LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is a protocol used to access and manage directory information services over a network, enabling efficient authentication and authorization. It stores and organizes user credentials, groups, and permissions, providing a centralized way to control access across your organization's IT environment. Explore the full article to understand how LDAP enhances security and streamlines identity management in your network.
Table of Comparison
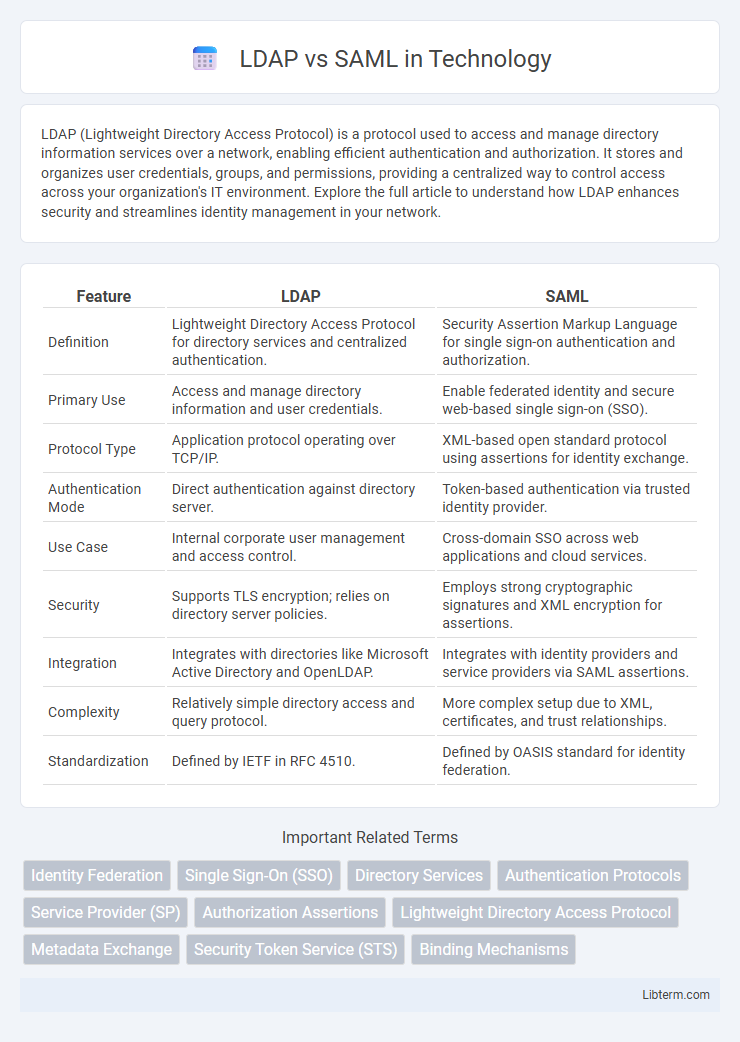
| Feature | LDAP | SAML |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol for directory services and centralized authentication. | Security Assertion Markup Language for single sign-on authentication and authorization. |
| Primary Use | Access and manage directory information and user credentials. | Enable federated identity and secure web-based single sign-on (SSO). |
| Protocol Type | Application protocol operating over TCP/IP. | XML-based open standard protocol using assertions for identity exchange. |
| Authentication Mode | Direct authentication against directory server. | Token-based authentication via trusted identity provider. |
| Use Case | Internal corporate user management and access control. | Cross-domain SSO across web applications and cloud services. |
| Security | Supports TLS encryption; relies on directory server policies. | Employs strong cryptographic signatures and XML encryption for assertions. |
| Integration | Integrates with directories like Microsoft Active Directory and OpenLDAP. | Integrates with identity providers and service providers via SAML assertions. |
| Complexity | Relatively simple directory access and query protocol. | More complex setup due to XML, certificates, and trust relationships. |
| Standardization | Defined by IETF in RFC 4510. | Defined by OASIS standard for identity federation. |
Introduction to LDAP and SAML
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is a protocol used for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services, primarily to manage user credentials and organizational data in a hierarchical structure. SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an open standard designed for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, enabling Single Sign-On (SSO) for secure web-based access. LDAP focuses on directory-based authentication, while SAML is centered on federated identity management through standardized assertions.
