Security by Design integrates robust protection measures during the initial stages of product development, ensuring vulnerabilities are minimized before deployment. This proactive approach emphasizes encryption, secure coding practices, and continuous risk assessments to safeguard systems from emerging threats. Discover how adopting Security by Design principles can strengthen Your organization's defenses and why it's essential in today's digital landscape by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
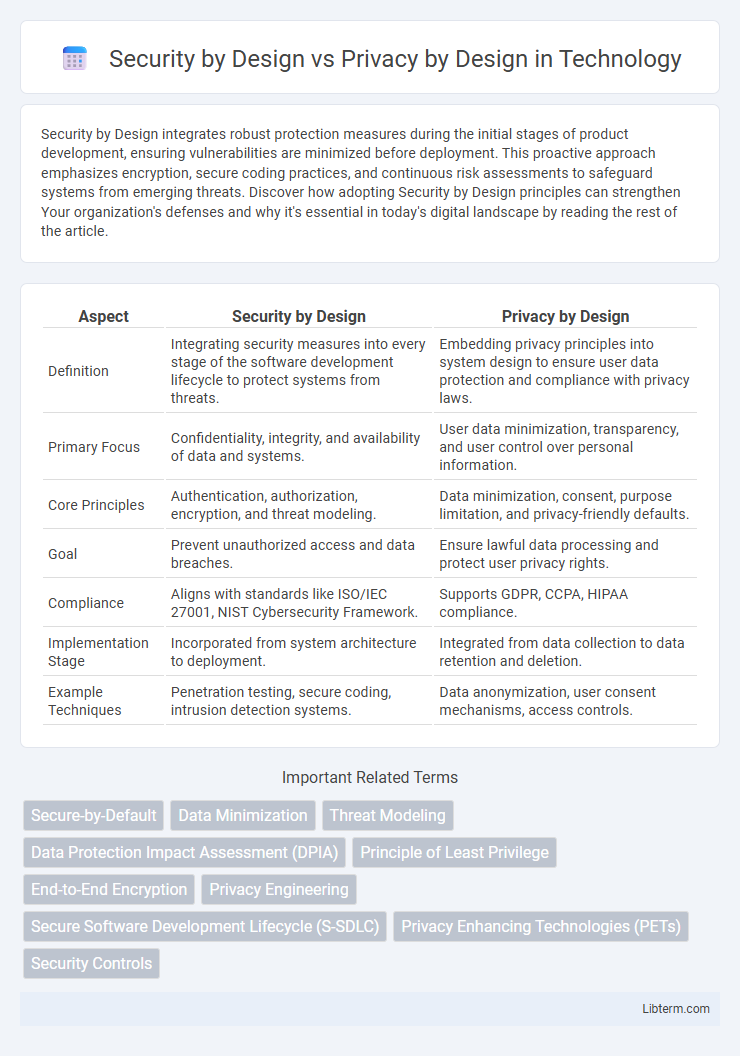
| Aspect | Security by Design | Privacy by Design |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integrating security measures into every stage of the software development lifecycle to protect systems from threats. | Embedding privacy principles into system design to ensure user data protection and compliance with privacy laws. |
| Primary Focus | Confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data and systems. | User data minimization, transparency, and user control over personal information. |
| Core Principles | Authentication, authorization, encryption, and threat modeling. | Data minimization, consent, purpose limitation, and privacy-friendly defaults. |
| Goal | Prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. | Ensure lawful data processing and protect user privacy rights. |
| Compliance | Aligns with standards like ISO/IEC 27001, NIST Cybersecurity Framework. | Supports GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA compliance. |
| Implementation Stage | Incorporated from system architecture to deployment. | Integrated from data collection to data retention and deletion. |
| Example Techniques | Penetration testing, secure coding, intrusion detection systems. | Data anonymization, user consent mechanisms, access controls. |
Introduction to Security by Design and Privacy by Design
Security by Design integrates protective measures into the development process, ensuring systems are built with robust defenses against threats from the outset. Privacy by Design emphasizes embedding privacy controls and data protection principles into technology and organizational practices to safeguard personal information proactively. Both frameworks prioritize proactive risk management, with Security by Design focusing on mitigating security vulnerabilities and Privacy by Design concentrating on maintaining user confidentiality and compliance with data protection regulations.
