KMS (Key Management System) plays a vital role in securing your digital environment by efficiently generating, storing, and distributing cryptographic keys. Robust KMS solutions ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and compliance with industry standards, making them essential for businesses handling sensitive information. Discover the critical components and benefits of KMS in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
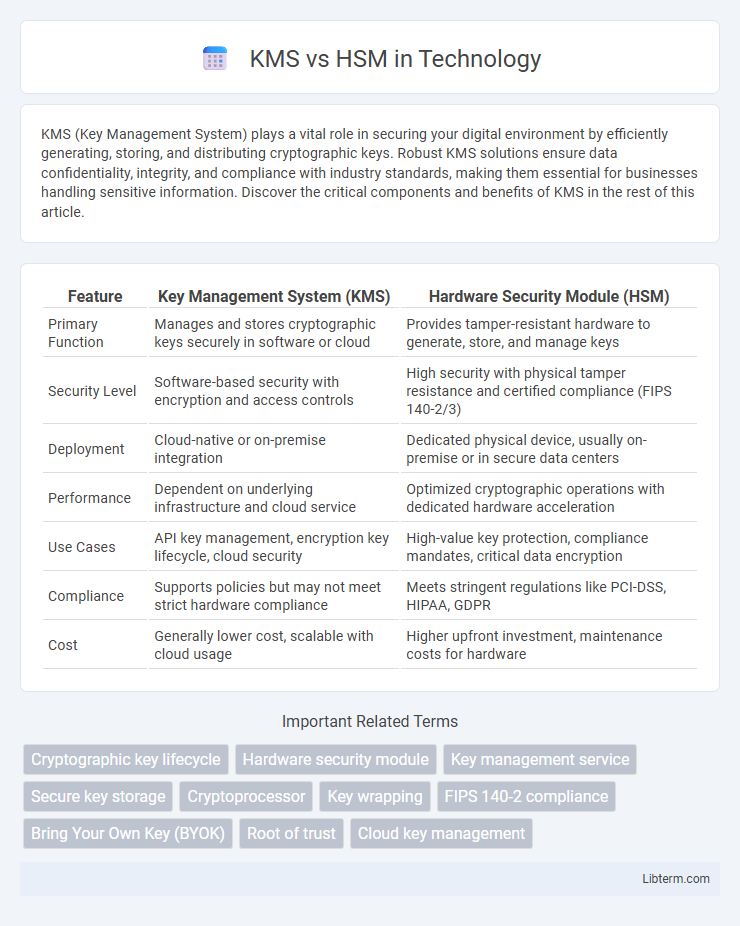
| Feature | Key Management System (KMS) | Hardware Security Module (HSM) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Manages and stores cryptographic keys securely in software or cloud | Provides tamper-resistant hardware to generate, store, and manage keys |
| Security Level | Software-based security with encryption and access controls | High security with physical tamper resistance and certified compliance (FIPS 140-2/3) |
| Deployment | Cloud-native or on-premise integration | Dedicated physical device, usually on-premise or in secure data centers |
| Performance | Dependent on underlying infrastructure and cloud service | Optimized cryptographic operations with dedicated hardware acceleration |
| Use Cases | API key management, encryption key lifecycle, cloud security | High-value key protection, compliance mandates, critical data encryption |
| Compliance | Supports policies but may not meet strict hardware compliance | Meets stringent regulations like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, scalable with cloud usage | Higher upfront investment, maintenance costs for hardware |
Introduction to KMS and HSM
Key Management Systems (KMS) provide centralized control over encryption keys, enabling secure generation, storage, and management primarily through software-based solutions integrated with cloud services. Hardware Security Modules (HSM) are dedicated physical devices designed to safeguard and manage cryptographic keys within tamper-resistant hardware, ensuring enhanced security through isolated processing environments. Both KMS and HSM play critical roles in cryptographic infrastructure, with KMS offering scalability and ease of integration, while HSM emphasizes hardware-enforced security and compliance.
What is a Key Management Service (KMS)?
