EventBridge enables seamless integration and real-time event processing across multiple AWS services and third-party applications. It enhances your cloud architecture by facilitating automated workflows and simplifying event-driven application development. Explore the full article to understand how EventBridge can transform your event management strategy.
Table of Comparison
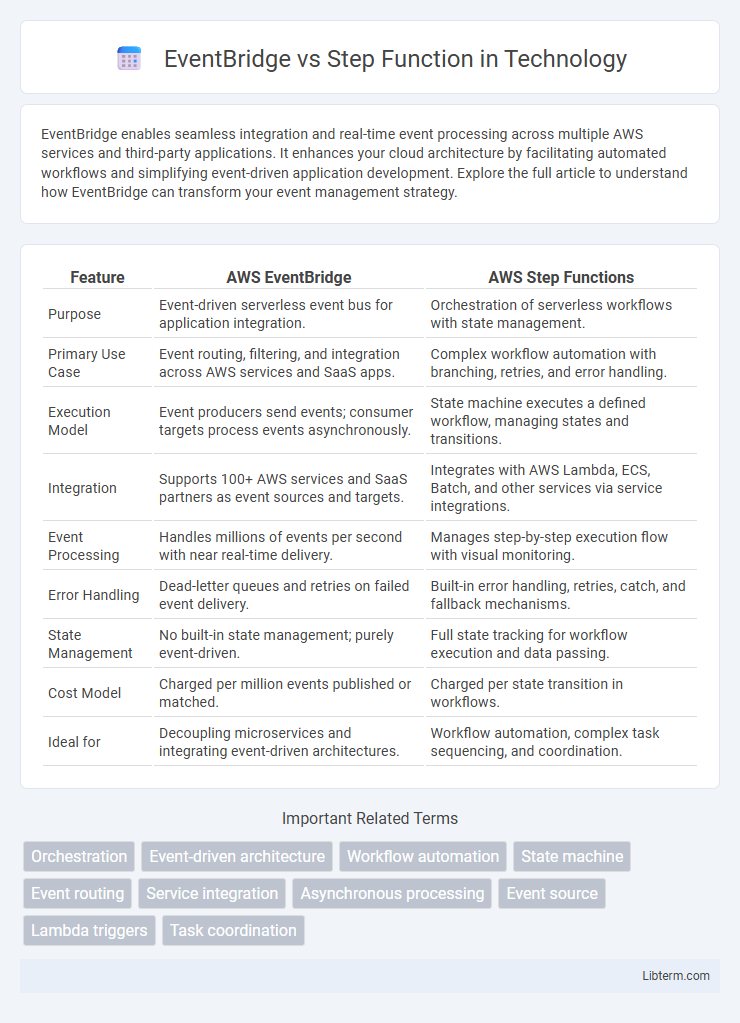
| Feature | AWS EventBridge | AWS Step Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Event-driven serverless event bus for application integration. | Orchestration of serverless workflows with state management. |
| Primary Use Case | Event routing, filtering, and integration across AWS services and SaaS apps. | Complex workflow automation with branching, retries, and error handling. |
| Execution Model | Event producers send events; consumer targets process events asynchronously. | State machine executes a defined workflow, managing states and transitions. |
| Integration | Supports 100+ AWS services and SaaS partners as event sources and targets. | Integrates with AWS Lambda, ECS, Batch, and other services via service integrations. |
| Event Processing | Handles millions of events per second with near real-time delivery. | Manages step-by-step execution flow with visual monitoring. |
| Error Handling | Dead-letter queues and retries on failed event delivery. | Built-in error handling, retries, catch, and fallback mechanisms. |
| State Management | No built-in state management; purely event-driven. | Full state tracking for workflow execution and data passing. |
| Cost Model | Charged per million events published or matched. | Charged per state transition in workflows. |
| Ideal for | Decoupling microservices and integrating event-driven architectures. | Workflow automation, complex task sequencing, and coordination. |
Introduction to EventBridge and Step Functions
Amazon EventBridge enables seamless event-driven architecture by connecting application data from various sources, facilitating real-time event routing and integration across AWS services and third-party applications. AWS Step Functions orchestrate complex workflows by coordinating multiple AWS services into serverless workflows with visual state machines, enabling scalable and reliable execution of sequential tasks. Both services support event-driven applications but serve different purposes: EventBridge focuses on event streaming and routing, while Step Functions emphasize workflow orchestration and task automation.
