Secure credential storage is essential for protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential breaches. Implementing encryption and following best practices ensures that your passwords, keys, and tokens remain confidential and intact. Discover effective methods to safeguard your credentials by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
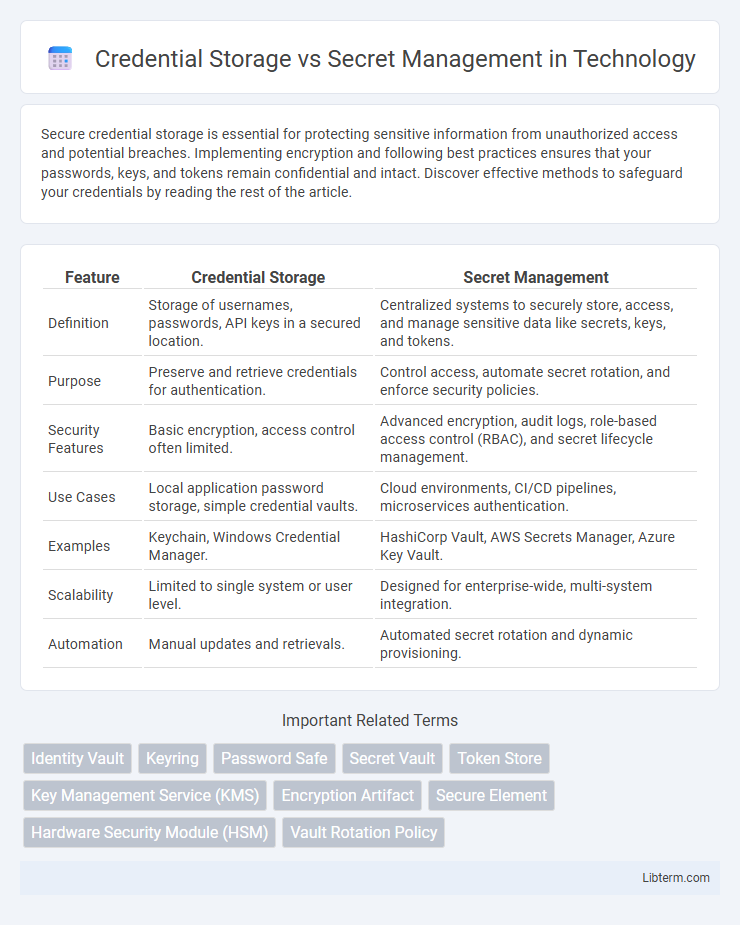
| Feature | Credential Storage | Secret Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Storage of usernames, passwords, API keys in a secured location. | Centralized systems to securely store, access, and manage sensitive data like secrets, keys, and tokens. |
| Purpose | Preserve and retrieve credentials for authentication. | Control access, automate secret rotation, and enforce security policies. |
| Security Features | Basic encryption, access control often limited. | Advanced encryption, audit logs, role-based access control (RBAC), and secret lifecycle management. |
| Use Cases | Local application password storage, simple credential vaults. | Cloud environments, CI/CD pipelines, microservices authentication. |
| Examples | Keychain, Windows Credential Manager. | HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault. |
| Scalability | Limited to single system or user level. | Designed for enterprise-wide, multi-system integration. |
| Automation | Manual updates and retrievals. | Automated secret rotation and dynamic provisioning. |
Introduction to Credential Storage and Secret Management
Credential storage involves securely saving usernames, passwords, tokens, and API keys to protect access to systems and applications. Secret management goes beyond storage by providing automated handling, rotation, and access control of sensitive information to minimize security risks. Both practices are essential for maintaining confidentiality, integrity, and availability of critical credentials in modern IT environments.
Understanding Credential Storage
Credential storage refers to the secure saving of authentication data such as usernames, passwords, and API keys, often within encrypted files or specialized hardware modules like TPMs. Effective credential storage minimizes unauthorized access risks by implementing strong encryption standards, access controls, and regular key rotation policies. Understanding credential storage is crucial for ensuring that sensitive information remains protected from breaches and unauthorized use in various applications and systems.
What is Secret Management?
Secret management involves securely storing, accessing, and distributing sensitive information such as API keys, passwords, certificates, and encryption keys within software applications or IT infrastructure. Unlike credential storage, which primarily holds usernames and passwords, secret management platforms provide automated retrieval, rotation, and auditing capabilities to minimize security risks and ensure compliance. Tools like HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, and Azure Key Vault are widely used for centralized, encrypted, and policy-driven secret management.
Key Differences Between Credential Storage and Secret Management
Credential storage primarily involves securely saving user credentials such as usernames and passwords, often within local systems or applications. Secret management extends beyond basic storage by providing dynamic handling, access control, rotation, and auditing of sensitive data like API keys, tokens, and encryption keys. Key differences include secret management's emphasis on automated lifecycle management and centralized control, which enhance security and compliance compared to static credential storage.
Common Use Cases for Credential Storage
Credential storage is primarily used for securely saving user passwords, API keys, and access tokens to facilitate authentication processes in applications and systems. It supports scenarios such as user login management, automated service authentication, and secure access to databases or cloud resources. Safe credential storage prevents unauthorized access and reduces the risk of security breaches in identity management and access control.
Typical Applications of Secret Management
Secret management is essential for securing sensitive data such as API keys, passwords, and certificates in cloud environments, DevOps pipelines, and microservices architectures. It enables dynamic secret generation, fine-grained access control, and automatic rotation, significantly reducing the risk of credential leakage. Common tools like HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, and Azure Key Vault automate secret lifecycle management, enhancing security and compliance in modern application deployments.
Security Risks: Credential Storage vs Secret Management
Storing credentials in plain text or unencrypted files exposes sensitive data to unauthorized access and potential breaches, increasing the risk of credential leakage and exploitation. Secret management solutions enforce encryption, access control, and audit logging, significantly reducing the attack surface and enhancing confidentiality for sensitive information. Misconfigured or poorly managed secret storage can lead to privilege escalation, data theft, and compromised systems, highlighting the importance of robust secret management practices over simple credential storage.
Implementation Best Practices
Implementing credential storage involves encrypting sensitive data at rest using strong algorithms like AES-256 and restricting access with role-based permissions to minimize exposure risks. Secret management solutions are best implemented by integrating automated rotation policies, audit logging, and secure APIs for dynamic secret injection into applications. Employing multi-factor authentication and regularly updating keys or secrets ensures robust defenses against unauthorized access and credential leakage.
Tools and Solutions Comparison
Credential storage tools like HashiCorp Vault and AWS Secrets Manager specialize in securely storing authentication information such as API keys, passwords, and tokens with encryption at rest and strict access controls. Secret management solutions extend beyond simple storage by offering features like automated secret rotation, dynamic secrets generation, and detailed audit logging to enhance security posture and compliance. Comparing tools, CyberArk emphasizes enterprise-grade privileged access management, while open-source options like Doppler and Bitwarden provide cost-effective, scalable secret management suitable for development environments and cloud-native applications.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Selecting the right approach between credential storage and secret management depends on your organization's scale, security requirements, and compliance needs. Credential storage often suits smaller environments with limited access control, while secret management systems provide centralized, automated handling of sensitive information, ideal for dynamic and large-scale infrastructures. Implementing a dedicated secret management tool enhances auditability, reduces risk of exposure, and simplifies secret rotation policies.
Credential Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com