Client Credentials Grant is an OAuth 2.0 authentication method designed for server-to-server interactions where no user is involved. It enables your application to securely obtain an access token by presenting its own credentials directly to the authorization server. Discover how implementing this grant type can streamline your API security and enhance your application's authentication process in the full article.
Table of Comparison
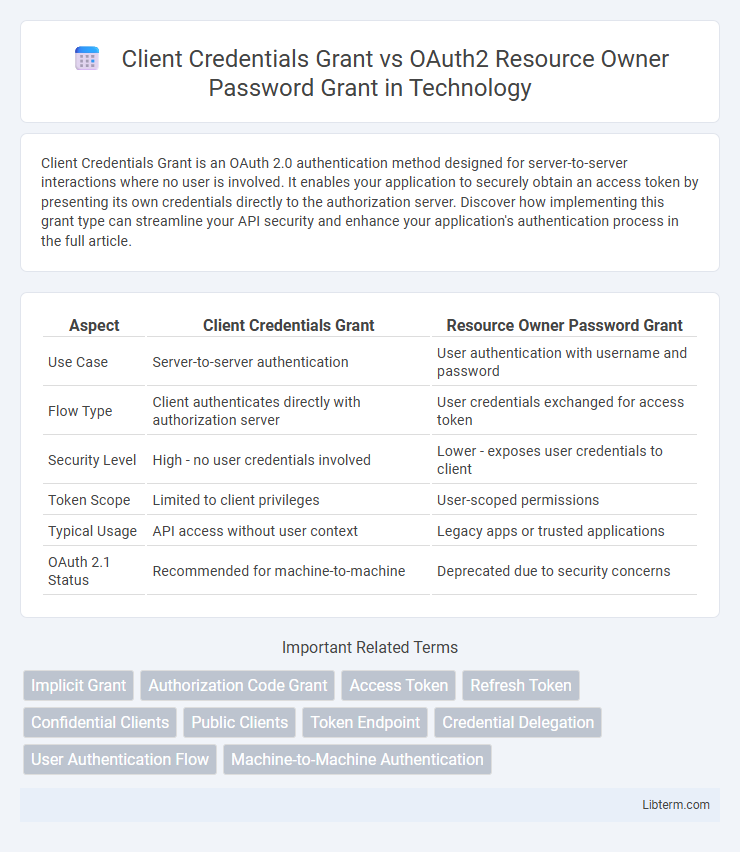
| Aspect | Client Credentials Grant | Resource Owner Password Grant |
|---|---|---|
| Use Case | Server-to-server authentication | User authentication with username and password |
| Flow Type | Client authenticates directly with authorization server | User credentials exchanged for access token |
| Security Level | High - no user credentials involved | Lower - exposes user credentials to client |
| Token Scope | Limited to client privileges | User-scoped permissions |
| Typical Usage | API access without user context | Legacy apps or trusted applications |
| OAuth 2.1 Status | Recommended for machine-to-machine | Deprecated due to security concerns |
Understanding OAuth2 Grant Types
Client Credentials Grant enables machine-to-machine authentication by allowing applications to obtain access tokens using their own credentials without user involvement, ideal for server-to-server interactions. OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant requires the user to provide their username and password directly to the application, enabling the app to exchange these credentials for an access token, suitable for highly trusted applications. Understanding these OAuth2 grant types involves recognizing the security implications and use cases for each: Client Credentials Grant prioritizes secure client authentication, while Resource Owner Password Grant offers direct user credential exchange but introduces higher security risks.
What is Client Credentials Grant?
Client Credentials Grant is an OAuth 2.0 authorization flow designed for server-to-server interactions where the client application authenticates directly with the authorization server using its own credentials, without involving a resource owner. This grant type issues an access token based solely on the client's identity, making it suitable for machine-to-machine communication and services accessing protected APIs. Unlike the Resource Owner Password Grant, Client Credentials Grant does not require user credentials, enhancing security in automated workflows.
What is Resource Owner Password Grant?
Resource Owner Password Grant in OAuth2 allows users to provide their username and password directly to the client application, which then exchanges these credentials for an access token from the authorization server. This grant type is suitable for highly trusted applications but poses higher security risks due to direct exposure of user credentials. Unlike Client Credentials Grant, which involves client authentication without user involvement, Resource Owner Password Grant requires the user's credentials for token issuance.
Key Differences Between Client Credentials and Password Grants
Client Credentials Grant uses only client authentication to obtain an access token, ideal for server-to-server communication without user involvement. Resource Owner Password Grant requires the user's username and password, allowing the application to access resources on behalf of the user, making it suitable for trusted applications. Client Credentials Grant does not involve user context, whereas Password Grant directly involves user credentials, impacting security and use case scenarios.
When to Use Client Credentials Grant
Client Credentials Grant is ideal for server-to-server authentication where no user context is involved, such as backend services accessing APIs securely. It should be used when applications need to authenticate themselves rather than a user, typically for machine-to-machine communication. This grant type offers higher security by avoiding user credential handling, making it suitable for automated processes and trusted system interactions.
When to Use Resource Owner Password Grant
Resource Owner Password Grant is best used in highly trusted applications where the user directly provides credentials to the client, such as legacy applications or first-party clients with full control over the user environment. It supports scenarios requiring immediate access to the resource owner's protected resources without redirection, ideal when user credentials are securely handled. This grant type should be avoided in third-party or public apps due to security risks and is recommended only when other OAuth2 flows like Authorization Code Grant are impractical.
Security Implications: Client Credentials vs Password Grant
Client Credentials Grant exclusively uses client authentication, eliminating the need for user credentials, which reduces exposure to phishing and credential leakage attacks. OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant requires users to share their username and password with the application, increasing risks of password compromise and unauthorized access. The Client Credentials Grant is generally more secure for machine-to-machine communication, whereas the Password Grant is less recommended due to its inherent security vulnerabilities with password handling.
Pros and Cons of Each Grant Type
Client Credentials Grant enables secure server-to-server authentication without user involvement, ideal for machine-to-machine interactions, but lacks user context and consent management, limiting its use in user-centric applications. OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant allows direct handling of user credentials for quick access token acquisition, simplifying legacy app integration, but risks compromising user credentials and is discouraged for new implementations due to security concerns. Choosing between them depends on the application's need for user context, security posture, and the nature of client-server interactions.
Real-World Use Cases and Examples
Client Credentials Grant is commonly used for server-to-server authentication where no user interaction is involved, such as machine-to-machine communication in microservices or API integrations between backend systems. OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant is suitable for legacy applications or trusted first-party clients requiring direct user credential input, like native mobile apps or internal tools where users authenticate with their username and password. Enterprises use Client Credentials Grant for automated workflows and service accounts, while Resource Owner Password Grant enables user-specific access but is less favored due to security concerns compared to more secure flows like Authorization Code Grant.
Choosing the Right OAuth2 Grant for Your Application
Selecting the appropriate OAuth2 grant depends on the application's context and security needs, with Client Credentials Grant suited for server-to-server communication where no user is involved, offering secure token exchange based on client identity alone. OAuth2 Resource Owner Password Grant allows users to provide credentials directly, making it suitable for trusted applications but posing higher security risks due to potential credential exposure. Evaluating factors like user interaction, trust level, and security requirements ensures optimal grant selection for effective authentication and authorization workflows.
Client Credentials Grant Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com