Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers cloud-based applications accessible via the internet, eliminating the need for complex installations or maintenance. This model offers scalable solutions that enhance productivity and reduce IT costs, ideal for businesses aiming to streamline operations. Discover how SaaS can transform your workflow by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
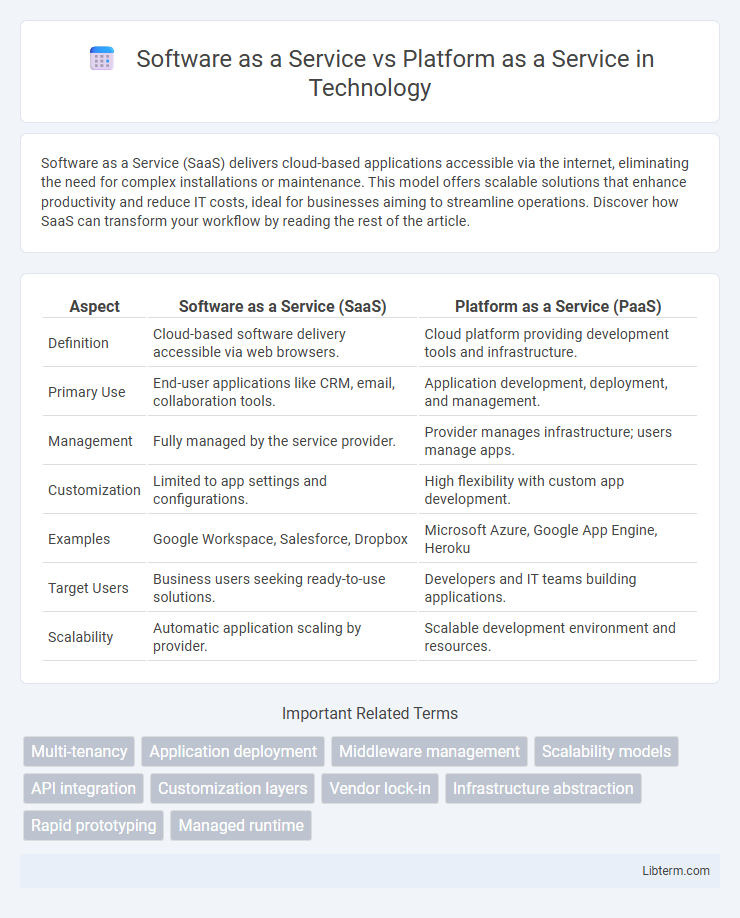
| Aspect | Software as a Service (SaaS) | Platform as a Service (PaaS) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud-based software delivery accessible via web browsers. | Cloud platform providing development tools and infrastructure. |
| Primary Use | End-user applications like CRM, email, collaboration tools. | Application development, deployment, and management. |
| Management | Fully managed by the service provider. | Provider manages infrastructure; users manage apps. |
| Customization | Limited to app settings and configurations. | High flexibility with custom app development. |
| Examples | Google Workspace, Salesforce, Dropbox | Microsoft Azure, Google App Engine, Heroku |
| Target Users | Business users seeking ready-to-use solutions. | Developers and IT teams building applications. |
| Scalability | Automatic application scaling by provider. | Scalable development environment and resources. |
Introduction to SaaS and PaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers fully functional software applications over the internet, enabling users to access programs like email, CRM, and collaboration tools without managing infrastructure or platforms. Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a cloud-based environment with tools and frameworks for developers to build, test, and deploy custom applications, streamlining the development process by abstracting hardware and middleware management. Both SaaS and PaaS eliminate the need for on-premises resources but serve different purposes: SaaS offers ready-to-use applications, while PaaS facilitates application creation and development.
Defining Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers cloud-based applications over the internet, allowing users to access software without local installation or management. SaaS solutions typically include email, customer relationship management (CRM), and collaboration tools, enabling seamless updates and scalability. This model contrasts with Platform as a Service (PaaS), which provides a development environment for building and deploying custom applications.
Defining Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides developers with a complete environment to build, test, and deploy applications without managing underlying infrastructure. PaaS offers tools, middleware, and runtime environments, enabling faster development and scalability compared to traditional software delivery methods. Unlike Software as a Service (SaaS), which delivers fully functional applications to end-users, PaaS focuses on the application development lifecycle, supporting customization and integration.
Core Features of SaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers fully functional applications hosted on the cloud, accessible via web browsers without local installation, emphasizing ease of use and automatic updates. Core features of SaaS include multi-tenancy architecture, subscription-based billing, scalability, and integrated security protocols ensuring data protection. Unlike Platform as a Service (PaaS), which provides development environments and tools for building customized applications, SaaS focuses on ready-made software solutions for end-users.
Core Features of PaaS
Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a cloud environment for developers to build, test, and deploy applications without managing underlying infrastructure, featuring core components like integrated development tools, middleware, and database management systems. Unlike Software as a Service (SaaS), which delivers fully functional applications to end-users, PaaS offers scalability, version control, and collaboration frameworks to streamline application lifecycle management. Key PaaS features include automated provisioning, runtime environment, API management, and multi-tenant architecture supporting diverse programming languages and frameworks.
Key Differences Between SaaS and PaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers fully functional applications over the internet, eliminating the need for users to manage underlying infrastructure or platforms. Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides a cloud-based environment with tools, libraries, and services to build, deploy, and manage custom applications, enabling developers to focus on coding without handling hardware or operating systems. The key difference lies in SaaS offering ready-to-use software accessible via browsers, whereas PaaS supplies a development framework for creating software tailored to specific business requirements.
Use Cases: When to Choose SaaS
SaaS is ideal for businesses seeking ready-to-use applications such as email, CRM, or collaboration tools without managing the underlying infrastructure. It suits organizations prioritizing rapid deployment, minimal maintenance, and scalable user access across devices. Use cases include customer relationship management with Salesforce, communication with Microsoft 365, and project management using Asana.
Use Cases: When to Choose PaaS
PaaS is ideal for developers seeking a ready-made environment to build, test, and deploy applications rapidly without managing underlying infrastructure, making it perfect for custom app development and collaborative projects. It supports scalable and flexible application hosting, integration with various development tools, and seamless workflow automation, which is crucial for startups and businesses with dynamic development needs. Choose PaaS when your focus is on accelerating development cycles, reducing operational complexity, and leveraging pre-configured middleware and runtime environments.
Pros and Cons of SaaS vs. PaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS) offers ease of use, automatic updates, and minimal infrastructure management, making it ideal for end-users requiring ready-to-use applications, but it limits customization and control over the underlying platform. Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides flexible development environments, scalability, and integration capabilities, enabling developers to build and deploy custom applications rapidly, though it requires more technical expertise and management commitment. SaaS reduces operational costs and accelerates deployment, whereas PaaS fosters innovation and customization at the expense of greater complexity and potential vendor lock-in.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Business
Choosing between Software as a Service (SaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS) depends on your business needs and technical capabilities. SaaS offers ready-to-use applications for streamlined operations and minimal IT management, ideal for businesses seeking quick deployment and scalability. PaaS provides a development environment with tools and infrastructure, suited for companies looking to build customized applications while reducing the complexity of hardware and software management.
Software as a Service Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com