The Repository Pattern centralizes data access logic by providing a consistent interface for querying and persisting domain objects, promoting separation of concerns and easier testability. It abstracts the data layer, allowing your application to switch between different data sources without affecting business logic. Explore the rest of the article to discover how implementing this pattern can streamline your data management strategies.
Table of Comparison
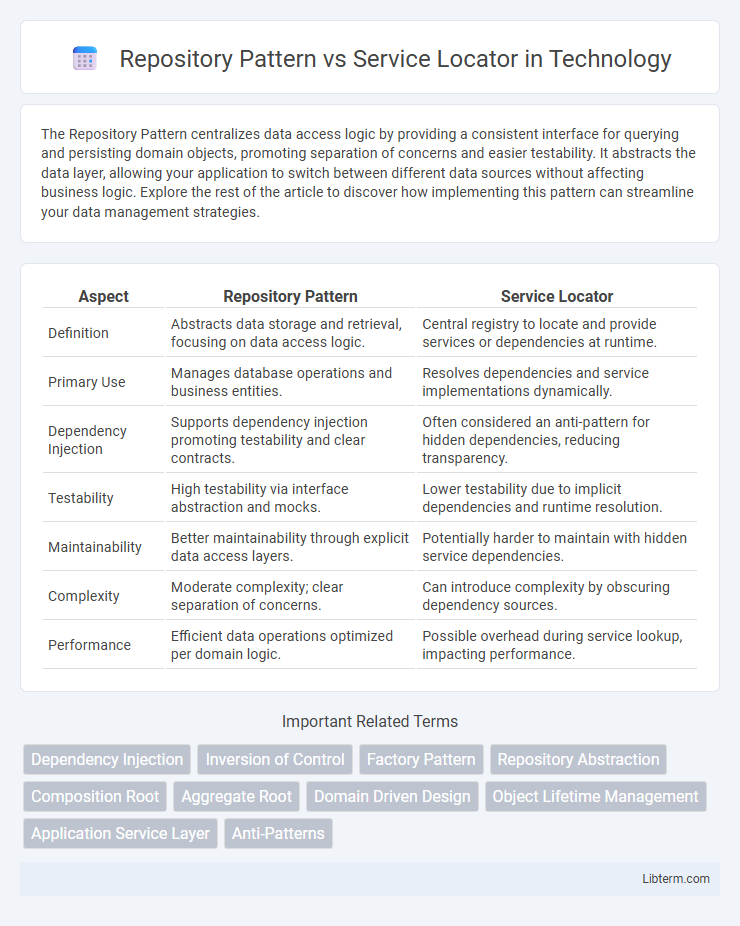
| Aspect | Repository Pattern | Service Locator |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Abstracts data storage and retrieval, focusing on data access logic. | Central registry to locate and provide services or dependencies at runtime. |
| Primary Use | Manages database operations and business entities. | Resolves dependencies and service implementations dynamically. |
| Dependency Injection | Supports dependency injection promoting testability and clear contracts. | Often considered an anti-pattern for hidden dependencies, reducing transparency. |
| Testability | High testability via interface abstraction and mocks. | Lower testability due to implicit dependencies and runtime resolution. |
| Maintainability | Better maintainability through explicit data access layers. | Potentially harder to maintain with hidden service dependencies. |
| Complexity | Moderate complexity; clear separation of concerns. | Can introduce complexity by obscuring dependency sources. |
| Performance | Efficient data operations optimized per domain logic. | Possible overhead during service lookup, impacting performance. |
Introduction to Repository Pattern and Service Locator
The Repository Pattern abstracts data access logic by providing a collection-like interface for querying and persisting domain objects, promoting separation of concerns and testability in software design. Service Locator centralizes object creation and dependency resolution, acting as a container that provides services when requested, which can obscure dependencies and hinder maintainability. Both patterns aim to manage dependencies, but the Repository Pattern emphasizes clear data operations while Service Locator prioritizes centralized service provisioning.