Core Concepts and Architecture
Amazon EventBridge is a serverless event bus service designed to connect applications using events from various sources, enabling event-driven architectures with real-time data routing and filtering. AWS Step Functions orchestrate distributed applications and microservices by defining workflows as state machines, managing tasks with built-in error handling, retries, and parallel execution. EventBridge focuses on event ingestion and routing, while Step Functions emphasize workflow orchestration and state management within complex distributed processes.
Key Features Comparison
EventBridge offers event-driven integration with a flexible event bus supporting custom, SaaS, and AWS service events, ideal for real-time application workflows and decoupling microservices. Step Functions provide stateful orchestration with visual workflows, enabling complex task sequences, error handling, and retries for long-running processes and distributed transactions. Both services integrate with AWS Lambda and support event-driven architectures, but EventBridge excels in event routing while Step Functions specialize in orchestrating multi-step business logic.
Use Cases for EventBridge
EventBridge excels in event-driven architecture by enabling seamless integration between AWS services, SaaS applications, and custom event sources to build scalable, loosely coupled applications. It is ideal for real-time monitoring, application integration, and automating workflows triggered by system events, such as responding to changes in data lakes or orchestrating microservices. EventBridge supports complex event routing and filtering, making it suitable for use cases like multi-tenant SaaS platforms, event-driven ETL pipelines, and dynamic resource provisioning.
Use Cases for Step Functions
AWS Step Functions excel in orchestrating complex workflows involving multiple AWS services with stateful, long-running processes and error handling. Use cases include coordinating microservices, managing ETL pipelines, and automating business processes requiring conditional branching and retries. Step Functions provide robust state management, making them ideal for scenarios demanding sequential execution and transactional integrity.
Integration Capabilities
EventBridge offers seamless integration with over 200 AWS services and SaaS applications, enabling event-driven architectures by routing real-time events from various sources. Step Functions excels in orchestrating complex workflows by integrating AWS Lambda functions, API Gateway, and other services through stateful executions with built-in error handling and retry mechanisms. Both services enhance application scalability, but EventBridge focuses on event routing while Step Functions specializes in coordinating distributed application components.
Performance and Scalability
AWS EventBridge offers superior scalability by natively supporting millions of events per second with low latency, making it ideal for real-time event-driven architectures. Step Functions provide robust performance for orchestrating complex workflows, managing state transitions, and executing sequential or parallel tasks with predictable execution timing. EventBridge excels in event distribution across multiple targets, while Step Functions optimize stateful process execution, enabling reliable scaling of application logic.
Pricing and Cost Considerations
EventBridge pricing is based on the number of events published and matched, with a cost of $1.00 per million events after the free tier of 100,000 events per month. Step Functions pricing depends on the number of state transitions executed, charged at $0.025 per 1,000 state transitions, making it potentially more expensive for workflows with high complexity and numerous steps. Cost optimization requires analyzing event volume in EventBridge versus state transition counts in Step Functions to determine the most economical service for your specific workflow needs.
Security and Compliance
EventBridge provides robust security features including encryption at rest and in transit, fine-grained access controls via AWS IAM policies, and integration with AWS CloudTrail for detailed event logging, ensuring compliance with industry standards such as SOC, HIPAA, and GDPR. Step Functions enhance security through state machine encryption using AWS KMS, strict IAM role-based access for task execution, and auditability with CloudTrail logs that capture every state transition, supporting compliance frameworks like PCI DSS and FedRAMP. Both services enable secure orchestration of workflows with comprehensive monitoring and control mechanisms to meet enterprise security and regulatory requirements.
Choosing the Right Service for Your Workflow
EventBridge excels in event-driven architectures by enabling seamless integration and routing of events across multiple AWS services and applications, offering high scalability and real-time event processing. Step Functions provide robust orchestration for complex workflows with built-in error handling, state management, and sequential task execution, ideal for long-running, multi-step processes. Choose EventBridge when your workflow requires event routing and loosely coupled components; opt for Step Functions to coordinate intricate, stateful business logic within your AWS environment.
EventBridge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com