Hardware wallets provide a secure way to store your cryptocurrency private keys offline, protecting them from online hacks and malware. These devices are designed with advanced encryption and physical security features to ensure your digital assets remain safe even if your computer is compromised. Discover how hardware wallets can safeguard your investments by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
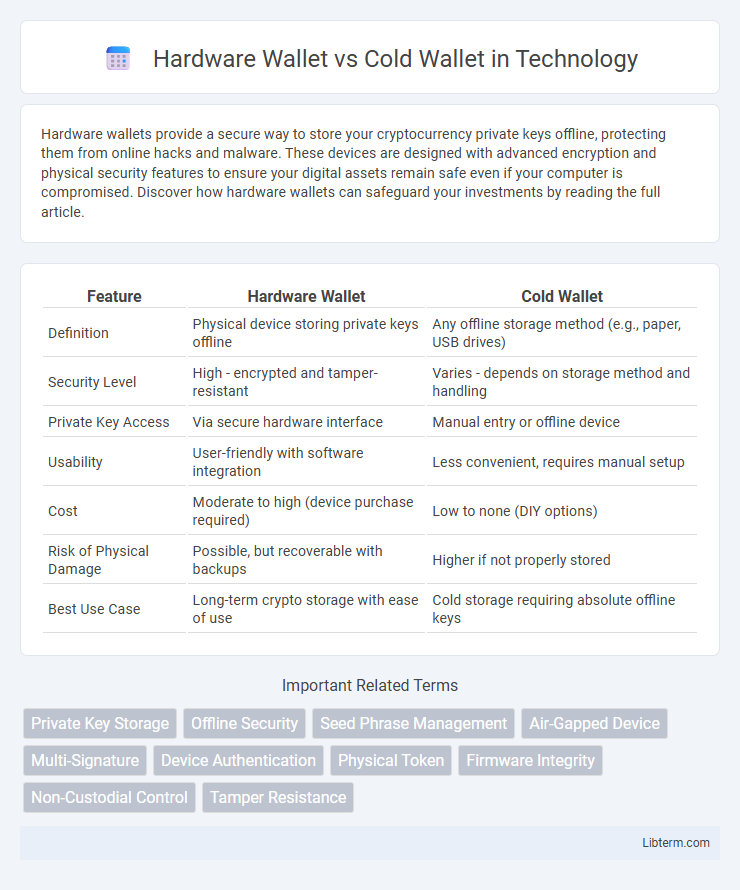
| Feature | Hardware Wallet | Cold Wallet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Physical device storing private keys offline | Any offline storage method (e.g., paper, USB drives) |
| Security Level | High - encrypted and tamper-resistant | Varies - depends on storage method and handling |
| Private Key Access | Via secure hardware interface | Manual entry or offline device |
| Usability | User-friendly with software integration | Less convenient, requires manual setup |
| Cost | Moderate to high (device purchase required) | Low to none (DIY options) |
| Risk of Physical Damage | Possible, but recoverable with backups | Higher if not properly stored |
| Best Use Case | Long-term crypto storage with ease of use | Cold storage requiring absolute offline keys |
Understanding Hardware Wallets
Hardware wallets are specialized physical devices designed to securely store cryptocurrency private keys offline, significantly reducing the risk of hacking or malware attacks. Unlike cold wallets, which can include various offline storage methods such as paper wallets or air-gapped computers, hardware wallets combine ease of use with robust security features like PIN protection and encrypted storage. Popular hardware wallet models, including Ledger Nano S and Trezor, support multiple cryptocurrencies and offer backup and recovery options to ensure asset safety even if the device is lost or damaged.
Defining Cold Wallets
Cold wallets refer to cryptocurrency storage solutions that remain completely offline to prevent unauthorized access, significantly reducing the risk of hacking and theft. Hardware wallets, a subset of cold wallets, are physical devices specifically designed to securely store private keys offline while allowing safe transaction signing. Both types provide robust security for digital assets by isolating private keys from internet exposure, crucial for long-term crypto asset protection.
