Efficiency maximizes output while minimizing wasted resources, time, and effort, boosting productivity across various tasks and industries. Implementing efficient strategies can help you achieve goals faster and improve overall performance. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for enhancing your efficiency.
Table of Comparison
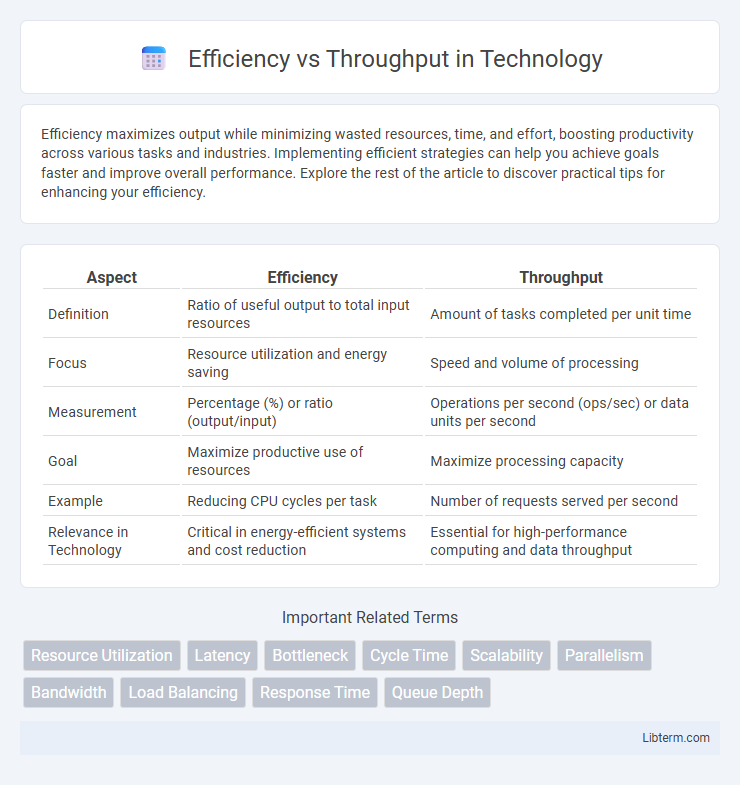
| Aspect | Efficiency | Throughput |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ratio of useful output to total input resources | Amount of tasks completed per unit time |
| Focus | Resource utilization and energy saving | Speed and volume of processing |
| Measurement | Percentage (%) or ratio (output/input) | Operations per second (ops/sec) or data units per second |
| Goal | Maximize productive use of resources | Maximize processing capacity |
| Example | Reducing CPU cycles per task | Number of requests served per second |
| Relevance in Technology | Critical in energy-efficient systems and cost reduction | Essential for high-performance computing and data throughput |
Understanding Efficiency: Definition and Importance
Efficiency measures the ratio of useful output to total input, highlighting how resources are utilized in a process. It is crucial for minimizing waste, reducing costs, and maximizing productivity in operations across manufacturing, computing, and business workflows. High efficiency ensures optimal use of energy, time, and materials, directly impacting overall performance and sustainability.
Throughput Explained: Key Concepts and Metrics
Throughput measures the rate at which a system processes tasks, often quantified as transactions per second or data units per hour, reflecting overall performance capacity. Key metrics include peak throughput, average throughput, and effective throughput, which consider processing speed, resource utilization, and latency impacts. Understanding throughput helps optimize system design by balancing processing volume and quality, ensuring maximum output without excessive delays or resource wastage.
Efficiency vs Throughput: Core Differences
Efficiency measures the ratio of useful output to total input, highlighting how well resources like time, energy, or materials are utilized in a system. Throughput refers to the total number of tasks or units processed within a specific time frame, emphasizing the system's capacity and speed. Core differences lie in efficiency optimizing resource utilization, while throughput maximizes production quantity regardless of resource expenditure.
How Efficiency Impacts Operational Performance
Efficiency directly influences operational performance by reducing resource waste and minimizing downtime, enabling processes to achieve maximum output with optimal input utilization. Higher efficiency results in streamlined workflows, faster task completion, and lower operational costs, thereby enhancing overall productivity. Efficient operations also improve service quality and customer satisfaction by ensuring timely delivery and consistent product standards.
The Role of Throughput in Business Success
Throughput plays a crucial role in business success by directly measuring the rate at which goods or services are produced and delivered to customers, impacting overall revenue and market competitiveness. High throughput enables companies to meet growing customer demand efficiently, reduce lead times, and enhance customer satisfaction. Focusing on increasing throughput often leads to improved operational performance and sustainable growth in fast-paced industries.
Factors Affecting Efficiency and Throughput
Factors affecting efficiency include resource utilization, process optimization, and equipment performance, while throughput is primarily influenced by system capacity, bottleneck constraints, and workflow design. High efficiency reduces waste and maximizes output per unit input, whereas high throughput emphasizes the total amount of products or services completed over time. Balancing machine reliability, operator skill, and material quality is crucial to optimizing both efficiency and throughput in production environments.
Balancing Efficiency and Throughput: Best Practices
Balancing efficiency and throughput requires optimizing resource allocation to minimize waste while maximizing output. Implementing lean manufacturing principles and continuous process improvement can enhance operational flow and reduce bottlenecks without sacrificing quality. Regular performance monitoring and adaptive scheduling ensure that production meets demand efficiently, maintaining both high throughput and effective use of resources.
Common Trade-offs Between Efficiency and Throughput
Efficiency often measures resource utilization per unit of output, while throughput emphasizes the total volume produced within a timeframe. Common trade-offs arise when optimizing for high throughput reduces efficiency due to increased resource consumption or bottlenecks, whereas maximizing efficiency can limit throughput by slowing processes or underutilizing capacity. Balancing these metrics depends on system goals, such as prioritizing cost-effectiveness or meeting demand.
Measuring and Improving Efficiency and Throughput
Efficiency measures the ratio of useful output to total input, while throughput quantifies the actual production rate over a specific period. Measuring efficiency often involves tracking the utilization of resources such as time, labor, and materials, whereas throughput focuses on the quantity of products or tasks completed per unit of time. Improving efficiency requires optimizing processes and reducing waste, while increasing throughput depends on streamlining workflows and enhancing capacity.
Real-world Examples: Efficiency vs Throughput in Action
Efficiency measures how well resources are utilized to minimize waste, such as a factory reducing energy consumption per unit produced, while throughput focuses on the total output over time, like a call center handling the maximum number of customer calls per hour. In logistics, efficiency could refer to minimizing fuel usage per delivery, whereas throughput evaluates how many packages are shipped daily. Software development teams often optimize efficiency by reducing coding errors, but throughput is gauged by the number of features deployed within a sprint.
Efficiency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com