API Gateway acts as a critical intermediary that manages all client requests to backend services, ensuring seamless communication, security, and scalability. It handles authentication, request routing, and rate limiting to optimize your application's performance and protect it from malicious traffic. Discover how leveraging an API Gateway can dramatically improve your system architecture by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
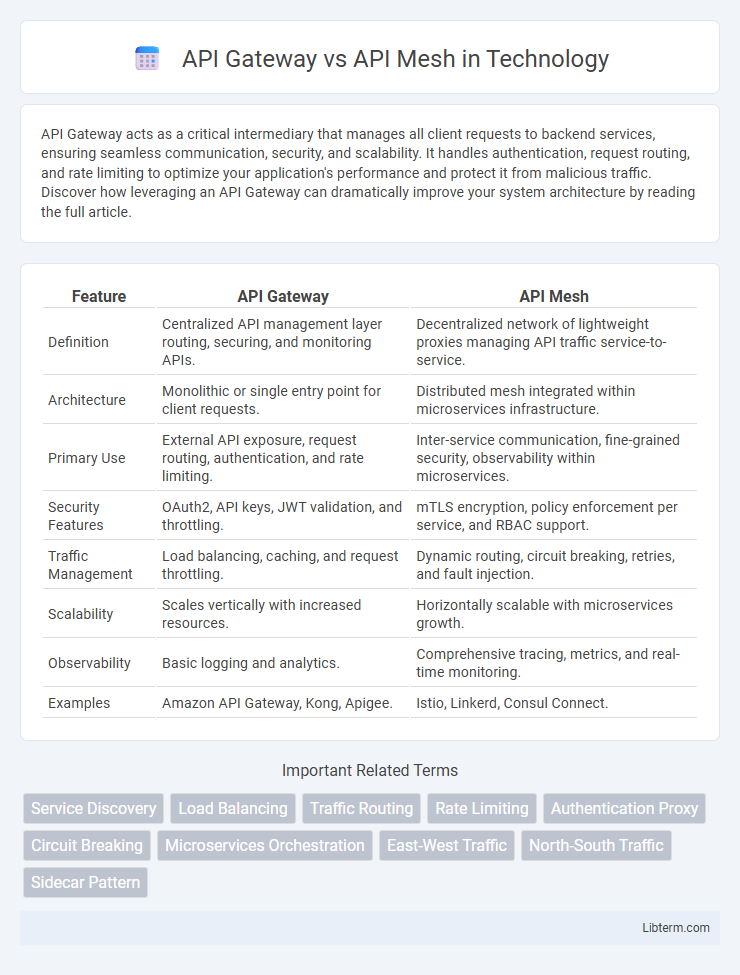
| Feature | API Gateway | API Mesh |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized API management layer routing, securing, and monitoring APIs. | Decentralized network of lightweight proxies managing API traffic service-to-service. |
| Architecture | Monolithic or single entry point for client requests. | Distributed mesh integrated within microservices infrastructure. |
| Primary Use | External API exposure, request routing, authentication, and rate limiting. | Inter-service communication, fine-grained security, observability within microservices. |
| Security Features | OAuth2, API keys, JWT validation, and throttling. | mTLS encryption, policy enforcement per service, and RBAC support. |
| Traffic Management | Load balancing, caching, and request throttling. | Dynamic routing, circuit breaking, retries, and fault injection. |
| Scalability | Scales vertically with increased resources. | Horizontally scalable with microservices growth. |
| Observability | Basic logging and analytics. | Comprehensive tracing, metrics, and real-time monitoring. |
| Examples | Amazon API Gateway, Kong, Apigee. | Istio, Linkerd, Consul Connect. |
Introduction to API Gateway and API Mesh
API Gateway serves as a centralized entry point managing client requests, handling authentication, rate limiting, and routing in microservices architectures. API Mesh offers a decentralized infrastructure for managing API interactions, emphasizing service discovery, load balancing, and security across distributed systems. Both solutions optimize API communication but differ in architecture, with API Gateway centralizing traffic and API Mesh distributing control throughout the network.
