Elastic scaling allows your applications to automatically adjust resources based on current demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency. This dynamic approach helps prevent under-provisioning during traffic spikes and reduces waste during low usage periods. Discover how elastic scaling can transform your infrastructure by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
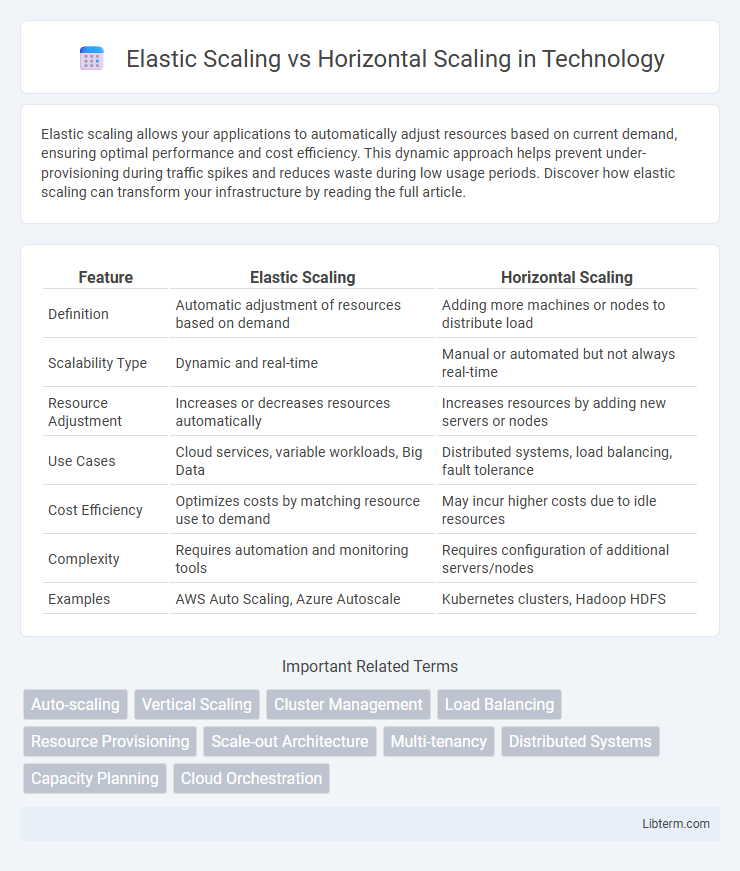
| Feature | Elastic Scaling | Horizontal Scaling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automatic adjustment of resources based on demand | Adding more machines or nodes to distribute load |
| Scalability Type | Dynamic and real-time | Manual or automated but not always real-time |
| Resource Adjustment | Increases or decreases resources automatically | Increases resources by adding new servers or nodes |
| Use Cases | Cloud services, variable workloads, Big Data | Distributed systems, load balancing, fault tolerance |
| Cost Efficiency | Optimizes costs by matching resource use to demand | May incur higher costs due to idle resources |
| Complexity | Requires automation and monitoring tools | Requires configuration of additional servers/nodes |
| Examples | AWS Auto Scaling, Azure Autoscale | Kubernetes clusters, Hadoop HDFS |
Introduction to Elastic Scaling and Horizontal Scaling
Elastic scaling dynamically adjusts computing resources based on real-time demand, enabling systems to respond efficiently to workload fluctuations without manual intervention. Horizontal scaling, also known as scaling out, involves adding more machines or instances to distribute the load and increase capacity, enhancing performance and fault tolerance. Both strategies optimize resource utilization but differ in flexibility, with elastic scaling offering automatic adaptability while horizontal scaling requires planned infrastructure expansion.
Defining Elastic Scaling: Key Features
Elastic scaling dynamically adjusts computing resources based on real-time demand, enabling automatic scaling up or down without manual intervention. Key features include rapid resource provisioning, cost efficiency by matching supply with workload, and enhanced application performance during fluctuating traffic. This approach contrasts with horizontal scaling, which involves adding or removing fixed numbers of servers or nodes manually.
What is Horizontal Scaling? Core Concepts
Horizontal scaling, also known as scaling out, involves adding more servers or nodes to a system to distribute the workload and increase capacity. This method enhances fault tolerance and load balancing by spreading tasks across multiple machines, improving overall system performance and availability. It contrasts with vertical scaling, which increases resources within a single server.
Elastic vs Horizontal Scaling: Fundamental Differences
Elastic scaling dynamically adjusts computing resources based on real-time demand, enabling automatic expansion or contraction of capacity for optimal performance and cost efficiency. Horizontal scaling involves adding more nodes or instances to distribute workloads, enhancing capacity and fault tolerance by increasing the number of servers. The fundamental difference lies in elasticity's automatic responsiveness to workload fluctuations versus horizontal scaling's manual or predefined addition of resources to handle increased loads.
Benefits of Elastic Scaling in Modern Infrastructure
Elastic scaling in modern infrastructure offers dynamic resource allocation that adapts to fluctuating workloads, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency. Unlike traditional horizontal scaling, elastic scaling leverages automated adjustments based on real-time demand, minimizing over-provisioning and reducing downtime during traffic spikes. Cloud-native environments benefit from elastic scaling by maintaining application availability and enhancing user experience through seamless capacity expansion and contraction.
When to Choose Horizontal Scaling: Use Cases
Horizontal scaling, or scaling out, is ideal for applications requiring high availability and fault tolerance, such as web services handling millions of concurrent users. It suits distributed systems, like cloud-native applications and big data platforms, where load balancing across multiple servers enhances performance and resiliency. Choosing horizontal scaling is crucial for businesses anticipating rapid traffic growth and needing seamless scaling without downtime.
Performance Impacts: Elastic vs Horizontal Scaling
Elastic scaling dynamically adjusts resources in real-time based on workload demands, minimizing latency and maintaining optimal application performance during traffic fluctuations. Horizontal scaling, involving the addition of more servers or nodes, enhances fault tolerance and distributes workloads, but may introduce overhead from inter-node communication affecting latency. Performance impacts of elastic scaling often result in more efficient resource utilization, while horizontal scaling provides steady performance gains at the cost of increased complexity in load balancing and network coordination.
Cost Considerations: Elastic and Horizontal Approaches
Elastic scaling dynamically adjusts resources based on real-time demand, optimizing costs by reducing resource usage during low traffic periods and preventing over-provisioning. Horizontal scaling involves adding or removing fixed units of resources, often incurring higher expenses due to the need for maintaining more hardware or instances even during low usage. Cost efficiency in elastic scaling is achieved through granular resource allocation and pay-as-you-go pricing models, whereas horizontal scaling typically involves upfront investment and ongoing operational costs for additional infrastructure.
Real-World Examples and Scenarios
Elastic scaling enables cloud services like Amazon Web Services to automatically adjust computing resources in real-time during traffic spikes, such as e-commerce websites handling Black Friday sales. Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers or instances, commonly used by Netflix to manage increased streaming demand by expanding its server pools across global data centers. Both strategies optimize performance and cost-effectiveness in dynamic environments requiring rapid capacity changes.
Choosing the Right Scaling Strategy for Your Needs
Elastic scaling automatically adjusts resource allocation based on real-time demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost-efficiency during fluctuating workloads. Horizontal scaling involves adding or removing servers to distribute load and enhance system capacity, ideal for applications requiring high availability and fault tolerance. Selecting the appropriate strategy depends on workload variability, application architecture, and budget constraints to balance responsiveness and scalability.
Elastic Scaling Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com