Understanding LDAP: Core Concepts
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) serves as a protocol for accessing and maintaining distributed directory information services over an IP network, primarily used for authenticating users and managing user information within centralized databases. It organizes data in a hierarchical structure of entries, composed of attributes and distinguished names (DNs), facilitating efficient querying and modification of user credentials and permissions. LDAP plays a crucial role in identity management systems by supporting secure access control and integration with various applications through a standardized approach to directory service communication.
What is SAML? Key Principles
SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) is an open standard for exchanging authentication and authorization data between parties, primarily between an identity provider and a service provider. It operates on key principles such as single sign-on (SSO), enabling users to authenticate once and gain access to multiple applications without re-entering credentials. SAML uses XML-based assertions that securely communicate user identity information, enhancing security and user experience across diverse systems.
LDAP vs SAML: Authentication Mechanisms
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) authenticates users by querying directory services to verify credentials, primarily using username and password pairs stored in centralized databases. SAML (Security Assertion Markup Language) relies on exchanging XML-based authentication assertions between an identity provider and a service provider, enabling single sign-on (SSO) across multiple applications. Unlike LDAP's direct credential verification, SAML shifts the authentication responsibility to an external trusted identity provider, enhancing federated identity management and reducing password exposure.
Security Features: LDAP Versus SAML
LDAP provides centralized directory services enabling authentication and authorization through secure protocols like LDAPS and StartTLS, ensuring encrypted data transmission. SAML offers robust federated identity management with strong security features such as cryptographic signatures, encryption of assertions, and support for single sign-on (SSO) across multiple domains. Both protocols enhance security by mitigating unauthorized access risks, but SAML's federated approach excels in cross-organizational authentication compared to LDAP's internal directory focus.
Use Cases: When to Use LDAP or SAML
LDAP is ideal for internal applications requiring centralized directory services, such as employee authentication and access control within corporate intranets. SAML excels in federated identity management, enabling secure single sign-on (SSO) across multiple web domains and cloud-based services. Organizations use LDAP for managing user credentials in local environments, while SAML is preferred for seamless authentication between different organizational boundaries or third-party service providers.
Integration and Compatibility Differences
LDAP offers direct directory access for authentication and user management, making it highly compatible with internal applications and legacy systems that require centralized credential storage. SAML, designed for web-based single sign-on (SSO), integrates seamlessly with cloud applications and identity providers using standardized XML-based assertions for secure user authentication. Compatibility-wise, LDAP suits on-premises environments needing granular access control, while SAML excels in cross-domain federated identity scenarios where interoperability with multiple service providers is critical.
Performance and Scalability Considerations
LDAP delivers fast directory queries with low latency, optimized for handling numerous read operations across large user directories, making it suitable for environments demanding high-speed authentication. SAML, relying on XML-based assertions and web-based communication, introduces higher latency and processing overhead but scales efficiently in federated identity scenarios across multiple domains. Performance tuning for LDAP involves indexing and caching strategies, while SAML scalability benefits from distributed identity providers and assertion validation caching.
Pros and Cons of LDAP and SAML
LDAP offers efficient directory-based authentication and centralized user management with fast query performance, but it lacks robust support for federated identity and relies on on-premise infrastructure. SAML excels in enabling single sign-on (SSO) across multiple domains and supports secure, federated authentication with strong token-based mechanisms, although it can introduce complexity in setup and depends heavily on proper configuration for security. Choosing between LDAP and SAML involves balancing LDAP's simplicity and speed against SAML's flexibility for cross-organizational access control and enhanced security features.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Organization
Choosing the right protocol for your organization depends on your specific authentication and access management needs. LDAP excels in managing user directories and providing centralized authentication within an internal network, making it ideal for enterprise environments requiring granular control over user permissions. SAML is better suited for enabling secure single sign-on (SSO) across multiple web applications and external services, streamlining user access while enhancing security in cloud-centric or federated identity ecosystems.
LDAP Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com