Serverless architecture enables developers to build and run applications without managing servers, allowing automatic scaling and reduced operational costs. This approach improves agility and efficiency by handling backend infrastructure through cloud providers. Discover how serverless solutions can transform your development process in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
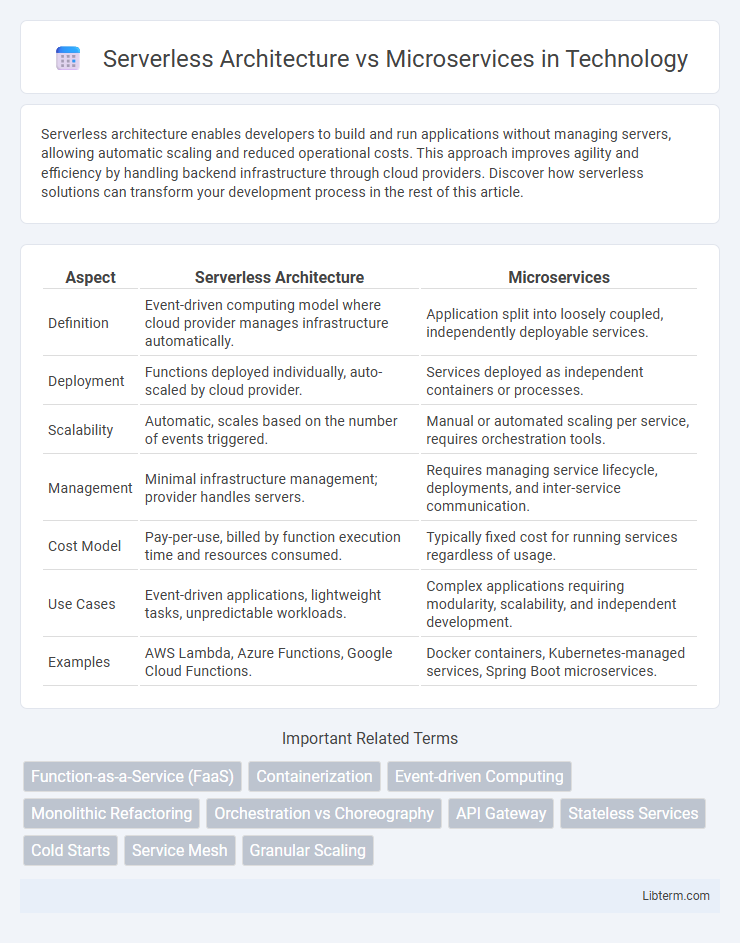
| Aspect | Serverless Architecture | Microservices |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Event-driven computing model where cloud provider manages infrastructure automatically. | Application split into loosely coupled, independently deployable services. |
| Deployment | Functions deployed individually, auto-scaled by cloud provider. | Services deployed as independent containers or processes. |
| Scalability | Automatic, scales based on the number of events triggered. | Manual or automated scaling per service, requires orchestration tools. |
| Management | Minimal infrastructure management; provider handles servers. | Requires managing service lifecycle, deployments, and inter-service communication. |
| Cost Model | Pay-per-use, billed by function execution time and resources consumed. | Typically fixed cost for running services regardless of usage. |
| Use Cases | Event-driven applications, lightweight tasks, unpredictable workloads. | Complex applications requiring modularity, scalability, and independent development. |
| Examples | AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions. | Docker containers, Kubernetes-managed services, Spring Boot microservices. |
Introduction to Serverless Architecture and Microservices
Serverless architecture enables developers to build and run applications without managing server infrastructure, relying on cloud providers like AWS Lambda and Azure Functions to automatically handle scaling and execution. Microservices architecture structures an application as a collection of loosely coupled services, each responsible for a specific business capability, facilitating independent development and deployment. Both paradigms aim to improve agility and scalability, with serverless focusing on event-driven execution and microservices emphasizing modular service isolation.
