Data binding seamlessly connects your application's UI elements to underlying data sources, ensuring real-time synchronization and reducing the need for manual updates. This technique enhances development efficiency by enabling automatic reflection of data changes in the interface. Explore the rest of the article to understand how mastering data binding can elevate your app's responsiveness and user experience.
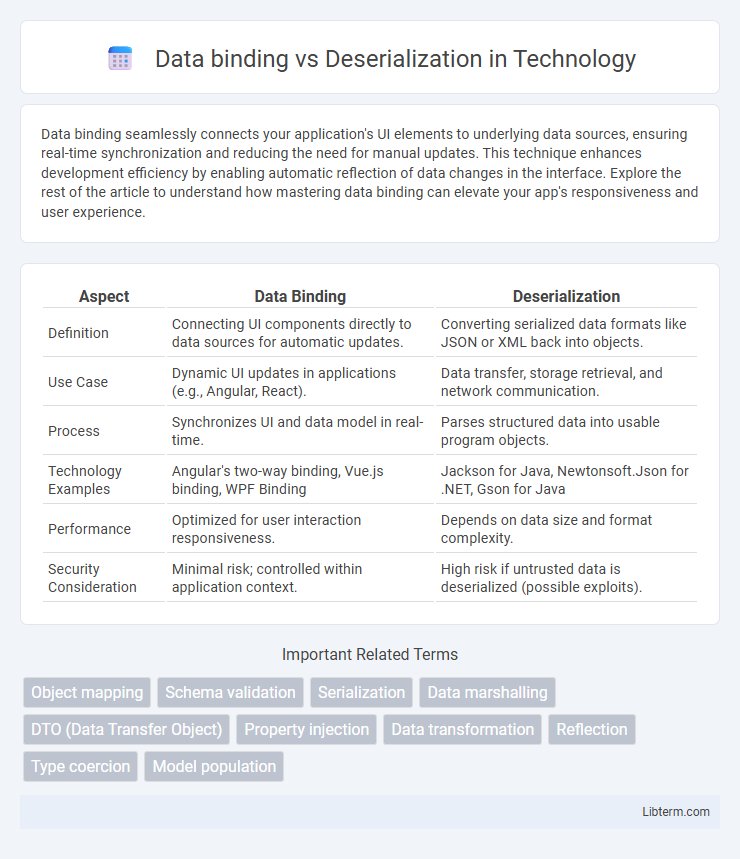
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Data Binding | Deserialization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Connecting UI components directly to data sources for automatic updates. | Converting serialized data formats like JSON or XML back into objects. |
| Use Case | Dynamic UI updates in applications (e.g., Angular, React). | Data transfer, storage retrieval, and network communication. |
| Process | Synchronizes UI and data model in real-time. | Parses structured data into usable program objects. |
| Technology Examples | Angular's two-way binding, Vue.js binding, WPF Binding | Jackson for Java, Newtonsoft.Json for .NET, Gson for Java |
| Performance | Optimized for user interaction responsiveness. | Depends on data size and format complexity. |
| Security Consideration | Minimal risk; controlled within application context. | High risk if untrusted data is deserialized (possible exploits). |
Introduction to Data Binding and Deserialization
Data binding is a process that connects UI components with data sources, allowing automatic synchronization between the user interface and data models, enhancing interactive application development. Deserialization refers to converting data from formats like JSON or XML back into objects or data structures that a program can use, enabling data exchange and persistence. Both techniques are essential in software engineering for handling data flow, with data binding streamlining UI updates and deserialization facilitating data input and reconstruction.
Defining Data Binding
Data binding is the process of connecting UI elements to data sources, enabling automatic synchronization between the view and the model in software development. This technique streamlines the development of dynamic interfaces by ensuring that changes in the data source automatically reflect on the UI without manual intervention. Unlike deserialization, which converts data formats into objects, data binding emphasizes real-time data flow and seamless interaction within applications.
Understanding Deserialization
Deserialization is the process of converting data from a byte stream or structured format like JSON or XML into a usable object or data structure in programming, enabling seamless data exchange between different systems. It requires strict adherence to data schemas and security measures to prevent vulnerabilities such as code injection or data tampering. Understanding deserialization involves recognizing its role in restoring the state of an object and its critical function in APIs, remote communication, and data storage systems.
Core Differences Between Data Binding and Deserialization
Data binding directly maps data structures, such as JSON or XML, to in-memory objects with automatic synchronization, enabling real-time updates between UI and data models. Deserialization converts serialized data streams into objects without maintaining ongoing synchronization, primarily focusing on reconstructing data for immediate use. The core difference lies in data binding's continuous link and synchronization between data and objects, whereas deserialization is a one-time transformation from data format to object state.
Use Cases for Data Binding
Data binding is primarily used in user interface frameworks to synchronize UI components with underlying data models, enabling real-time updates and interactive applications. It excels in scenarios such as form inputs, dynamic content rendering, and live data visualization where automatic propagation of data changes enhances user experience. Unlike deserialization, which focuses on converting data formats into objects, data binding emphasizes continuous synchronization between data sources and UI elements.
Common Scenarios for Deserialization
Deserialization commonly occurs when reconstructing objects from formats like JSON or XML in API responses, configuration files, or data storage retrieval. It enables applications to convert raw data streams into usable objects, facilitating data manipulation and interaction in programming environments such as Java, C#, and Python. Common scenarios include web services consuming RESTful APIs, reading settings from external files, and processing messages in distributed systems.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Data Binding
Data binding simplifies UI development by automatically synchronizing data between the model and view, reducing boilerplate code and minimizing manual updates, which enhances productivity and maintainability. However, its tight coupling of UI and data models can lead to complex debugging and potentially degrade performance in large-scale applications with frequent data changes. Data binding also requires learning specific frameworks or libraries, which may increase the initial development time compared to straightforward deserialization that converts data into usable objects without direct UI integration.
Pros and Cons of Deserialization
Deserialization efficiently converts data formats like JSON or XML into usable objects, enabling seamless data exchange between systems but poses security risks such as code injection and malformed data attacks. Its pros include easy data manipulation and integration with APIs, while cons involve vulnerability to remote code execution and difficulties handling corrupted or incompatible serialized data. Ensuring secure deserialization practices and thorough input validation is critical to mitigate these risks.
Data Binding vs Deserialization: Performance Comparison
Data binding and deserialization both transform data formats into objects, but differ significantly in performance. Data binding, which maps data directly to application models, typically offers faster processing by leveraging optimized parsing and type inference. Deserialization, involving the conversion of raw data streams into objects, can be slower due to additional overhead from serialization frameworks and format conversion steps.
Choosing the Right Approach: Data Binding or Deserialization
Choosing between data binding and deserialization depends on the complexity and structure of the data being processed. Data binding is ideal for applications requiring direct interaction with user interface elements and real-time updates, while deserialization suits scenarios involving raw data conversion from formats like JSON or XML into usable objects. Assessing performance needs, data format compatibility, and development context ensures selecting the most efficient approach for seamless data handling.
Data binding Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com