Magic links provide a secure and seamless way to authenticate users without the need for passwords, enhancing user experience and reducing login friction. These one-time, time-limited links are sent directly to your email, allowing instant access with a simple click. Discover how magic links can transform your login process and boost security by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
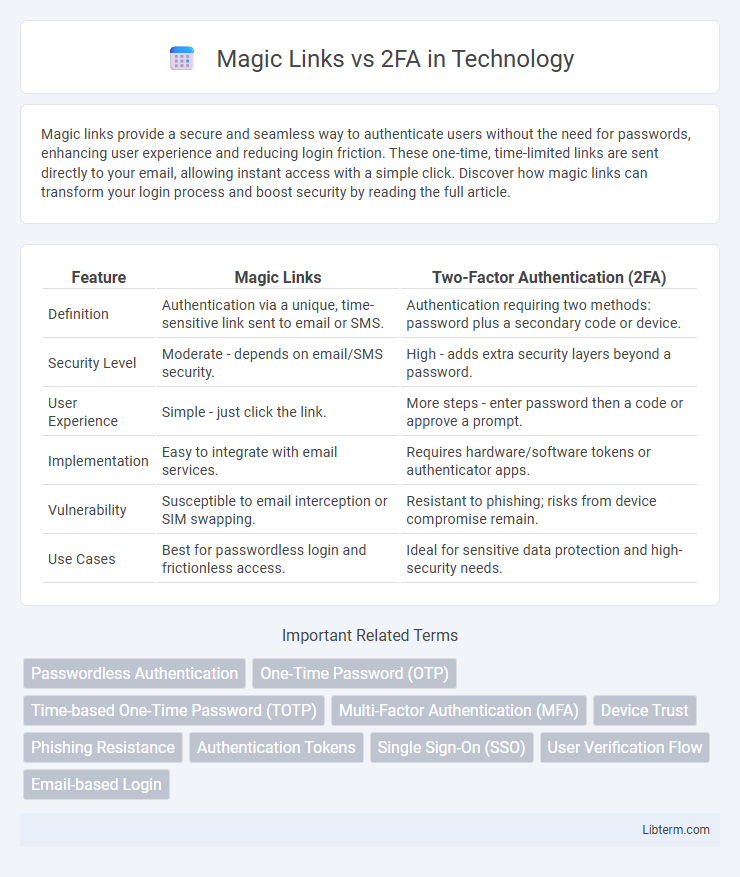
| Feature | Magic Links | Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Authentication via a unique, time-sensitive link sent to email or SMS. | Authentication requiring two methods: password plus a secondary code or device. |
| Security Level | Moderate - depends on email/SMS security. | High - adds extra security layers beyond a password. |
| User Experience | Simple - just click the link. | More steps - enter password then a code or approve a prompt. |
| Implementation | Easy to integrate with email services. | Requires hardware/software tokens or authenticator apps. |
| Vulnerability | Susceptible to email interception or SIM swapping. | Resistant to phishing; risks from device compromise remain. |
| Use Cases | Best for passwordless login and frictionless access. | Ideal for sensitive data protection and high-security needs. |
Introduction to Magic Links and Two-Factor Authentication
Magic Links provide a seamless authentication experience by sending a unique, time-sensitive link to the user's email, allowing password-free access with a single click. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) enhances security by requiring users to verify their identity through two separate factors, typically combining something they know (password) with something they have (a mobile device or hardware token). Both methods aim to strengthen user authentication, with Magic Links optimizing convenience and 2FA emphasizing multi-layered security.
How Magic Links Work
Magic Links provide passwordless authentication by sending a unique, time-sensitive URL to the user's registered email, allowing instant access with a single click. This method eliminates the need for memorizing passwords or inputting codes, enhancing user convenience and reducing friction during login. Magic Links rely on secure token generation and expiration to maintain account safety without requiring additional verification steps like two-factor authentication.
How 2FA Works
Two-factor authentication (2FA) enhances security by requiring users to provide two distinct forms of verification before granting access, typically combining something they know (password) with something they have (a time-sensitive code sent to a smartphone or generated by an authenticator app). This process reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if the password is compromised. Common 2FA methods include SMS codes, authenticator apps like Google Authenticator, and hardware tokens, each offering varying degrees of security and user convenience.
Security Benefits of Magic Links
Magic Links provide secure, passwordless authentication by generating time-sensitive, single-use URLs sent directly to a user's verified email, reducing the risk of password theft and phishing attacks. They eliminate the need for memorized credentials, enhancing user convenience while maintaining secure access control through encrypted, short-lived tokens. By bypassing traditional passwords and avoiding SMS-based vulnerabilities common in 2FA, Magic Links strengthen overall account security with streamlined, user-friendly verification.
Security Advantages of 2FA
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) significantly enhances security by requiring users to provide two distinct forms of verification, typically combining something they know (password) with something they have (a mobile device or hardware token). Unlike Magic Links, which rely solely on email access and can be vulnerable to phishing or compromised email accounts, 2FA reduces the risk of unauthorized access through multiple independent authentication factors. This layered security approach makes 2FA a more robust method for protecting sensitive accounts and data against credential theft and account takeover attacks.
User Experience Comparison: Magic Links vs 2FA
Magic Links provide a seamless user experience by allowing instant access through email-based authentication without the need for passwords or additional devices, reducing friction during login. In contrast, Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) requires users to input a secondary code via SMS, authenticator apps, or hardware tokens, adding a layer of security but often increasing login time and complexity. The choice between Magic Links and 2FA hinges on balancing user convenience with security demands, where Magic Links excel in speed and simplicity while 2FA enhances protection against unauthorized access.
Implementation Challenges for Magic Links and 2FA
Magic Links require a robust email delivery system and secure token generation to prevent interception or replay attacks, posing challenges in scalability and user experience consistency. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) demands integrating multiple verification methods, such as SMS, authenticator apps, or hardware tokens, which complicates development and increases friction for users. Both methods require careful handling of session management and fallback mechanisms to ensure security without compromising usability.
Use Cases and Industry Adoption
Magic links offer seamless passwordless authentication ideal for consumer-facing apps prioritizing user convenience and quick access, commonly adopted by media streaming services and e-commerce platforms. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) provides enhanced security through multi-layer verification, favored in finance, healthcare, and enterprise sectors where data protection and regulatory compliance are critical. Many industries implement a hybrid approach, combining magic links for low-risk interactions and 2FA for sensitive account activities to balance usability and security.
Potential Vulnerabilities and Risks
Magic Links rely on emailed authentication tokens, making them vulnerable to email account compromises and interception during transmission. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) introduces an extra layer by requiring a separate verification method, reducing the risk of unauthorized access but potentially exposing users to SIM swapping and phishing attacks targeting the second factor. Both methods carry inherent risks, but 2FA typically offers stronger protection against credential theft compared to magic link systems.
Which Authentication Method is Right for You?
Choosing between Magic Links and Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) depends on your security needs and user experience priorities. Magic Links offer passwordless, seamless access by sending a time-sensitive login link via email, ideal for low-risk applications seeking simplicity and frictionless entry. In contrast, 2FA enhances security by requiring a second verification step, such as a code from an authenticator app or SMS, making it suitable for high-security environments where protecting sensitive data is critical.
Magic Links Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com