Volume Group is a crucial concept in data storage management, allowing the aggregation of multiple physical storage devices into a single logical unit for improved performance and flexibility. Managing Volume Groups effectively can optimize your system's storage capacity, simplify administration, and enhance data redundancy. Explore the rest of the article to understand how Volume Groups can transform your storage strategy.
Table of Comparison
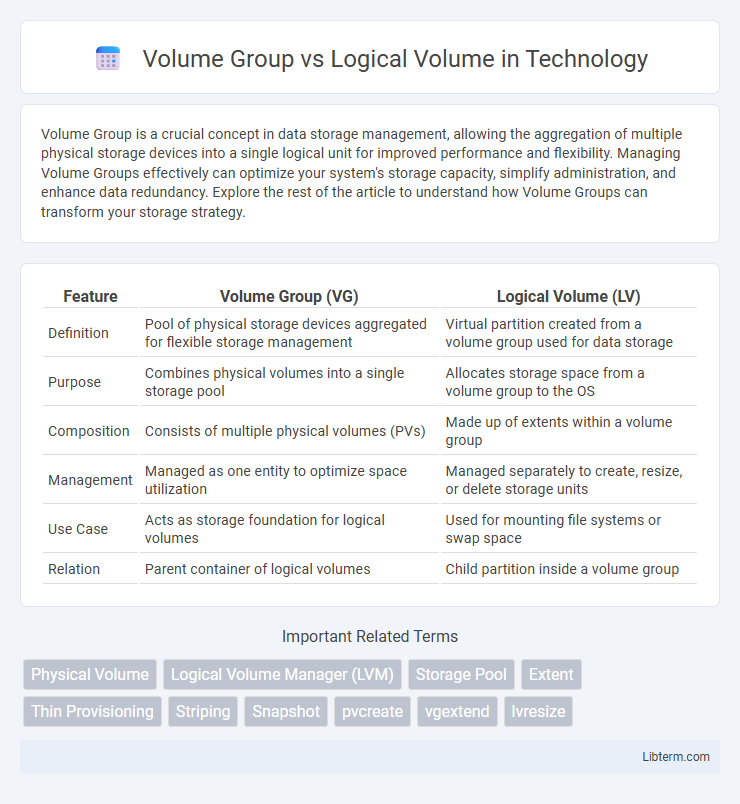
| Feature | Volume Group (VG) | Logical Volume (LV) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Pool of physical storage devices aggregated for flexible storage management | Virtual partition created from a volume group used for data storage |
| Purpose | Combines physical volumes into a single storage pool | Allocates storage space from a volume group to the OS |
| Composition | Consists of multiple physical volumes (PVs) | Made up of extents within a volume group |
| Management | Managed as one entity to optimize space utilization | Managed separately to create, resize, or delete storage units |
| Use Case | Acts as storage foundation for logical volumes | Used for mounting file systems or swap space |
| Relation | Parent container of logical volumes | Child partition inside a volume group |
Introduction to Volume Groups and Logical Volumes
Volume Groups (VGs) serve as a pool of storage in Logical Volume Management (LVM), aggregating multiple physical volumes into a single storage entity. Logical Volumes (LVs) are virtual partitions created within Volume Groups, allowing flexible, dynamic space allocation for file systems. This structure enhances disk management by enabling resizing, snapshots, and efficient utilization of underlying physical storage.
What is a Volume Group?
A Volume Group (VG) is a storage pool in Logical Volume Management (LVM) that aggregates multiple physical volumes into a single, manageable entity. It allows flexible allocation of storage space, enabling the creation of Logical Volumes (LVs) that act as virtual partitions. Volume Groups simplify disk management by providing scalability and efficient use of storage resources across physical devices.
What is a Logical Volume?
A Logical Volume (LV) is a virtual storage unit created from Physical Volumes (PVs) grouped into a Volume Group (VG) in Linux Logical Volume Manager (LVM). Unlike fixed-size partitions, LVs offer flexible resizing and efficient storage management by abstracting physical disks into easily adjustable volumes. Logical Volumes enable dynamic allocation of storage space, snapshots, and improved disk utilization compared to traditional partitioning methods.
Key Differences Between Volume Groups and Logical Volumes
Volume Groups (VGs) aggregate multiple physical storage devices into a single storage pool, enabling flexible space management across disks. Logical Volumes (LVs) are virtual partitions carved out from Volume Groups, functioning as mountable and resizable drives for the operating system. Key differences include that VGs organize physical storage under one namespace, while LVs provide the end-user interface for file systems and applications by appearing as logical disks.
How Volume Groups Work in LVM
Volume Groups (VGs) in Logical Volume Management (LVM) act as pools of storage composed of multiple Physical Volumes (PVs), aggregating the capacity of several disks into a single, manageable entity. Within a VG, Logical Volumes (LVs) are created as virtual partitions, allowing dynamic resizing and flexible allocation of storage space without concern for physical disk boundaries. This abstraction enables efficient space management, data redundancy, and performance optimization tailored to various workload requirements.
How Logical Volumes Operate in LVM
Logical Volumes (LVs) in LVM function as flexible, resizable storage units within Volume Groups (VGs), abstracting physical storage devices into manageable blocks. They operate by allocating extents--fixed-size storage chunks--from the pool of available space in the Volume Group, allowing dynamic resizing and efficient disk space utilization. LVs enable features such as snapshots, striping, and mirroring, enhancing data protection and system performance in storage management.
Benefits of Using Volume Groups
Volume Groups aggregate multiple physical storage devices into a single storage pool, enabling flexible and efficient disk space management. This consolidation allows Logical Volumes to be resized dynamically without downtime, improving system performance and storage utilization. By abstracting physical storage, Volume Groups enhance data redundancy and simplify backup processes, providing robust data protection.
Advantages of Logical Volumes
Logical Volumes offer superior flexibility and scalability compared to Volume Groups by enabling dynamic resizing without disrupting system operations. They support advanced features such as snapshots, striping, and mirroring, enhancing data management and fault tolerance. Logical Volumes allow for efficient storage utilization by abstracting physical storage details, simplifying volume management in complex environments.
Use Cases: When to Use VG vs LV
Volume Groups (VGs) serve as pooled storage resources combining multiple physical volumes to optimize capacity and flexibility, making them ideal for managing large-scale storage environments requiring dynamic allocation and scaling. Logical Volumes (LVs) are carved out from Volume Groups to create manageable, resizable partitions suitable for hosting file systems or applications with specific storage demands such as databases, virtual machines, or user data. Use Volume Groups when consolidating physical storage devices for centralized management and Logical Volumes when allocating, resizing, or snapshotting partitions tailored to individual workload requirements.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Volume Group and Logical Volume
Choosing between a Volume Group (VG) and a Logical Volume (LV) depends on your storage management needs, as a VG acts as a pool of physical storage devices while an LV is a partition carved out from that pool for specific use. Volume Groups provide flexibility by aggregating multiple physical volumes, enabling dynamic resizing and efficient space allocation, whereas Logical Volumes offer granular control for file systems or applications. Understanding the role of VGs for overall storage capacity and LVs for targeted data management ensures optimal disk utilization and system performance.
Volume Group Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com