Remote management enables efficient control and monitoring of IT systems from any location, improving operational flexibility and reducing downtime. It leverages secure connections and centralized platforms to streamline updates, troubleshooting, and resource allocation. Discover how remote management can transform Your business technology in the following article.
Table of Comparison
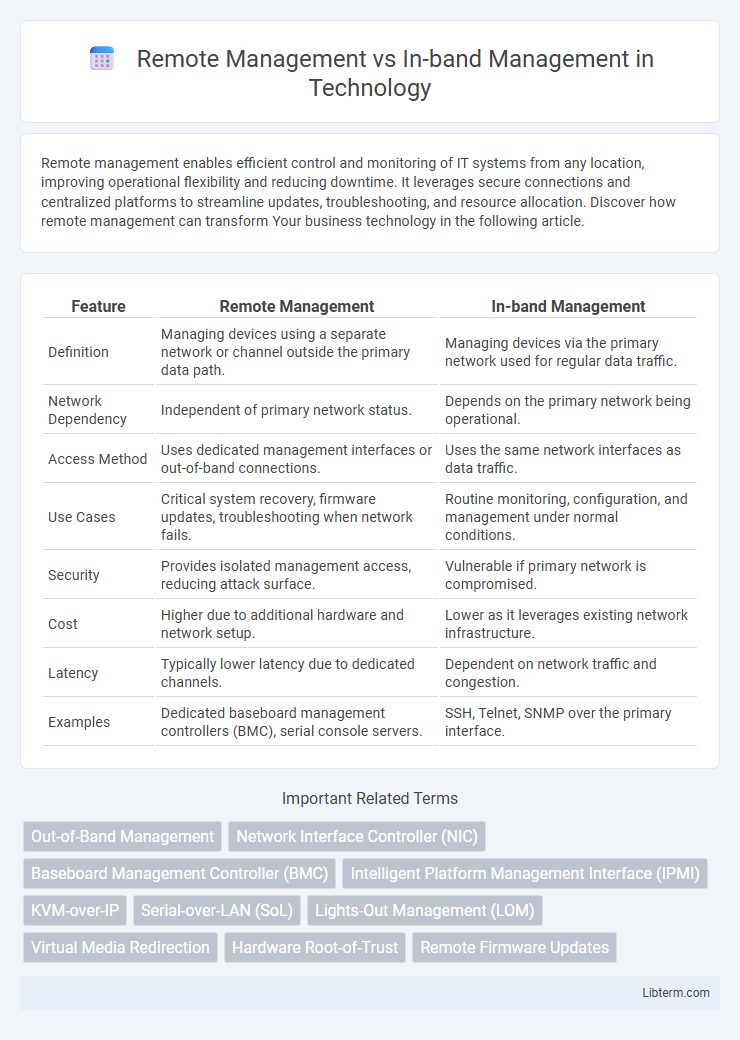
| Feature | Remote Management | In-band Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Managing devices using a separate network or channel outside the primary data path. | Managing devices via the primary network used for regular data traffic. |
| Network Dependency | Independent of primary network status. | Depends on the primary network being operational. |
| Access Method | Uses dedicated management interfaces or out-of-band connections. | Uses the same network interfaces as data traffic. |
| Use Cases | Critical system recovery, firmware updates, troubleshooting when network fails. | Routine monitoring, configuration, and management under normal conditions. |
| Security | Provides isolated management access, reducing attack surface. | Vulnerable if primary network is compromised. |
| Cost | Higher due to additional hardware and network setup. | Lower as it leverages existing network infrastructure. |
| Latency | Typically lower latency due to dedicated channels. | Dependent on network traffic and congestion. |
| Examples | Dedicated baseboard management controllers (BMC), serial console servers. | SSH, Telnet, SNMP over the primary interface. |
Overview of Remote and In-band Management
Remote management enables administrators to control and monitor IT systems from any location using network-based tools such as IPMI, iLO, or DRAC. In-band management relies on accessing devices through the primary network connection and operating system interface, requiring the system to be powered on and functional. Both methods serve critical roles in IT infrastructure management by providing different levels of access and control depending on operational states and security requirements.
