Access control is essential for safeguarding sensitive information by regulating who can view or use resources in a computing environment. Implementing robust authentication and authorization mechanisms ensures that only authorized users gain access, thereby minimizing security risks. Explore the article to learn about effective strategies and best practices for enhancing your access control systems.
Table of Comparison
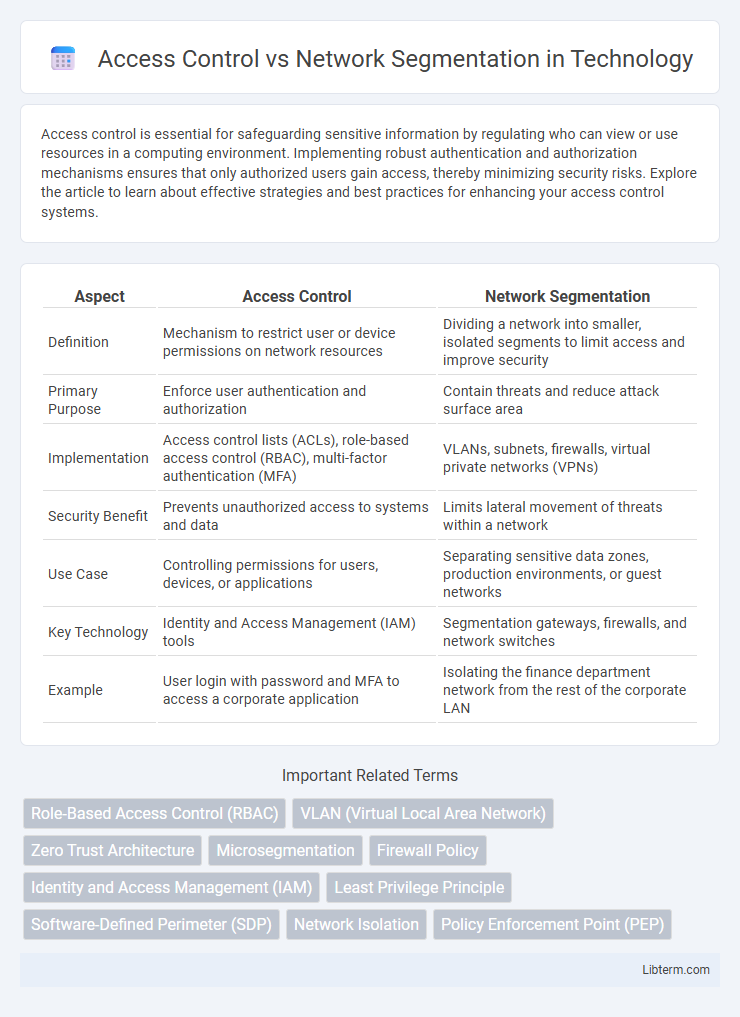
| Aspect | Access Control | Network Segmentation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Mechanism to restrict user or device permissions on network resources | Dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments to limit access and improve security |
| Primary Purpose | Enforce user authentication and authorization | Contain threats and reduce attack surface area |
| Implementation | Access control lists (ACLs), role-based access control (RBAC), multi-factor authentication (MFA) | VLANs, subnets, firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs) |
| Security Benefit | Prevents unauthorized access to systems and data | Limits lateral movement of threats within a network |
| Use Case | Controlling permissions for users, devices, or applications | Separating sensitive data zones, production environments, or guest networks |
| Key Technology | Identity and Access Management (IAM) tools | Segmentation gateways, firewalls, and network switches |
| Example | User login with password and MFA to access a corporate application | Isolating the finance department network from the rest of the corporate LAN |
Introduction to Access Control and Network Segmentation
Access control defines who or what can view or use resources in a computing environment, ensuring that only authorized users gain access to sensitive data and systems. Network segmentation divides a computer network into smaller parts to improve security and performance by isolating traffic and limiting the spread of potential threats. Implementing both access control and network segmentation strengthens cybersecurity posture by minimizing attack surfaces and containing breaches.
