Innovating drives progress by introducing new ideas and improving existing processes to boost efficiency and creativity. Embracing innovation helps businesses stay competitive and adapt to rapidly changing markets. Discover how you can harness innovation to transform your strategies by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
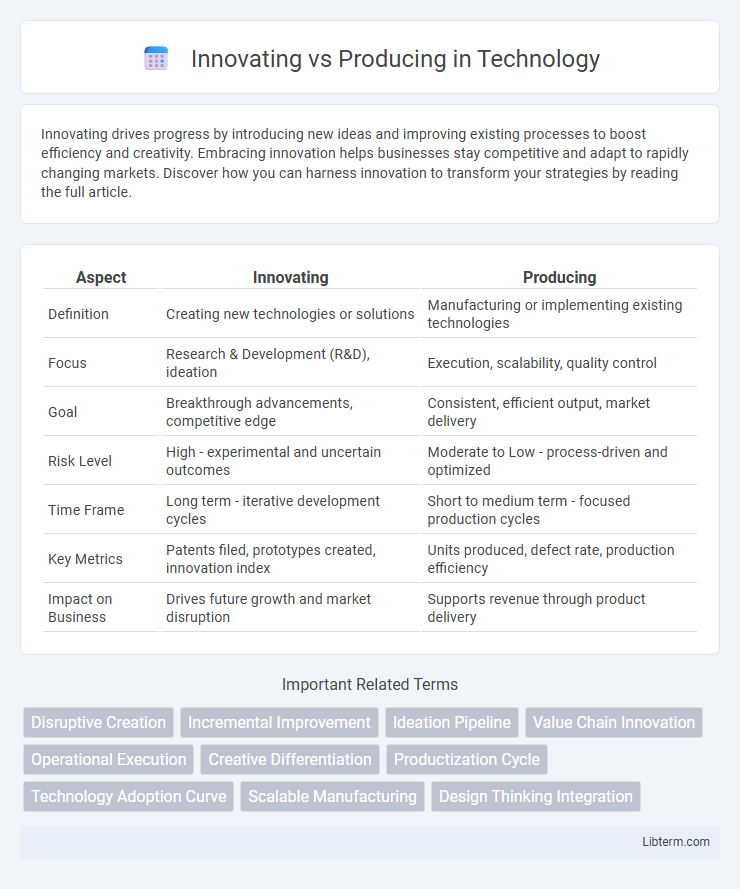
| Aspect | Innovating | Producing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Creating new technologies or solutions | Manufacturing or implementing existing technologies |
| Focus | Research & Development (R&D), ideation | Execution, scalability, quality control |
| Goal | Breakthrough advancements, competitive edge | Consistent, efficient output, market delivery |
| Risk Level | High - experimental and uncertain outcomes | Moderate to Low - process-driven and optimized |
| Time Frame | Long term - iterative development cycles | Short to medium term - focused production cycles |
| Key Metrics | Patents filed, prototypes created, innovation index | Units produced, defect rate, production efficiency |
| Impact on Business | Drives future growth and market disruption | Supports revenue through product delivery |
Understanding Innovation and Production
Understanding innovation involves recognizing the process of generating novel ideas, methods, or products that create value and drive competitive advantage. Production, on the other hand, focuses on the efficient transformation of resources and inputs into finished goods or services for market consumption. Balancing innovation and production ensures organizations can develop groundbreaking solutions while maintaining operational efficiency and scalable output.
Key Differences Between Innovating and Producing
Innovating involves creating new ideas, products, or processes that introduce significant improvements or breakthroughs, emphasizing creativity and experimentation. Producing focuses on efficiently manufacturing or delivering goods and services based on existing designs or concepts, prioritizing consistency and quality control. Key differences include innovation's emphasis on originality and risk-taking, whereas production centers on operational efficiency and repeatability.
The Role of Creativity in Innovation
Creativity serves as the driving force behind innovation, enabling the development of original ideas that challenge existing norms and generate novel solutions. Unlike producing, which focuses on the efficient execution and replication of established processes, innovation relies heavily on imaginative thinking to identify opportunities for improvement and breakthrough advancements. Organizations that foster creative environments enhance their capacity to innovate, leading to sustained competitive advantages through unique products and services.
Efficiency and Consistency in Production
Innovating drives efficiency by introducing advanced technologies and processes that streamline production workflows, reducing time and resource consumption. Producing emphasizes consistency, ensuring products meet quality standards and customer expectations through standardized methods and rigorous quality control. Balancing innovation with production allows companies to enhance operational efficiency while maintaining reliable output and market competitiveness.
Balancing Innovation with Scalable Production
Balancing innovation with scalable production requires integrating cutting-edge research and development processes with efficient manufacturing systems that can meet increasing demand. Employing modular production techniques and flexible automation allows companies to rapidly iterate on new ideas while maintaining consistent quality and output. Strategic collaboration between R&D teams and production units ensures that innovation translates into viable products without compromising scalability or cost-effectiveness.
Challenges Faced by Innovators and Producers
Innovators face challenges such as high uncertainty in market acceptance, significant R&D costs, and the need to continuously adapt to rapid technological changes. Producers often struggle with optimizing manufacturing efficiency, maintaining consistent quality control, and managing supply chain complexities. Both groups must address regulatory compliance and shifting consumer demands to remain competitive.
Impact on Business Growth and Competitiveness
Innovating drives business growth by fostering unique value propositions and opening new market opportunities, directly enhancing competitiveness in dynamic industries. Producing efficiently scales operations and optimizes cost structures, ensuring consistent delivery that supports market presence and customer retention. Balancing innovation with production enables companies to sustain long-term growth while adapting quickly to evolving market demands.
Real-World Examples: Innovating vs Producing
Tesla revolutionized the automotive industry by innovating electric vehicle technology, creating high-performance batteries and autonomous driving systems that disrupted traditional manufacturing approaches. Toyota exemplifies efficient producing through its lean manufacturing techniques, maintaining consistent quality and mass output while minimizing waste. SpaceX combines innovation and production by developing reusable rockets and scaling production to reduce launch costs, demonstrating the synergy between groundbreaking technology and optimized manufacturing.
Strategies for Integrating Innovation and Production
Effective strategies for integrating innovation and production include fostering cross-functional teams that collaborate closely from ideation to manufacturing, ensuring seamless knowledge transfer between R&D and production departments. Implementing agile manufacturing processes allows rapid adaptation of innovative designs into scalable production, minimizing time-to-market. Leveraging real-time data analytics and digital twins enhances decision-making, optimizing both innovation cycles and production efficiency.
Future Trends in Innovation and Production
Emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, IoT, and additive manufacturing are reshaping future trends in innovation and production by enabling smarter, more agile processes and customized outputs. Digital twins and predictive analytics enhance efficiency and reduce downtime, while sustainable materials and circular economy principles drive eco-friendly production models. Companies investing in R&D and integrating automation are positioned to lead in dynamic markets, balancing rapid innovation with scalable, cost-effective manufacturing.
Innovating Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com