Key Differences Between Remote and In-band Management
Remote management enables administrators to control devices over a network without being physically present, often using out-of-band channels like dedicated management interfaces or modems, ensuring access even during system failures. In-band management requires administrators to access devices through the same network interfaces used for regular data traffic, making it dependent on the device's operational state and network availability. Key differences include the reliability and security of access, with remote (out-of-band) management providing independent control paths and in-band management relying on the primary network, potentially limiting remote troubleshooting during outages.
How Remote Management Works
Remote management operates by utilizing secure network protocols such as SSH, IPMI, or proprietary software to control and monitor devices from off-site locations. It enables administrators to access system configurations, perform updates, troubleshoot issues, and reboot hardware without physical interaction, often through web interfaces or command-line tools. This method improves operational efficiency by providing continuous access to equipment regardless of geographical barriers or power status, unlike in-band management that requires direct connection within the device's operating environment.
How In-band Management Operates
In-band management operates by utilizing the same network channels that carry regular data traffic, allowing administrators to manage devices remotely through standard IP-based protocols such as SSH, Telnet, or HTTP/HTTPS. This method requires devices to be reachable over the data network, enabling configuration, monitoring, and troubleshooting without physical access. Its reliance on the primary network means any network failure can restrict access, distinguishing it from out-of-band counterparts which use separate, dedicated channels.
Advantages of Remote Management
Remote management offers significant advantages over in-band management, including the ability to monitor and control network devices independently of the network status, enhancing reliability during outages or failures. It facilitates proactive maintenance and troubleshooting from any location, reducing downtime and operational costs. Enhanced security features like dedicated management channels and out-of-band access provide a safer way to manage critical infrastructure remotely.
Benefits of In-band Management
In-band management provides direct control over network devices through the same communication channel used for regular data traffic, enabling seamless monitoring and configuration without the need for additional hardware. This approach reduces complexity and operational costs by eliminating separate management networks while enhancing real-time responsiveness to network issues. By leveraging in-band management, organizations ensure efficient resource utilization and maintain consistent connectivity even during routine administration tasks.
Limitations and Risks of Remote Management
Remote management faces limitations such as dependency on network connectivity, which can lead to inaccessibility during network outages or cyberattacks. Security risks are significant, including potential unauthorized access, data interception, and exploitation of remote management protocols if not properly secured. Unlike in-band management, remote management requires robust security measures like VPNs, multi-factor authentication, and encryption to mitigate these vulnerabilities.
Challenges of In-band Management
In-band management faces significant challenges such as network congestion and security vulnerabilities due to sharing the same communication channels with regular data traffic. This overlap can result in delayed or lost management commands during high traffic periods, impacting system reliability. Furthermore, exposure to common network threats increases risks of unauthorized access or attacks on management functions.
Use Cases: When to Use Each Management Method
Remote management is ideal for managing devices across dispersed locations, such as cloud servers or branch office equipment, enabling administrators to perform updates, troubleshoot, and monitor systems without physical access. In-band management suits scenarios where network devices like routers or switches are accessible through the primary network, allowing configuration changes and performance monitoring via the same data channels that carry user traffic. Use remote management for out-of-band access during network failures or emergencies, while in-band management is efficient for routine operations within a stable network environment.
Choosing the Right Management Approach for Your Network
Choosing the right management approach for your network depends on factors such as network complexity, security requirements, and administrative convenience. Remote management allows administrators to control devices from any location via out-of-band connections, ensuring access during outages but requiring dedicated management interfaces. In-band management uses the same network data path for both regular traffic and device control, offering simplicity but posing risks if the network goes down or is compromised.
Remote Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com