Manual programming involves writing code by hand to create software applications, allowing for precise control over the program's functionality and optimization. This approach requires deep understanding of programming languages and logic, ensuring your software meets specific needs without relying on automated tools. Explore the rest of the article to discover how manual programming can enhance your development skills and project outcomes.
Table of Comparison
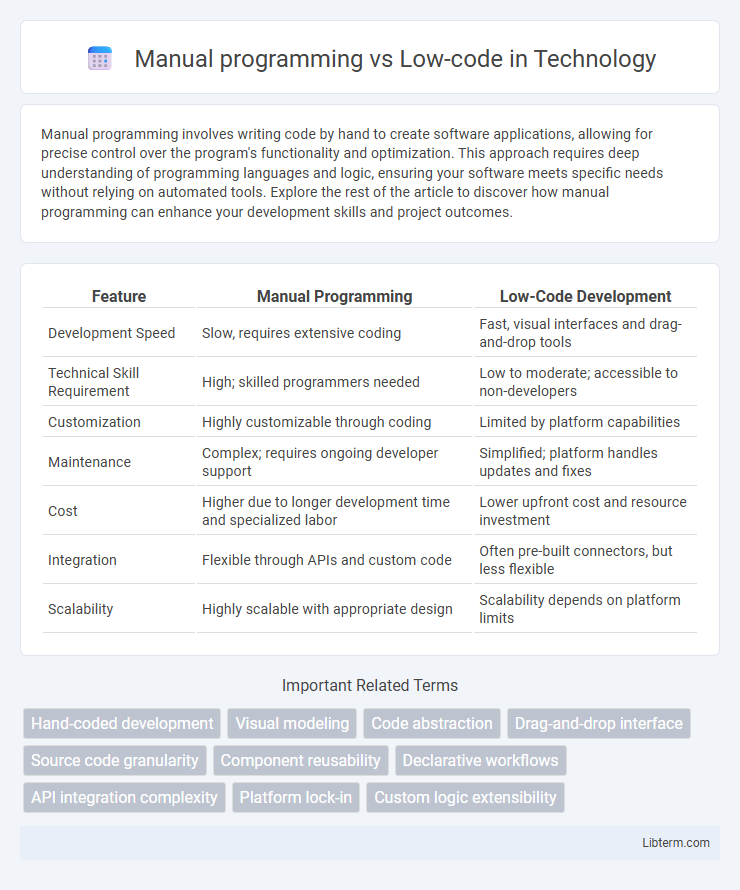
| Feature | Manual Programming | Low-Code Development |
|---|---|---|
| Development Speed | Slow, requires extensive coding | Fast, visual interfaces and drag-and-drop tools |
| Technical Skill Requirement | High; skilled programmers needed | Low to moderate; accessible to non-developers |
| Customization | Highly customizable through coding | Limited by platform capabilities |
| Maintenance | Complex; requires ongoing developer support | Simplified; platform handles updates and fixes |
| Cost | Higher due to longer development time and specialized labor | Lower upfront cost and resource investment |
| Integration | Flexible through APIs and custom code | Often pre-built connectors, but less flexible |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with appropriate design | Scalability depends on platform limits |
Introduction to Manual Programming and Low-Code
Manual programming involves writing code directly using languages such as Python, Java, or C++, offering full control over application development and customization. Low-code platforms provide visual development environments that enable rapid application creation with minimal hand-coding, accelerating deployment and reducing the need for extensive programming expertise. Choosing between manual programming and low-code depends on project complexity, scalability requirements, and development speed.
Key Differences Between Manual Programming and Low-Code
Manual programming requires extensive coding skills and allows complete control over software development with customized, flexible solutions, whereas low-code platforms enable faster application creation through visual interfaces and pre-built components, reducing the need for deep coding knowledge. Manual programming is ideal for complex, highly specialized projects demanding precision, while low-code suits rapid prototyping and business process automation with less technical resource investment. Scalability and maintainability differ significantly; manual coding offers granular optimization, whereas low-code platforms depend on vendor capabilities and may face limitations in handling intricate system requirements.
Benefits of Manual Programming
Manual programming offers unparalleled flexibility and control, enabling developers to create highly customized applications tailored to specific business needs. It allows for fine-tuning performance and integration at a granular level, which is essential for complex systems requiring optimized efficiency. Skilled programmers can leverage advanced coding techniques to implement innovative solutions beyond the constraints of low-code platforms.
Advantages of Low-Code Development
Low-code development significantly reduces application delivery time by using visual interfaces and pre-built components, enabling faster prototyping and iteration. It empowers non-developers and business users to contribute actively, fostering collaboration and reducing reliance on specialized programming skills. This approach enhances scalability and adaptability, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to changing market demands and streamline digital transformation initiatives.
Scalability and Flexibility Comparison
Manual programming offers unparalleled scalability and flexibility by allowing developers to customize code extensively for complex, large-scale applications and evolving business requirements. Low-code platforms increase development speed but may face limitations in handling highly scalable systems and intricate customizations due to predefined components and constraints. Enterprises prioritizing rapid deployment with moderate scalability often choose low-code solutions, while those needing robust, customizable infrastructure favor manual programming for long-term growth.
Speed and Time-to-Market Analysis
Manual programming typically requires extensive coding efforts and debugging, leading to longer development cycles and delayed time-to-market. Low-code platforms accelerate application delivery by enabling faster prototyping and simplified integration with pre-built components, significantly reducing development time. Companies adopting low-code solutions record up to 80% faster deployment times compared to traditional manual programming approaches.
Skill Requirements and Learning Curve
Manual programming demands in-depth knowledge of programming languages, algorithms, and debugging, making it essential for developers to have strong coding and problem-solving skills. Low-code platforms reduce the learning curve by offering visual interfaces and pre-built components, enabling users with limited technical backgrounds to create applications more quickly. While manual programming requires extensive training and experience, low-code solutions prioritize accessibility and faster deployment, minimizing the need for advanced programming expertise.
Security Considerations in Manual vs Low-Code
Manual programming offers granular control over security protocols, enabling developers to integrate customized authentication, encryption, and data validation methods tailored to specific application needs. Low-code platforms provide built-in security features such as automatic patching, standardized compliance tools, and role-based access controls, but may expose organizations to platform vulnerabilities and limited customization in security configurations. Evaluating the trade-offs between manual coding flexibility and low-code platform constraints is essential for mitigating risks related to data breaches, unauthorized access, and regulatory compliance.
Cost Implications and Resource Allocation
Manual programming often incurs higher upfront costs due to the need for specialized developers, extended development timelines, and ongoing maintenance expenses, which can strain budget allocations. Low-code platforms reduce initial and operational costs by enabling faster development cycles and allowing non-technical staff to contribute, optimizing resource allocation. Companies balancing cost-efficiency and resource management typically choose low-code solutions to accelerate deployment while minimizing dependency on high-cost technical talent.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Manual programming offers complete control and customization, ideal for complex projects requiring tailored solutions and intricate functionalities. Low-code platforms accelerate development with pre-built components and visual interfaces, making them suitable for rapid prototyping and projects with limited coding expertise. Evaluating project complexity, timeline, budget, and team skills ensures selecting the optimal approach for efficient and effective software delivery.
Manual programming Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com