Hybrid cloud environments combine private and public cloud resources to optimize flexibility, security, and cost-efficiency for businesses of all sizes. By integrating on-premises infrastructure with cloud services, organizations can scale operations seamlessly while maintaining control over sensitive data. Discover how leveraging hybrid cloud solutions can transform Your IT strategy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
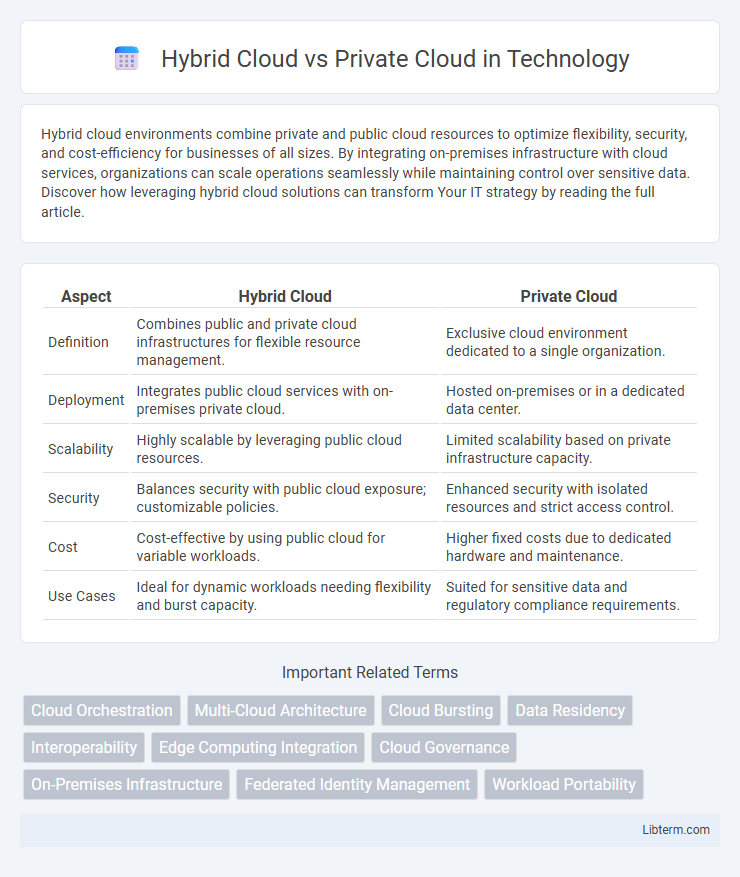
| Aspect | Hybrid Cloud | Private Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combines public and private cloud infrastructures for flexible resource management. | Exclusive cloud environment dedicated to a single organization. |
| Deployment | Integrates public cloud services with on-premises private cloud. | Hosted on-premises or in a dedicated data center. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable by leveraging public cloud resources. | Limited scalability based on private infrastructure capacity. |
| Security | Balances security with public cloud exposure; customizable policies. | Enhanced security with isolated resources and strict access control. |
| Cost | Cost-effective by using public cloud for variable workloads. | Higher fixed costs due to dedicated hardware and maintenance. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for dynamic workloads needing flexibility and burst capacity. | Suited for sensitive data and regulatory compliance requirements. |
Introduction to Cloud Computing Models
Hybrid cloud integrates private and public cloud infrastructures, offering businesses flexibility, scalability, and enhanced security by leveraging the strengths of both environments. Private cloud provides dedicated resources within a secure infrastructure, ideal for organizations requiring strict data control and compliance. Understanding these cloud computing models enables enterprises to select solutions that align with their operational needs and regulatory requirements.
What is Hybrid Cloud?
Hybrid Cloud integrates on-premises private cloud resources with third-party public cloud services, enabling organizations to optimize workload distribution and enhance scalability. It combines the control and security of a private cloud with the flexibility and cost-efficiency of public cloud infrastructure. This model supports dynamic resource allocation, data privacy compliance, and seamless application deployment across multiple environments.
What is Private Cloud?
Private cloud refers to a dedicated cloud computing environment exclusively used by a single organization, offering enhanced security, control, and customization compared to public cloud services. It typically utilizes on-premises infrastructure or a third-party hosted environment to provide scalable resources while maintaining strict compliance with data privacy regulations. Enterprises choose private clouds to support critical workloads requiring high levels of data protection and regulatory adherence.
Key Differences Between Hybrid Cloud and Private Cloud
Hybrid cloud combines on-premises private cloud resources with public cloud services, offering greater flexibility and scalability compared to private cloud, which is solely dedicated to a single organization. Private cloud environments provide enhanced security and control by isolating data and infrastructure, whereas hybrid cloud enables workload portability and dynamic resource allocation across multiple platforms. Cost-efficiency varies as hybrid cloud can optimize expenses through public cloud pay-as-you-go models, while private cloud requires significant upfront investment in hardware and maintenance.
Security Comparison: Hybrid vs Private Cloud
Hybrid cloud combines on-premises private cloud resources with public cloud services, offering flexible security controls tailored to workload sensitivity. Private cloud provides dedicated infrastructure with enhanced data isolation and strict access management, reducing exposure to external threats. Security in hybrid cloud requires robust integration of policies and encryption across environments, while private cloud focuses on internal risk mitigation and compliance adherence.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Hybrid cloud offers scalable resources by combining private infrastructure with public cloud services, optimizing operational costs through flexible workload allocation and pay-as-you-go pricing models. Private cloud entails higher upfront capital expenditures for dedicated hardware and maintenance but ensures predictable long-term costs and enhanced security, which can lead to greater ROI for organizations with stable, critical workloads. Evaluating total cost of ownership (TCO) and specific business requirements, hybrid cloud can reduce expenses with dynamic scalability, while private cloud investments often yield strong returns in compliance-heavy industries.
Performance and Scalability
Hybrid cloud environments leverage both private and public clouds, optimizing performance by dynamically allocating workloads to the most appropriate infrastructure based on real-time demand. Private clouds deliver consistent, high-performance computing with dedicated resources, ensuring predictable scalability within a controlled environment. Hybrid cloud scalability exceeds private cloud limits by integrating virtually unlimited public cloud resources, enabling rapid expansion without compromising core application performance.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Hybrid cloud solutions offer scalable infrastructure for industries such as healthcare and finance, enabling secure data management alongside flexible public cloud resources for analytics and application deployment. Private cloud environments suit sectors with strict compliance requirements like government and banking, providing enhanced control, data sovereignty, and custom security protocols. Manufacturing and retail industries leverage hybrid clouds to optimize supply chain operations and customer experiences through a mix of on-premises resources and cloud services.
Challenges and Limitations
Hybrid cloud faces challenges in managing data security across multiple environments, often complicating compliance with industry regulations such as GDPR and HIPAA. Private cloud limitations include high upfront capital expenditure and scalability constraints, which can hinder rapid deployment and resource flexibility. Both models require robust network infrastructure to ensure consistent performance and seamless integration between on-premises and cloud resources.
Choosing the Right Cloud Model for Your Business
Choosing the right cloud model depends on your business's need for scalability, control, and security. Hybrid cloud offers flexibility by combining public and private clouds, enabling workloads to move between environments for optimized performance. Private cloud provides enhanced security and dedicated resources, ideal for businesses with strict compliance and sensitive data requirements.
Hybrid Cloud Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com