Decryption transforms encoded data back into its original form, ensuring that sensitive information remains accessible only to authorized users. This process is essential for maintaining data privacy and security across digital communications. Discover how decryption techniques protect your information as you explore the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
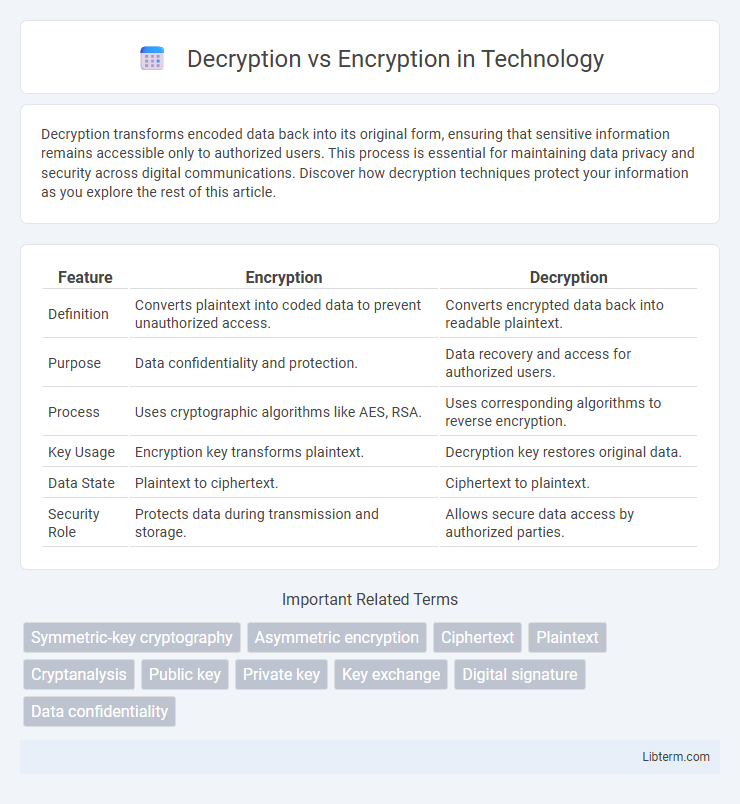
| Feature | Encryption | Decryption |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Converts plaintext into coded data to prevent unauthorized access. | Converts encrypted data back into readable plaintext. |
| Purpose | Data confidentiality and protection. | Data recovery and access for authorized users. |
| Process | Uses cryptographic algorithms like AES, RSA. | Uses corresponding algorithms to reverse encryption. |
| Key Usage | Encryption key transforms plaintext. | Decryption key restores original data. |
| Data State | Plaintext to ciphertext. | Ciphertext to plaintext. |
| Security Role | Protects data during transmission and storage. | Allows secure data access by authorized parties. |
Understanding Encryption: Definition and Purpose
Encryption transforms readable data into an encoded format to prevent unauthorized access, protecting sensitive information during transmission or storage. It uses algorithms and cryptographic keys to convert plaintext into ciphertext, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity. Decryption reverses this process, converting ciphertext back into its original readable form for authorized users.
What is Decryption? An Overview
Decryption is the process of converting encrypted data back into its original readable form using a specific key or algorithm, ensuring authorized access to the information. It reverses the encryption process, which secures data by transforming it into an unreadable format to protect confidentiality. Understanding decryption is essential for secure communication, data protection, and information integrity in cryptographic systems.
The Key Differences: Encryption vs Decryption
Encryption converts readable data (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) using an algorithm and an encryption key, securing information from unauthorized access. Decryption reverses this process, transforming ciphertext back into plaintext with the help of a decryption key, restoring data to its original form for authorized users. The key difference lies in their functions--encryption protects data by locking it, while decryption unlocks the data to make it accessible and understandable.
How Encryption Works: Methods and Algorithms
Encryption transforms readable data, or plaintext, into an unreadable format called ciphertext using algorithms such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), and Blowfish. Symmetric encryption employs a single key for both encrypting and decrypting data, while asymmetric encryption uses a public key to encrypt and a private key to decrypt, enhancing security in communication. These methods leverage complex mathematical functions and cryptographic keys to ensure data confidentiality during transmission or storage.
Exploring Decryption Techniques
Decryption techniques involve converting encrypted data back into its original readable format using specific algorithms and keys, essential for secure communication and data protection. Common methods include symmetric decryption, which uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, and asymmetric decryption, which employs a paired private key to unlock data encrypted with a public key. Advances in cryptanalysis and computational power continue to refine these techniques, balancing security with efficiency in various applications such as secure messaging and data recovery.
Symmetric vs Asymmetric Encryption Explained
Symmetric encryption uses a single secret key for both encryption and decryption, offering faster processing but requiring secure key distribution. Asymmetric encryption employs a paired public key for encryption and a private key for decryption, enhancing security by eliminating the need to share secret keys. Understanding the trade-offs between symmetric and asymmetric methods is essential for selecting appropriate cryptographic solutions in data protection.
Real-World Applications of Encryption and Decryption
Encryption transforms sensitive data into coded text to protect information during transmission and storage, essential in online banking, secure communications, and cloud services. Decryption reverses this process, allowing authorized users to access the original data, critical for authentication systems, ransomware recovery, and digital rights management. Together, encryption and decryption secure internet transactions, protect personal information, and enable confidential communication across industries like finance, healthcare, and government.
Common Encryption and Decryption Tools
Common encryption tools such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) are widely used to secure data by converting plaintext into unreadable ciphertext. Decryption tools, often integrated within the same cryptographic software, reverse this process by restoring the original data using secret keys or public/private key pairs. Popular tools like OpenSSL, GnuPG, and VeraCrypt offer robust encryption and decryption capabilities, supporting a variety of algorithms to protect sensitive information across different platforms.
Security Challenges in Encryption and Decryption
Encryption and decryption face critical security challenges, including key management flaws, susceptibility to brute-force attacks, and vulnerabilities in cryptographic algorithms. Weak or improperly stored keys can lead to unauthorized access during decryption, compromising sensitive data. The evolving sophistication of cyber threats demands continuous updates to encryption standards and protocols to maintain data confidentiality and integrity.
The Future of Data Security: Trends in Encryption and Decryption
Emerging trends in encryption and decryption emphasize quantum-resistant algorithms and homomorphic encryption, enhancing data security against future cyber threats. Advances in artificial intelligence-driven cryptanalysis necessitate adaptive encryption protocols to safeguard sensitive information. The integration of blockchain technology ensures decentralized and tamper-proof data verification, shaping the future landscape of cryptographic security.
Decryption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com