Cognitive analytics leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to mimic human thought processes, enabling businesses to derive deeper insights from complex data sets. By combining natural language processing, pattern recognition, and predictive analytics, it enhances decision-making accuracy and uncovers hidden opportunities. Discover how cognitive analytics can transform your data strategy by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
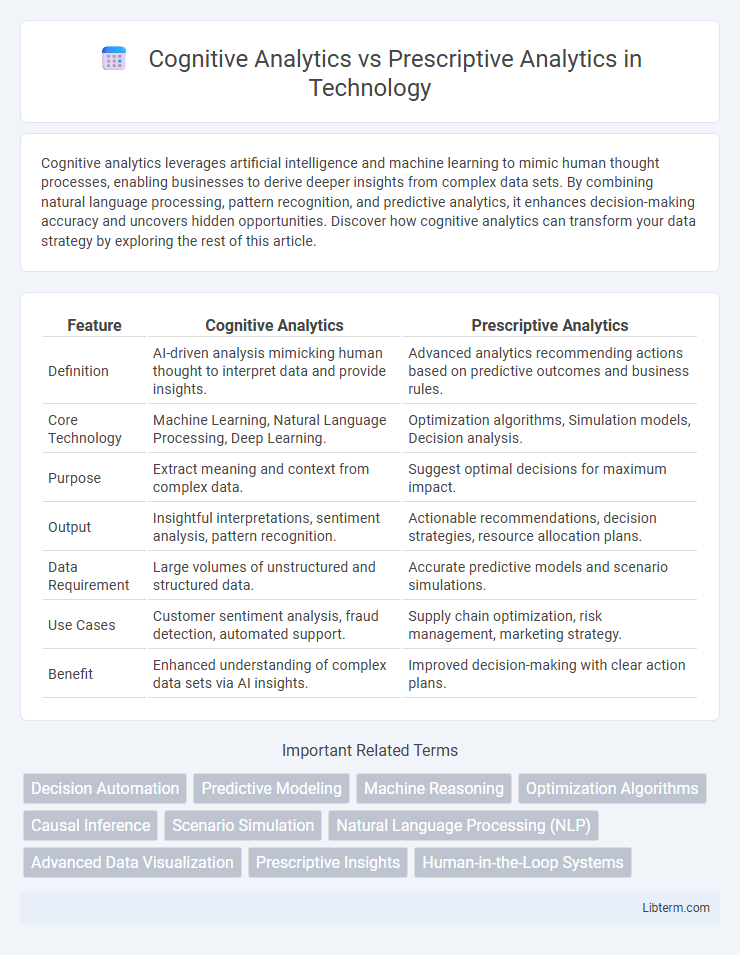
| Feature | Cognitive Analytics | Prescriptive Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | AI-driven analysis mimicking human thought to interpret data and provide insights. | Advanced analytics recommending actions based on predictive outcomes and business rules. |
| Core Technology | Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, Deep Learning. | Optimization algorithms, Simulation models, Decision analysis. |
| Purpose | Extract meaning and context from complex data. | Suggest optimal decisions for maximum impact. |
| Output | Insightful interpretations, sentiment analysis, pattern recognition. | Actionable recommendations, decision strategies, resource allocation plans. |
| Data Requirement | Large volumes of unstructured and structured data. | Accurate predictive models and scenario simulations. |
| Use Cases | Customer sentiment analysis, fraud detection, automated support. | Supply chain optimization, risk management, marketing strategy. |
| Benefit | Enhanced understanding of complex data sets via AI insights. | Improved decision-making with clear action plans. |
Introduction to Cognitive Analytics and Prescriptive Analytics
Cognitive Analytics utilizes artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to simulate human thought processes, enabling data interpretation, pattern recognition, and decision-making in complex scenarios. Prescriptive Analytics builds on predictive models to recommend specific actions that optimize outcomes by evaluating various decision paths and their potential impacts. Together, these analytics approaches enhance business intelligence by not only forecasting future events but also suggesting actionable strategies for improved performance.