Core Concepts: Understanding Serverless vs Microservices
Serverless architecture eliminates server management by automatically scaling functions in response to events, enabling developers to focus solely on code execution without infrastructure concerns. Microservices architecture decomposes applications into small, independent services that communicate over APIs, allowing granular deployment and scalability of components. Understanding the distinction highlights serverless as a cloud-native execution model, whereas microservices represent a design pattern for modular software development.
Key Differences Between Serverless Architecture and Microservices
Serverless architecture eliminates the need for server management by running code in response to events, whereas microservices involve designing applications as a collection of loosely coupled services independently deployed. Serverless functions are ephemeral and event-driven, focusing on scalability and cost-efficiency, while microservices maintain persistent services with dedicated resources and inter-service communication via APIs. The key differences lie in deployment models, state management, and scalability approaches, with serverless emphasizing event-based execution and microservices prioritizing modular service autonomy.
Scalability and Performance Comparison
Serverless architecture offers automatic scaling based on demand, enabling efficient resource utilization without manual intervention, which can significantly improve performance during variable workloads. Microservices architectures allow for granular scaling of individual services, providing flexibility to optimize performance for specific components but often require more complex orchestration and resource management. Both architectures enhance scalability and performance, yet serverless excels in event-driven, bursty workloads, while microservices provide robust control for sustained, complex application environments.
Development and Deployment Workflow
Serverless architecture accelerates development by abstracting server management, allowing developers to focus solely on code with automatic scaling and event-driven execution, which simplifies deployment workflows. Microservices architecture requires designing, building, and deploying independently deployable services, providing granular control over development but introducing complexity in managing inter-service communication and deployment pipelines. Both architectures promote modular development, but serverless reduces infrastructure overhead, while microservices offer greater flexibility for complex application ecosystems.
Cost Implications: Serverless vs Microservices
Serverless architecture reduces cost by charging only for actual usage, minimizing idle resource expenses, while microservices often require continuous provisioning of containers or VMs, leading to higher fixed infrastructure costs. Serverless eliminates operational overhead such as maintenance and scaling, lowering DevOps expenses compared to microservices, which necessitate dedicated teams for deployment and management of multiple services. However, unpredictable workloads in serverless can sometimes lead to cost spikes, whereas microservices provide more predictable resource allocation and budgeting.
Security Considerations in Both Approaches
Serverless architecture offers built-in security features such as automatic patching and isolated execution environments, reducing the attack surface compared to traditional infrastructure, but it introduces challenges in managing function-level permissions and event-driven vulnerabilities. Microservices require robust inter-service communication security, including mutual TLS, API gateways, and service mesh implementations to ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized access in a distributed system. Both approaches demand comprehensive security strategies encompassing identity and access management, secure coding practices, and continuous monitoring to mitigate risks inherent in highly decoupled and dynamic environments.
Use Cases and Suitable Scenarios
Serverless architecture excels in event-driven applications, real-time data processing, and rapid prototyping where automatic scaling and reduced operational overhead are critical. Microservices are ideal for complex, large-scale systems requiring independent deployment, fine-grained scalability, and clear service boundaries, such as e-commerce platforms or financial services. Use cases demanding high customization, detailed monitoring, and long-running processes favor microservices, while sporadic workloads with unpredictable traffic patterns benefit more from serverless solutions.
Challenges and Limitations
Serverless architecture faces challenges such as cold start latency, limited execution duration, and difficulty in managing complex stateful applications, which can impact performance and scalability. Microservices often encounter limitations including service orchestration complexity, inter-service communication overhead, and the need for robust monitoring and fault tolerance mechanisms. Both architectures require careful consideration of security vulnerabilities, deployment complexities, and debugging difficulties to ensure efficient operation in distributed environments.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Selecting the right approach between serverless architecture and microservices depends on factors such as scalability requirements, development speed, and operational complexity. Serverless architecture offers automatic scaling and reduced operational management, ideal for event-driven or unpredictable workloads. Microservices provide greater control, modularity, and flexibility, making them suitable for complex applications needing fine-grained service isolation and independent deployment cycles.
Serverless Architecture Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com