Integration streamlines processes by combining multiple systems into a unified platform, enhancing efficiency and data consistency. It enables seamless communication between applications, reducing errors and saving time. Discover how integration can transform your operations by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
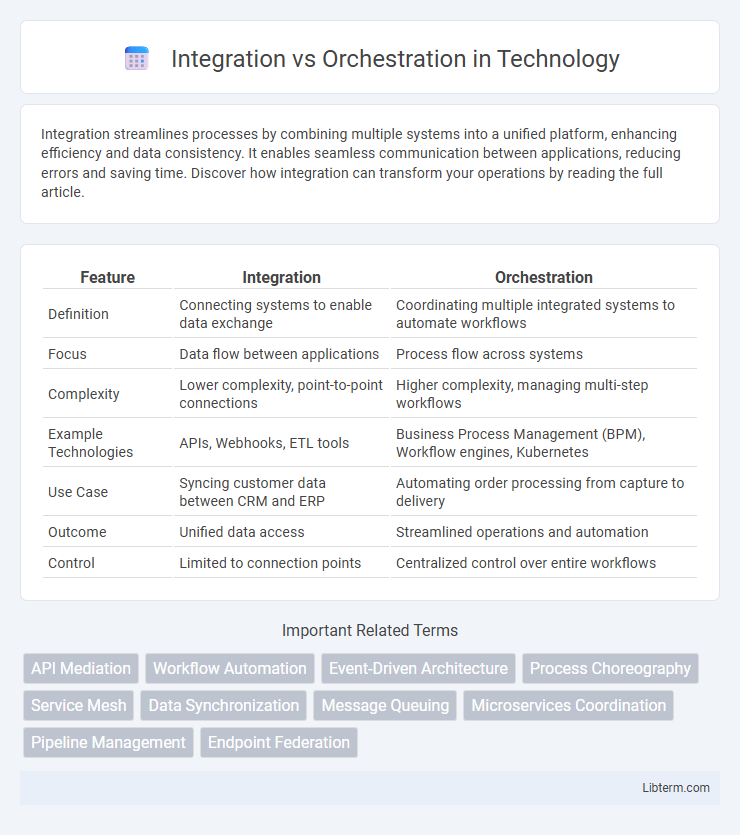
| Feature | Integration | Orchestration |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Connecting systems to enable data exchange | Coordinating multiple integrated systems to automate workflows |
| Focus | Data flow between applications | Process flow across systems |
| Complexity | Lower complexity, point-to-point connections | Higher complexity, managing multi-step workflows |
| Example Technologies | APIs, Webhooks, ETL tools | Business Process Management (BPM), Workflow engines, Kubernetes |
| Use Case | Syncing customer data between CRM and ERP | Automating order processing from capture to delivery |
| Outcome | Unified data access | Streamlined operations and automation |
| Control | Limited to connection points | Centralized control over entire workflows |
Understanding Integration and Orchestration
Integration involves connecting disparate systems or applications to enable seamless data exchange and functionality, often through APIs or middleware. Orchestration manages and coordinates multiple integrated services or processes to automate workflows and ensure efficient task execution. Understanding these concepts clarifies how integration provides the foundational connectivity while orchestration optimizes the overall system's operational flow.
Key Differences Between Integration and Orchestration
Integration involves connecting disparate systems or applications to enable seamless data exchange and functionality, while orchestration focuses on coordinating multiple integrated services to automate complex workflows. Integration emphasizes data interoperability and system compatibility, whereas orchestration prioritizes process management, execution order, and conditional logic across integrated components. Key differences include scope, with integration addressing connectivity and data sharing, and orchestration handling end-to-end process automation and service coordination.
Core Components of Integration
Core components of integration include APIs, middleware, data connectors, and integration platforms that enable seamless data exchange between disparate systems. These elements facilitate secure, real-time communication and ensure data consistency across cloud and on-premises applications. Effective integration relies on standardized protocols, transformation engines, and authentication mechanisms to support interoperability and scalability.
Essential Elements of Orchestration
Orchestration involves the automated coordination and management of complex workflows, integrating various services and applications to achieve seamless business processes. Essential elements of orchestration include centralized control, real-time monitoring, policy-based automation, and error handling to ensure efficient execution of interconnected tasks. Unlike basic integration, orchestration emphasizes end-to-end process optimization and dynamic decision-making across multiple systems.
Automation in Integration vs. Orchestration
Automation in integration streamlines data flow between disparate systems by enabling real-time data exchange and reducing manual intervention, improving overall efficiency. Orchestration automates complex workflows across multiple integrated services, coordinating tasks to execute business processes end-to-end seamlessly. This distinction highlights integration's role in connectivity, while orchestration focuses on automating the sequence and logic of automated tasks for holistic process management.
Use Cases: When to Use Integration
Integration is ideal for connecting disparate systems to enable seamless data exchange, especially in scenarios requiring real-time synchronization between applications like ERP and CRM platforms. It supports use cases such as consolidating customer information, automating workflows, and ensuring consistency across marketing, sales, and support systems. Integration excels when the primary goal is to create a unified data environment that reduces redundancy and enhances operational efficiency.
Use Cases: When to Use Orchestration
Use orchestration when managing complex workflows that require coordinating multiple automated tasks across various systems, such as in cloud resource provisioning, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines, and microservices management. Orchestration excels in scenarios demanding dynamic sequencing, error handling, and dependency management to ensure seamless end-to-end process execution. In contrast to simple integration, orchestration provides the control layer necessary for automating interconnected processes in real-time, enhancing operational efficiency and scalability.
Integration and Orchestration in Cloud Environments
Integration in cloud environments involves connecting disparate applications and services to enable seamless data flow and interoperability, often through APIs and middleware solutions. Orchestration goes beyond integration by automating the coordination and management of multiple cloud services and workflows to optimize resource utilization and operational efficiency. Cloud orchestration tools like Kubernetes, AWS Step Functions, and Azure Logic Apps provide advanced capabilities for scaling, monitoring, and managing complex cloud-based processes.
Challenges in Integrating and Orchestrating Systems
Challenges in integrating and orchestrating systems include handling diverse data formats and ensuring seamless communication between heterogeneous platforms. Complex workflows require robust coordination to maintain data consistency and system reliability across multiple services. Scalability issues and latency can arise when synchronizing numerous interconnected applications, complicating error handling and monitoring processes.
Best Practices for Combining Integration and Orchestration
Best practices for combining integration and orchestration emphasize creating seamless data flow between diverse systems while managing workflows effectively. Implementing clear API standards and centralized monitoring enhances both integration reliability and orchestration transparency, enabling quick detection and resolution of issues. Leveraging modular design and event-driven architectures supports scalability and flexibility, ensuring that integrated components can be orchestrated dynamically to meet evolving business processes.
Integration Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com