Data tokenization replaces sensitive information with unique identification symbols, enhancing security by minimizing exposure of actual data. It is widely used in industries like finance and healthcare to protect personal and payment information from breaches. Explore the full article to understand how tokenization safeguards your data in various applications.
Table of Comparison
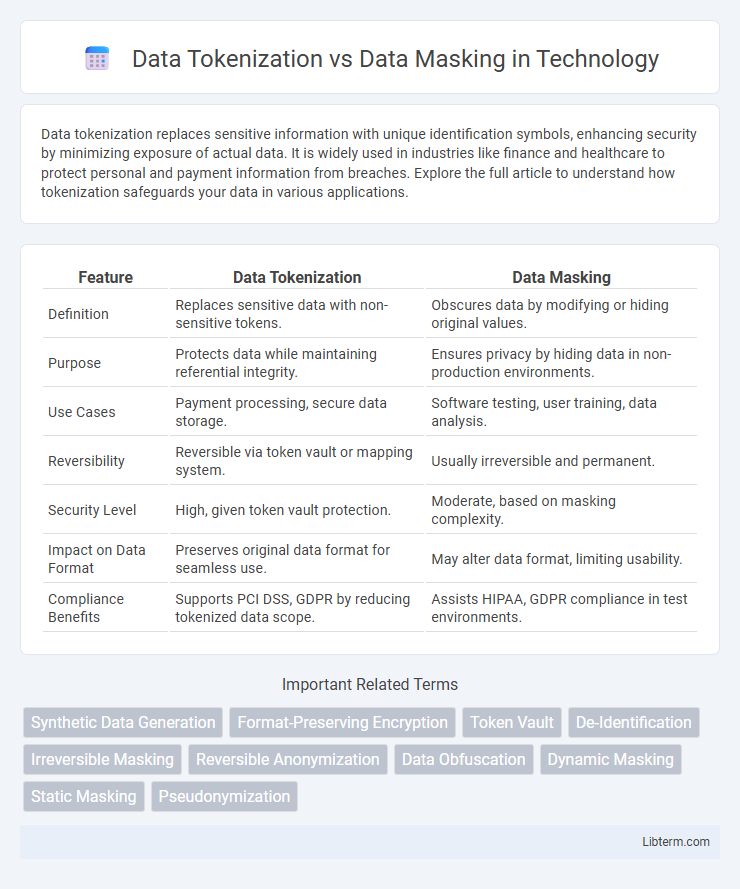
| Feature | Data Tokenization | Data Masking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive tokens. | Obscures data by modifying or hiding original values. |
| Purpose | Protects data while maintaining referential integrity. | Ensures privacy by hiding data in non-production environments. |
| Use Cases | Payment processing, secure data storage. | Software testing, user training, data analysis. |
| Reversibility | Reversible via token vault or mapping system. | Usually irreversible and permanent. |
| Security Level | High, given token vault protection. | Moderate, based on masking complexity. |
| Impact on Data Format | Preserves original data format for seamless use. | May alter data format, limiting usability. |
| Compliance Benefits | Supports PCI DSS, GDPR by reducing tokenized data scope. | Assists HIPAA, GDPR compliance in test environments. |
Introduction to Data Tokenization and Data Masking
Data tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive placeholders called tokens, preserving data format while enhancing security during storage and processing. Data masking involves obscuring specific data elements by altering original values to prevent unauthorized access, commonly used in testing and development environments. Both techniques reduce exposure risk but differ in application scope and reversibility, with tokenization allowing secure data detokenization and masking usually irreversible.
Key Differences Between Data Tokenization and Data Masking
Data tokenization replaces sensitive data with unique identification symbols or tokens that retain the essential information without exposing the original data, enabling secure data usage in applications and analytics. Data masking obscures data by altering or hiding characters to protect sensitive information, primarily used for testing or sharing datasets where original data is not necessary. Key differences include tokenization's reversible process for authorized use and masking's irreversible transformation focused on privacy protection during non-production use.
How Data Tokenization Works
Data tokenization works by replacing sensitive data elements with non-sensitive equivalents called tokens, which have no exploitable meaning or value outside the specific system. Tokens are generated using algorithms or token vaults that map the original data, enabling secure storage and transmission without exposing the actual information. This process ensures data protection by maintaining referential integrity while minimizing the risk of data breaches in environments such as payment processing or healthcare systems.
How Data Masking Works
Data masking works by replacing sensitive information with fictitious but realistic data, maintaining the format and structure to ensure usability in non-production environments. It uses techniques like substitution, shuffling, and encryption to protect personally identifiable information (PII) and confidential data while preserving data integrity for testing or analysis. This process prevents unauthorized access to original data, enabling secure data handling without compromising operational workflows.
Use Cases for Data Tokenization
Data tokenization is predominantly used in payment processing systems to replace sensitive credit card information with tokens, reducing the risk of data breaches while maintaining transactional integrity. It is also vital in healthcare for protecting patient identifiers, allowing secure sharing of medical records without exposing personal health information. Unlike data masking, which primarily supports non-production environments by obscuring data appearance, tokenization enables secure data usage in live environments, supporting compliance with regulations like PCI DSS.
Use Cases for Data Masking
Data masking is primarily used in non-production environments such as development, testing, and training to protect sensitive information while maintaining data usability. It enables organizations to comply with data privacy regulations like GDPR and HIPAA by ensuring personally identifiable information (PII) is obfuscated or replaced with fictitious data. Common use cases include securing customer data in software testing, preventing insider threats, and enabling safe data sharing with third-party vendors without exposing real data.
Security Benefits of Data Tokenization
Data tokenization replaces sensitive information with unique identification symbols, greatly reducing the risk of data breaches by ensuring that actual data is never exposed during transactions or storage. This method secures payment card information and personal data by isolating sensitive data within secure environments, minimizing compliance scope with standards like PCI DSS and GDPR. Unlike data masking, which obscures data temporarily and primarily for testing or development, tokenization offers robust, ongoing protection by rendering intercepted tokens useless to attackers.
Security Benefits of Data Masking
Data masking enhances security by replacing sensitive data with realistic but fictitious values, reducing the risk of unauthorized access during testing or development. Unlike tokenization, which substitutes data with tokens dependent on a token vault, masking ensures that reconstructed original data is not possible, thus providing stronger protection against data breaches. Organizations benefit from data masking through compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA, minimizing exposure of personally identifiable information (PII) in non-production environments.
Compliance Implications: Tokenization vs Masking
Data tokenization and data masking both enhance data security but differ vastly in compliance implications, particularly under regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS. Tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive placeholders, enabling secure processing and storage while maintaining regulatory adherence by minimizing exposure to actual data. Data masking obscures data for testing or analysis but does not eliminate sensitive data from the environment, often requiring stricter controls to comply with data privacy laws.
Choosing the Right Solution: Data Tokenization or Data Masking
Choosing between data tokenization and data masking hinges on the specific security requirements and use cases within an organization. Data tokenization replaces sensitive data with non-sensitive placeholders, preserving format and usability for authorized processes, making it ideal for payment processing and reducing PCI DSS scope. Data masking obscures data by altering it to prevent exposure, suitable for development and testing environments where realistic data is needed without risking actual sensitive information.
Data Tokenization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com