Defining Cognitive Analytics
Cognitive Analytics leverages artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing to simulate human thought processes and extract deeper insights from complex data sets. Unlike Prescriptive Analytics, which recommends specific actions based on predictive models, Cognitive Analytics focuses on understanding context, reasoning, and adapting to new information dynamically. This approach enables businesses to uncover hidden patterns and make decisions that require nuanced interpretation beyond traditional data analysis.
Understanding Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics uses advanced algorithms, machine learning, and optimization techniques to recommend specific actions based on predictive insights, aiming to maximize outcomes and efficiency. It goes beyond descriptive and diagnostic analytics by not only analyzing what happened and why but also suggesting the best course of action for future scenarios. Organizations leverage prescriptive analytics in sectors like supply chain management, healthcare, and finance to drive decision automation and strategic planning.
Key Differences Between Cognitive and Prescriptive Analytics
Cognitive analytics leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to simulate human thought processes, enabling the analysis of unstructured data and the generation of insights through natural language processing and pattern recognition. Prescriptive analytics focuses on recommending specific actions by using optimization, simulation, and decision analysis techniques based on predictive models and historical data. Key differences include cognitive analytics' emphasis on understanding context and reasoning from complex data types, whereas prescriptive analytics prioritizes actionable recommendations and scenario evaluations to guide decision-making.
Core Technologies Powering Cognitive Analytics
Core technologies powering cognitive analytics include artificial intelligence, natural language processing, machine learning, and neural networks, which enable systems to mimic human thought processes and interpret unstructured data. Cognitive analytics integrates advanced algorithms to analyze diverse data sources, facilitating decision-making through pattern recognition and contextual understanding. These technologies contrast with prescriptive analytics, which primarily relies on optimization models and simulations to recommend specific actions based on predictive insights.
Methodologies Behind Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics employs methodologies such as optimization, simulation, and decision analysis to recommend actionable solutions based on predictive insights. It integrates data from cognitive analytics, which interprets unstructured data using machine learning and natural language processing, to inform more accurate and dynamic decision-making frameworks. Key techniques include mathematical modeling, heuristics, and reinforcement learning, enabling organizations to identify the best course of action under varying scenarios and constraints.
Applications of Cognitive Analytics in Various Industries
Cognitive analytics leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to interpret complex data patterns, enhancing decision-making in healthcare, finance, and retail by enabling personalized treatments, fraud detection, and customer behavior analysis. In contrast to prescriptive analytics, which suggests specific actions based on data, cognitive analytics provides deeper insights by understanding context and natural language, driving innovation in sectors like education through adaptive learning and in manufacturing via predictive maintenance. Industries adopting cognitive analytics report improved operational efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced customer experiences.
Use Cases for Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics is crucial in supply chain management by optimizing inventory levels and reducing operational costs through actionable recommendations. It enhances healthcare by providing personalized treatment plans based on patient data and predictive insights. In finance, prescriptive analytics supports risk management and fraud detection by suggesting optimal strategies to mitigate potential threats.
Benefits and Limitations of Each Approach
Cognitive analytics enhances decision-making by leveraging artificial intelligence to interpret unstructured data and predict trends, but its complexity and high computational demands can limit accessibility for smaller organizations. Prescriptive analytics offers actionable recommendations by analyzing data patterns and simulating outcomes, providing clarity for strategic planning, though it may struggle with dynamic environments due to reliance on historical data accuracy. Both approaches improve business intelligence but require balancing technological investment and organizational readiness for effective implementation.
Choosing the Right Analytic Approach for Your Business
Cognitive analytics leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to understand data patterns and generate human-like insights, while prescriptive analytics uses optimization and simulation algorithms to recommend specific actions based on predictive outcomes. Choosing the right analytic approach depends on your business goals: cognitive analytics excels in exploring complex datasets for deeper understanding, whereas prescriptive analytics focuses on decision-making and strategy optimization. Evaluate factors such as data complexity, desired outcomes, and resource availability to align your analytics investment with your operational needs and competitive objectives.
Cognitive Analytics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com