Reliability ensures that products and services consistently meet established standards, providing dependable performance that builds customer trust. High reliability minimizes downtime and maintenance costs, improving overall operational efficiency. Discover how enhancing reliability can boost your business success by exploring the rest of this article.
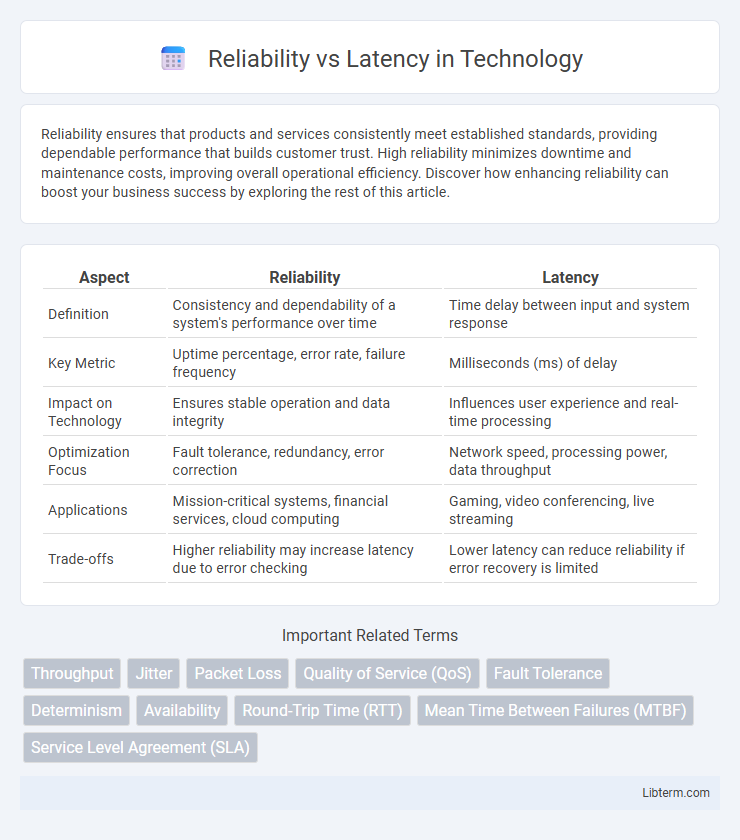
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Reliability | Latency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Consistency and dependability of a system's performance over time | Time delay between input and system response |
| Key Metric | Uptime percentage, error rate, failure frequency | Milliseconds (ms) of delay |
| Impact on Technology | Ensures stable operation and data integrity | Influences user experience and real-time processing |
| Optimization Focus | Fault tolerance, redundancy, error correction | Network speed, processing power, data throughput |
| Applications | Mission-critical systems, financial services, cloud computing | Gaming, video conferencing, live streaming |
| Trade-offs | Higher reliability may increase latency due to error checking | Lower latency can reduce reliability if error recovery is limited |
Understanding Reliability and Latency
Reliability measures the consistency and accuracy of data transmission, ensuring packets arrive without errors or loss, which is critical for applications like financial transactions and healthcare monitoring. Latency refers to the time delay between sending and receiving data, impacting real-time responsiveness in gaming, video conferencing, and autonomous vehicle control. Balancing high reliability with low latency is essential for optimizing network performance and user experience across various digital services.
Key Differences Between Reliability and Latency
Reliability refers to the ability of a system or network to consistently deliver data accurately and without loss, whereas latency measures the time delay between data transmission and reception. High reliability ensures error-free communication, often requiring retransmissions that can increase latency. Latency impacts real-time performance, making low delay critical for applications like video conferencing, but achieving low latency may sometimes compromise reliability when error correction is minimized.
Importance of Reliability in Modern Networks
Reliability in modern networks ensures consistent data delivery and minimizes packet loss, which is critical for applications such as financial transactions, healthcare monitoring, and autonomous vehicles. High reliability reduces retransmissions and network congestion, enhancing overall system performance and user experience. While latency impacts real-time responsiveness, reliability guarantees data integrity and service availability, making it a foundational requirement in mission-critical and IoT networks.
The Critical Role of Latency in User Experience
Latency directly impacts user experience by determining how quickly a system responds to input, with lower latency ensuring smoother interactions and higher satisfaction levels. While reliability guarantees consistent service availability, high latency can cause delays that frustrate users and degrade perceived performance. Optimizing latency is crucial in real-time applications like gaming, video conferencing, and financial trading where instant responsiveness is essential.
Factors Influencing Reliability
Reliability in network communications depends heavily on factors such as error rates, signal strength, and network congestion, which directly impact data transmission accuracy and consistency. Packet loss, retransmission protocols, and hardware stability also play critical roles in maintaining consistent connectivity. Understanding these elements helps optimize performance by balancing reliability needs against latency constraints.
Factors Affecting Latency
Latency is influenced by various factors including network congestion, distance between devices, and processing delays within routers and switches. Data packet size and transmission medium, such as fiber optic or wireless, significantly impact the speed at which information travels. Moreover, server performance and protocol inefficiencies can increase latency, affecting overall system reliability and responsiveness.
Balancing Reliability and Latency in System Design
Balancing reliability and latency in system design involves optimizing data transmission to ensure consistent performance while minimizing delays. High reliability often requires error-checking protocols and retransmissions that can increase latency, whereas low latency demands fast, streamlined processes potentially compromising data integrity. Implementing adaptive algorithms and prioritizing critical tasks enables systems to maintain low latency without sacrificing reliability in dynamic network environments.
Use Cases: When to Prioritize Reliability vs Latency
In mission-critical applications such as healthcare monitoring and financial transactions, prioritizing reliability ensures data integrity and system stability, minimizing the risk of errors and loss. Real-time systems like video conferencing, autonomous vehicles, and gaming demand low latency to maintain seamless user experience and rapid responsiveness, even if occasional minor delays occur. Choosing between reliability and latency depends on the specific use case requirements, where lossless data transmission trumps speed or vice versa based on operational priorities and acceptable risk.
Challenges in Achieving Both Low Latency and High Reliability
Achieving both low latency and high reliability in network systems faces challenges such as the inherent trade-off between error correction overhead and timely data delivery. Ensuring high reliability requires retransmissions and error-checking mechanisms, which can introduce delays that conflict with latency-sensitive applications like autonomous vehicles or real-time gaming. Optimizing protocols to balance packet loss rates, buffer sizes, and processing times remains critical for maintaining performance standards in 5G and edge computing environments.
Future Trends in Reliability and Latency Technologies
Emerging trends in reliability and latency technologies emphasize the integration of edge computing and 5G networks to reduce data transmission delays and enhance system dependability. Advances in AI-driven predictive maintenance enable real-time fault detection, significantly improving uptime and minimizing latency impacts in critical applications. Innovations in quantum communication promise ultra-low latency with near-perfect reliability, setting new benchmarks for future telecommunications infrastructure.
Reliability Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com