Key Differences Between API Gateway and API Mesh
API Gateway centralizes API management by providing a single entry point for API requests, handling tasks like authentication, rate limiting, and request routing. In contrast, API Mesh distributes these capabilities across multiple services, enabling fine-grained traffic control, observability, and policy enforcement within microservice architectures. While API Gateway simplifies external API consumption, API Mesh excels in internal service-to-service communication and complex, scalable environments.
Core Functions of an API Gateway
An API Gateway primarily functions as a single entry point that handles request routing, authentication, rate limiting, and policy enforcement, ensuring secure and efficient communication between clients and backend services. It manages core functions such as protocol translation, load balancing, and caching to optimize API performance and scalability. Unlike an API Mesh, which focuses on decentralized service-to-service communication within microservices environments, the API Gateway centralizes traffic management and simplifies client interactions.
Core Functions of an API Mesh
An API Mesh centralizes API discovery, routing, and management across multiple microservices, enabling dynamic traffic control and fine-grained security policies. Unlike API Gateways that act as a single entry point, API Mesh provides granular observability and resilience by handling service-to-service communication within distributed architectures. Core functions include load balancing, authentication, authorization, rate limiting, and detailed telemetry for seamless API orchestration across complex environments.
Use Cases for API Gateway
API Gateway is essential for managing, securing, and routing external client requests to microservices, handling tasks like authentication, rate limiting, and request transformation. It is ideal for use cases where a single entry point is needed to expose APIs to external consumers, optimize traffic, and enforce security policies. API Gateway excels in scenarios requiring centralized monitoring, caching, and seamless integration with identity providers for API management.
Use Cases for API Mesh
API Mesh excels in managing complex microservices architectures by providing dynamic API discovery, observability, and security across multiple API Gateways and services. It is ideal for environments requiring granular policy enforcement, real-time traffic shaping, and multi-cloud or hybrid deployments where seamless API communication is critical. Use cases include large-scale enterprises needing centralized control over distributed APIs and improving service resilience with advanced telemetry and traffic management.
Performance and Scalability Comparison
API Gateway centralizes API traffic control, providing efficient request routing, load balancing, and security enforcement to enhance performance in monolithic or simpler microservices environments. API Mesh distributes these capabilities across multiple microservices, enabling fine-grained, scalable performance by managing communication at the service-to-service level with lower latency and higher fault tolerance. Scalability favors API Mesh in complex, large-scale architectures due to its decentralized design, while API Gateway suits scenarios requiring straightforward scalability with centralized control.
Security Implications: Gateway vs Mesh
API Gateway centralizes security controls such as authentication, authorization, rate limiting, and threat detection, making it easier to enforce consistent policies at a single entry point. API Mesh distributes security responsibilities across multiple microservices, enhancing fine-grained policy enforcement and improving resilience against lateral attacks but requiring complex management to maintain uniform security posture. Enterprises must balance the simplicity of centralized API Gateway security with the granular, service-level protection offered by API Mesh architectures.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Architecture
API Gateway centralizes request routing, security, and rate limiting, making it ideal for straightforward, monolithic or microservices architectures with well-defined entry points. API Mesh offers fine-grained, service-to-service communication control and observability, suited for complex, distributed microservices environments requiring dynamic routing and policy enforcement across multiple clusters. Selecting the right solution depends on your architecture's complexity, scalability needs, and operational requirements for traffic management and security.
Future Trends in API Management
API Gateway remains crucial for centralized request routing and security, but API Mesh is gaining traction by enabling decentralized service-to-service communication with enhanced observability and control. Future trends in API management emphasize the integration of AI-driven analytics, automated policy enforcement, and real-time traffic shaping within API Mesh frameworks to facilitate scalability and resilience. Enterprises are increasingly adopting hybrid models combining API Gateway and API Mesh to optimize both edge traffic management and internal microservices orchestration.
API Gateway Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com