Core Concepts of Repository Pattern
The Repository Pattern centralizes data access logic by abstracting the database or external service interactions, enabling a clean separation between domain and data mapping layers. It provides a collection-like interface for querying and persisting domain entities, promoting testability and maintainability by isolating data retrieval details. Core concepts include encapsulating query logic, ensuring consistency in data access, and offering a uniform API for different data sources.
Fundamentals of Service Locator
Service Locator centralizes the process of obtaining service instances by maintaining a registry that maps service interfaces to their concrete implementations, enabling decoupled and flexible dependency management. Unlike the Repository Pattern, which abstracts data access logic through repositories tailored to specific entities, Service Locator emphasizes runtime resolution of dependencies without explicit injection. This pattern streamlines service retrieval but may obscure dependency flows, impacting code clarity and testability.
Key Differences Between Repository Pattern and Service Locator
The key differences between the Repository Pattern and Service Locator lie in their primary responsibilities and coupling; the Repository Pattern abstracts data access and provides a collection-like interface for querying and persisting domain objects, promoting a clear separation of concerns and testability. In contrast, the Service Locator Pattern centralizes service resolution by acting as a registry to retrieve dependencies, which can lead to hidden dependencies and tighter coupling within the application. Repository Pattern emphasizes domain-driven design and encapsulates data logic, whereas Service Locator focuses on decoupling service consumers from concrete implementations but risks obscuring system architecture.
Advantages of Using Repository Pattern
The Repository Pattern provides a clear abstraction layer between the data access logic and the business logic, enhancing code maintainability and testability by decoupling these concerns. It promotes a more predictable and consistent data access approach, enabling easier implementation of unit tests with mock repositories. Unlike the Service Locator, the Repository Pattern encourages explicit dependencies, which improve code readability and reduce hidden coupling in large-scale applications.
Pros and Cons of Service Locator
The Service Locator pattern centralizes service resolution, simplifying dependency management by providing a single access point to various services, which can reduce boilerplate code and improve modularity. However, it can obscure dependencies, making the codebase harder to understand and maintain, as services are retrieved dynamically rather than explicitly injected. This hidden coupling also complicates unit testing and increases the risk of runtime errors due to unresolved services.
Use Cases: When to Choose Each Pattern
Choose the Repository Pattern when you need a clear abstraction layer for data access, promoting testability and separation of concerns in complex domain-driven designs. Opt for the Service Locator pattern to manage dependencies dynamically in legacy systems or scenarios requiring flexible service resolution without extensive refactoring. Use the Repository Pattern for maintainable, testable codebases emphasizing persistent storage logic, while the Service Locator fits cases demanding runtime service discovery and decoupling in loosely-structured applications.
Impact on Code Maintainability and Testability
The Repository Pattern enhances code maintainability and testability by abstracting data access logic into separate repositories, allowing for easier mocking and clear separation of concerns. In contrast, the Service Locator introduces hidden dependencies that complicate dependency tracking and increase coupling, making unit testing more challenging and code maintenance harder. Adopting the Repository Pattern supports cleaner architecture, promoting better scalability and simplified refactoring in complex applications.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Repository Pattern often leads to over-abstraction, causing unnecessary complexity and making code harder to maintain or extend. Service Locator introduces hidden dependencies, which can result in tightly coupled code and difficulties in unit testing due to obscured service instantiation. Avoiding these pitfalls requires clear interface definitions for repositories and explicit dependency injection instead of relying on the Service Locator's hidden object retrieval.
Conclusion: Which Pattern Fits Your Project?
Choosing between the Repository Pattern and Service Locator depends on the project's complexity, maintainability needs, and testing requirements. The Repository Pattern suits projects aiming for a clear separation of concerns and easier unit testing through abstraction of data access, while the Service Locator fits scenarios demanding flexible service resolution but may introduce hidden dependencies and hinder testability. Evaluate the project's architecture goals and team skill set to select the pattern that enhances code clarity, scalability, and maintainability.
Repository Pattern Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com