A Key Management Service (KMS) is a cloud-based solution designed to create, store, and manage cryptographic keys for encrypting data, ensuring secure key lifecycle management and access control. KMS integrates with various cloud services and applications, enabling seamless encryption of data at rest, in transit, and in use, while automating key rotation and audit logging. Unlike Hardware Security Modules (HSMs), which provide dedicated physical devices for key protection and cryptographic operations, KMS offers scalable, software-based key management accessible via APIs without requiring specialized hardware.
Understanding Hardware Security Modules (HSM)
Hardware Security Modules (HSM) are dedicated physical devices designed to provide robust cryptographic key management and secure key storage, offering enhanced protection against unauthorized access and tampering compared to software-based Key Management Systems (KMS). HSMs perform encryption, decryption, and key generation within a hardware environment that complies with stringent security standards such as FIPS 140-2 or Common Criteria, ensuring uncompromised integrity of sensitive keys. Their use is critical in high-security environments like financial institutions and government agencies where compliance and advanced security controls are mandatory.
Core Functions: KMS vs HSM
Key Management Systems (KMS) primarily handle the creation, storage, rotation, and lifecycle management of cryptographic keys across various applications, ensuring secure and centralized key distribution. Hardware Security Modules (HSM) provide a physical, tamper-resistant environment for generating and safeguarding cryptographic keys, executing encryption and decryption processes directly within the hardware. KMS offers software-based key management capabilities, while HSM emphasizes hardware-backed security for critical cryptographic operations and key protection.
Security Architecture Differences
KMS (Key Management Service) centralizes cryptographic key management in a cloud environment, relying on software-based security controls to protect keys, which may introduce risks if the underlying infrastructure is compromised. HSM (Hardware Security Module) offers a dedicated physical device with tamper-resistant features that securely generates, stores, and manages keys, providing higher assurance through hardware isolation and cryptographic acceleration. The main security architecture difference lies in KMS's dependence on multi-tenant cloud infrastructure versus HSM's isolated, tamper-proof hardware environment for enhanced key protection.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
KMS (Key Management Service) offers rapid key provisioning and integration with cloud-native applications, supporting high scalability for large-scale environments with distributed workloads. HSM (Hardware Security Module) provides lower latency for cryptographic operations and stronger isolation, delivering superior performance for high-throughput, security-critical tasks. While KMS excels in ease of management and elastic scaling, HSM ensures dedicated resources and predictable performance under heavy cryptographic loads.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
KMS (Key Management Service) and HSM (Hardware Security Module) both support compliance with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS by offering secure key storage and cryptographic operations. HSMs provide tamper-resistant hardware that meets strict standards like FIPS 140-2 Level 3 or 4, ensuring higher assurance for sensitive workloads. KMS often integrates with cloud environments to simplify regulatory audits through centralized key management while leveraging HSM-backed key storage for enhanced security.
Cost Implications: KMS vs HSM
Key Management Services (KMS) typically offer lower upfront costs and scalable pricing based on usage, making them more cost-effective for small to medium-sized enterprises. Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) demand higher initial capital investment, including hardware procurement and maintenance expenses, suitable for organizations requiring extreme security and compliance. Operational costs for HSMs also include dedicated personnel and physical security, whereas KMS often requires less specialized management, impacting overall cost efficiency.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Key Management Systems (KMS) are widely used in cloud environments for managing encryption keys, supporting applications like data encryption, access control, and compliance in industries such as finance, healthcare, and retail. Hardware Security Modules (HSM) provide enhanced physical and logical protection for cryptographic keys, making them ideal for high-security use cases including payment processing, government data protection, and digital identity verification. Enterprises often implement KMS for scalable key lifecycle management, while HSMs are favored in sectors requiring tamper-resistant hardware and stringent regulatory adherence.
Choosing the Right Solution: KMS or HSM?
Choosing the right solution between Key Management Systems (KMS) and Hardware Security Modules (HSM) depends on security requirements and budget constraints. KMS offers scalable, cloud-based key management with ease of integration for software-driven encryption workflows, making it suitable for organizations prioritizing flexibility and cost-effectiveness. HSM provides dedicated, tamper-resistant hardware for cryptographic key storage and operation, delivering the highest level of physical security essential for compliance-heavy industries and mission-critical applications.
KMS Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com