Key Differences Between Hardware and Cold Wallets
Hardware wallets are physical devices designed to securely store private keys offline, providing strong protection against hacking and malware by generating and signing transactions within the device itself. Cold wallets refer to any form of offline storage, including hardware wallets, paper wallets, or air-gapped computers, emphasizing the complete disconnection from the internet to minimize exposure to cyber threats. The key difference lies in hardware wallets being specialized, tamper-resistant gadgets with user-friendly interfaces, while cold wallets broadly encompass all offline methods for safeguarding cryptocurrency keys.
Security Features Comparison
Hardware wallets and cold wallets both prioritize offline storage to enhance cryptocurrency security, but hardware wallets integrate secure elements and PIN protection, offering resistance against physical tampering and malware attacks. Cold wallets, such as paper wallets or air-gapped devices, rely on complete disconnection from the internet, minimizing exposure but lacking built-in authentication mechanisms and user-friendly recovery options. Comparing security features, hardware wallets provide encrypted private key storage and regular firmware updates, whereas cold wallets excel in eliminating network vulnerabilities but require meticulous manual management to prevent loss or theft.
Usability and Accessibility
Hardware wallets offer a secure and user-friendly experience, featuring physical devices with screens and buttons that simplify transaction verification and reduce phishing risks. Cold wallets encompass a broader category of offline storage methods, including hardware wallets, paper wallets, and air-gapped computers, each varying in accessibility and ease of use depending on the user's technical expertise. While hardware wallets provide streamlined interfaces and manufacturer support, cold wallets like paper backups may offer limited usability but higher versatility for long-term storage.
Supported Cryptocurrencies
Hardware wallets typically support a wide range of cryptocurrencies including Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin, and many ERC-20 tokens, offering extensive multi-asset management. Cold wallets, which often refer to offline storage methods like paper wallets or air-gapped devices, may have limited compatibility depending on the creation tool and the user's ability to manage various blockchain types securely. Users requiring support for diverse tokens frequently prefer hardware wallets for their built-in, regularly updated firmware that ensures broader ecosystem access.
Backup and Recovery Options
Hardware wallets offer secure backup and recovery through seed phrases or mnemonic codes, enabling users to restore access to their digital assets even if the device is lost or damaged. Cold wallets, including paper wallets and offline storage methods, require careful manual backup of private keys, with recovery entirely dependent on the physical security and condition of the stored data. Both solutions emphasize offline protection but vary significantly in user-friendliness and risk management during the backup and recovery process.
Cost Analysis: Hardware vs Cold Wallets
Hardware wallets typically range from $50 to $200 depending on brand and features, providing a physical device to securely store private keys offline. Cold wallets, which include paper wallets and air-gapped computers, often incur minimal or no upfront costs but may require time-intensive setup and higher risks if improperly managed. Cost analysis favors hardware wallets for users prioritizing ease of use and enhanced security despite initial expenditure, while cold wallets appeal to those seeking cost-free solutions with greater manual management.
Risks and Vulnerabilities
Hardware wallets store private keys offline, reducing exposure to phishing attacks and malware compared to cold wallets, which can include paper wallets vulnerable to physical damage or theft. Risks associated with hardware wallets involve device tampering, supply chain attacks, and potential firmware exploits, requiring users to verify authenticity and update securely. Cold wallets, while secure from online threats, face vulnerabilities such as loss, destruction, or interception during transfer, emphasizing the need for robust backup strategies and secure storage locations.
Choosing the Best Wallet for Your Needs
Hardware wallets are physical devices designed to securely store private keys offline, offering robust protection against online hacks and phishing attacks. Cold wallets encompass all offline storage methods, including hardware wallets, paper wallets, and air-gapped computers, prioritizing maximum security by isolating keys from internet exposure. Selecting the best wallet depends on factors such as ease of use, security level, asset diversity, and frequency of transactions to balance convenience with optimal protection for your cryptocurrency holdings.
Hardware Wallet Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com