Defining Security by Design
Security by Design integrates robust cybersecurity measures throughout the software development lifecycle to prevent vulnerabilities and protect data from unauthorized access or attacks. It emphasizes proactive identification and mitigation of risks by embedding encryption, authentication, and access controls into the architecture from the outset. This approach ensures systems are resilient against threats, reducing the potential for breaches and maintaining integrity and availability.
Defining Privacy by Design
Privacy by Design centers on embedding privacy controls and data protection mechanisms into the development process of products and systems from the outset, ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR. Unlike Security by Design, which primarily addresses safeguarding systems against threats and vulnerabilities, Privacy by Design prioritizes minimizing data collection, enforcing user consent, and maintaining transparency in data usage. This proactive approach fosters trust by integrating privacy features as fundamental components rather than afterthoughts in technology solutions.
Core Principles Compared
Security by Design emphasizes proactive identification and mitigation of threats through robust authentication, encryption, and access controls to protect systems from unauthorized access and attacks. Privacy by Design centers on integrating data minimization, user consent, and transparency to safeguard personal information throughout its lifecycle and comply with GDPR and other privacy regulations. Both frameworks prioritize risk management and prevention but differ in their focus: security targets system integrity and availability, while privacy targets personal data protection and user rights.
Key Differences between Security and Privacy Approaches
Security by Design focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access and ensuring system integrity through robust encryption, authentication, and threat mitigation strategies. Privacy by Design prioritizes user data minimization, transparency, and user control over personal information to comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. The key difference lies in Security emphasizing technical safeguards against breaches, while Privacy centers on ethical data handling and user consent throughout the data lifecycle.
Overlapping Objectives and Intersections
Security by Design and Privacy by Design share overlapping objectives centered on safeguarding user data and ensuring system integrity from the outset of development. Both frameworks emphasize proactive risk assessment, encryption, access controls, and minimizing data exposure to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. The intersection lies in their mutual goal to embed protection mechanisms that uphold confidentiality, integrity, and compliance with regulatory standards throughout the product lifecycle.
Implementation Challenges in Each Approach
Security by Design implementation challenges include integrating robust threat modeling and encryption early in development while ensuring system performance and usability are not compromised. Privacy by Design faces difficulties in embedding comprehensive data minimization and user consent mechanisms, especially under complex regulatory environments like GDPR or CCPA. Both approaches require ongoing adaptation to emerging threats and legal changes, demanding cross-functional collaboration between security experts, developers, and legal teams.
Best Practices for Integrating Both Frameworks
Implementing Security by Design and Privacy by Design together requires embedding robust access controls, encryption standards, and anonymization techniques throughout system architecture. Employ principles like least privilege, data minimization, and continuous monitoring to safeguard against breaches while protecting user privacy. Adopting cross-functional collaboration between security experts and privacy officers ensures compliance with regulations such as GDPR and NIST guidelines while maintaining operational integrity.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Security by Design emphasizes building robust protection measures into systems from the outset, as demonstrated by companies like Microsoft, which reduced vulnerabilities through proactive threat modeling. Privacy by Design prioritizes user data protection through integrated privacy controls, exemplified by Apple's success in maintaining strong user data privacy with minimal breaches. Failures in both approaches, such as the Cambridge Analytica scandal, highlight the consequences of neglecting privacy and security principles during the design phase.
Future Trends in Security and Privacy by Design
Security by Design integrates robust defense mechanisms from the earliest stages of system development, emphasizing proactive threat mitigation and resilience against cyberattacks. Privacy by Design prioritizes data minimization, user consent, and transparency to embed privacy controls seamlessly into technology frameworks. Future trends highlight the convergence of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance automated threat detection, adaptive privacy-preserving techniques like differential privacy, and regulatory alignment with evolving data protection standards such as GDPR and CCPA.
Security by Design Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com