Defining Access Control: Concepts and Types
Access control is a security technique that regulates who or what can view or use resources in a computing environment, ensuring authorized access while preventing unauthorized interactions. It encompasses various models such as discretionary access control (DAC), mandatory access control (MAC), role-based access control (RBAC), and attribute-based access control (ABAC), each defining specific rules for resource permissions. Implementing effective access control mechanisms is critical for protecting sensitive data, maintaining compliance, and minimizing security risks within network infrastructures.
Understanding Network Segmentation: Principles and Approaches
Network segmentation involves dividing a computer network into smaller, isolated segments to enhance security and improve performance by limiting traffic flow and controlling access between segments. Key principles include minimizing attack surfaces, enforcing granular policy controls, and containing potential breaches within segmented zones using techniques such as VLANs, firewalls, and micro-segmentation. Approaches vary from physical segmentation with dedicated hardware to virtual segmentation leveraging software-defined networking (SDN) and zero-trust models, emphasizing strict identity verification and least-privilege access.
Key Differences Between Access Control and Network Segmentation
Access control defines who or what can access specific resources within a network using permissions and authentication methods, while network segmentation divides the network into smaller, isolated segments to contain traffic and reduce attack surfaces. Access control primarily manages user and device privileges, enforcing rules at the point of entry, whereas network segmentation focuses on limiting lateral movement by separating network zones and applying firewalls or VLANs. Together, they enhance security but address different aspects: access control restricts access rights, and network segmentation controls network traffic flow and boundaries.
Benefits of Implementing Access Control
Implementing access control enhances security by restricting user permissions to only necessary resources, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches. It provides detailed audit trails and accountability, enabling organizations to monitor and respond to suspicious activities effectively. Access control supports regulatory compliance by enforcing policies aligned with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, safeguarding sensitive information.
Advantages of Network Segmentation in Cybersecurity
Network segmentation enhances cybersecurity by limiting the attack surface and containing potential breaches within isolated network segments, preventing lateral movement of threats. It improves traffic management and enforces stricter access controls, allowing organizations to apply tailored security policies for different network zones. This approach reduces the risk of widespread data breaches and supports compliance with regulatory standards such as PCI DSS and HIPAA.
Common Use Cases for Access Control
Access control is commonly used to restrict user permissions based on roles, ensuring sensitive data and critical systems are accessible only to authorized personnel. Typical use cases include enforcing least privilege policies, securing administrative access to servers, and regulating access to cloud resources and applications. This approach enhances security by minimizing insider threats and reducing the attack surface within organizational networks.
Real-World Applications of Network Segmentation
Network segmentation enhances cybersecurity by dividing a network into multiple isolated zones, limiting lateral movement of threats and improving performance through traffic management. In real-world applications, organizations deploy segmentation to protect sensitive data segments like payment processing systems, enforce compliance standards such as PCI-DSS, and isolate IoT devices from critical infrastructure to minimize exposure. This method complements access control by enforcing granular network policies that restrict unauthorized access beyond traditional user-based permissions.
Integrating Access Control with Network Segmentation
Integrating access control with network segmentation enhances security by limiting user and device privileges within specific network zones, reducing attack surfaces and minimizing lateral movement risks. Implementing role-based access control (RBAC) policies alongside micro-segmentation ensures that only authorized users can access segmented network resources based on least privilege principles. This combined strategy supports compliance requirements and improves overall network resilience against insider threats and external cyberattacks.
Best Practices and Recommendations for Enhanced Security
Implementing strict access control policies with role-based permissions significantly reduces unauthorized data access, while network segmentation isolates critical assets and limits lateral movement in case of breaches. Best practices emphasize the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA), continuous monitoring of access logs, and micro-segmentation to enforce granular security boundaries. Combining robust access controls with strategic network segmentation effectively minimizes attack surfaces and enhances overall cybersecurity resilience.
Access Control Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com