logical attacks, making them critical for secure key management in enterprises.
Key Differences Between PKI and HSM
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) manages digital certificates and public-key encryption to enable secure communication, while Hardware Security Modules (HSM) are physical devices designed to safeguard and manage cryptographic keys with high security. PKI primarily handles the creation, distribution, and validation of digital certificates, whereas HSM provides secure key storage and cryptographic operations such as encryption, decryption, and key generation within a tamper-resistant environment. The key difference lies in PKI's role in trust management and identity verification versus HSM's focus on hardware-enforced key protection and cryptographic processing.
Security Features: PKI vs HSM
PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) secures digital communications by managing keys, certificates, and encryption protocols, ensuring authentication, confidentiality, and non-repudiation through software-based key management. HSM (Hardware Security Module) offers enhanced security by physically storing cryptographic keys within tamper-resistant hardware, providing secure key generation, storage, and cryptographic processing that mitigate risks of key exposure and unauthorized access. While PKI relies on software trust models, HSM delivers robust hardware-enforced security features critical for high-assurance environments.
Use Cases and Applications
PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) is essential for secure digital identity management, encryption, and authentication in applications such as SSL/TLS certificates, email security, and user access control. HSM (Hardware Security Module) provides high-assurance cryptographic key generation, storage, and management, commonly used in payment processing, blockchain networks, and government-grade encryption. Combining PKI with HSM enhances security by leveraging HSM's tamper-resistant hardware to protect PKI keys, ensuring robust protection in financial services, cloud security, and IoT environments.
Integration and Deployment Challenges
Integrating Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) with Hardware Security Modules (HSM) often presents deployment challenges such as compatibility issues between diverse cryptographic standards and varying vendor-specific APIs. The complexity increases when scaling infrastructure, requiring careful coordination of certificate lifecycle management with secure key storage and backup strategies. Ensuring seamless interoperability demands thorough testing and robust configuration to prevent vulnerabilities and operational disruptions.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) offer superior cryptographic performance and scalability compared to traditional Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) software solutions by offloading intensive key operations to dedicated hardware, resulting in faster key generation, encryption, and decryption processes. HSMs support high transaction volumes with minimal latency due to their optimized architectures, enabling scalable deployment in enterprise environments requiring rapid and secure key management. In contrast, PKI implementations relying solely on software can experience bottlenecks under heavy workloads, limiting performance and scalability as demand increases.
Cost Considerations: PKI vs HSM
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) typically incurs lower initial setup costs compared to Hardware Security Modules (HSMs), which require significant investment in physical hardware and maintenance. PKI solutions leverage software-based key management, reducing operational expenses but potentially increasing risks that may lead to hidden costs over time. HSMs offer enhanced security and compliance benefits, justifying their higher upfront and ongoing costs for organizations with strict regulatory requirements or high-value digital assets.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Organization
Choosing between PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) and HSM (Hardware Security Module) depends on your organization's security requirements, scalability needs, and compliance mandates. PKI provides a comprehensive framework for managing digital certificates and encryption keys, ideal for securing communications and authentication across large networks. HSMs offer a hardened, tamper-resistant environment for generating, storing, and managing cryptographic keys, making them essential for high-security applications and regulatory compliance in industries such as finance and healthcare.
PKI Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com