Application Performance Monitoring (APM) tools provide real-time insights into your software's efficiency, helping to detect and resolve performance bottlenecks swiftly. By tracking metrics like response time, error rates, and throughput, APM ensures seamless user experiences and system reliability. Explore the rest of the article to understand how APM can optimize your applications and drive business success.
Table of Comparison
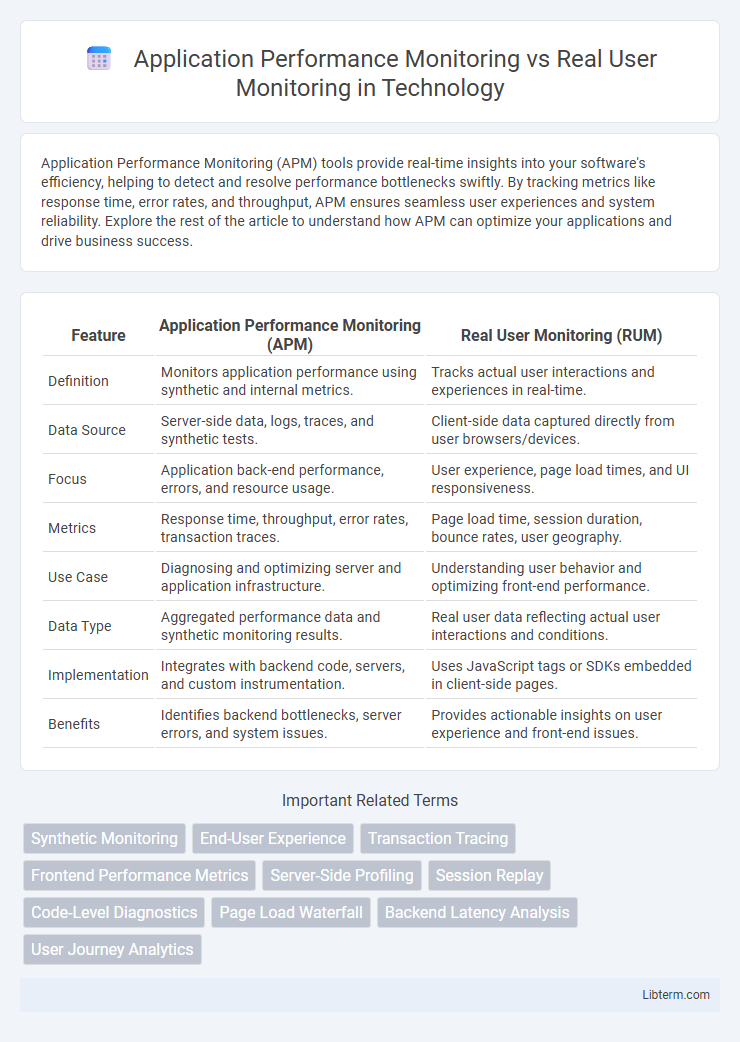
| Feature | Application Performance Monitoring (APM) | Real User Monitoring (RUM) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monitors application performance using synthetic and internal metrics. | Tracks actual user interactions and experiences in real-time. |
| Data Source | Server-side data, logs, traces, and synthetic tests. | Client-side data captured directly from user browsers/devices. |
| Focus | Application back-end performance, errors, and resource usage. | User experience, page load times, and UI responsiveness. |
| Metrics | Response time, throughput, error rates, transaction traces. | Page load time, session duration, bounce rates, user geography. |
| Use Case | Diagnosing and optimizing server and application infrastructure. | Understanding user behavior and optimizing front-end performance. |
| Data Type | Aggregated performance data and synthetic monitoring results. | Real user data reflecting actual user interactions and conditions. |
| Implementation | Integrates with backend code, servers, and custom instrumentation. | Uses JavaScript tags or SDKs embedded in client-side pages. |
| Benefits | Identifies backend bottlenecks, server errors, and system issues. | Provides actionable insights on user experience and front-end issues. |
Introduction to Application Performance Monitoring (APM) and Real User Monitoring (RUM)
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) provides comprehensive insights into software application behavior by tracking key metrics such as response time, error rates, and transaction traces across the backend infrastructure. Real User Monitoring (RUM) captures actual user interactions in real-time, measuring page load times, user sessions, and device-specific performance to assess the end-user experience directly. Both APM and RUM are essential for optimizing digital services, with APM focusing on internal system diagnostics and RUM delivering client-side user experience analytics.
Defining Application Performance Monitoring (APM)
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) refers to the systematic process of tracking and managing the performance and availability of software applications to ensure optimal user experience and business outcomes. It involves collecting metrics such as response times, error rates, and transaction traces from servers and backend systems to detect, diagnose, and resolve performance bottlenecks. APM tools provide deep visibility into application components, enabling IT teams to proactively monitor and maintain system health in contrast to Real User Monitoring (RUM), which captures actual user interactions and experience in real time.
Understanding Real User Monitoring (RUM)
Real User Monitoring (RUM) captures and analyzes actual user interactions with a web application to provide insights into performance from the end-user perspective. It tracks metrics such as page load times, transaction paths, and user behavior across devices and locations, enabling the identification of real-world issues affecting experience. Unlike Application Performance Monitoring (APM), which focuses on backend processes and infrastructure, RUM offers a direct measurement of user experience by collecting data passively during live sessions.
Key Differences Between APM and RUM
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) focuses on tracking and analyzing backend processes, server metrics, and application code to identify performance bottlenecks and errors. Real User Monitoring (RUM) collects data directly from users' interactions, capturing real-time user experience metrics like page load times, transaction paths, and device-specific performance. The key difference lies in APM's proactive internal diagnostics versus RUM's passive, user-centric insights that reflect actual end-user behavior and environmental conditions.
Core Features of Application Performance Monitoring
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) core features include end-to-end transaction tracing, real-time performance metrics, error detection, and resource usage analysis, enabling deep insights into application behavior and backend services. Unlike Real User Monitoring (RUM), which captures actual user interactions and frontend performance, APM provides detailed diagnostics from server-side components and infrastructure layers. Key APM capabilities support faster root cause analysis and system optimization by monitoring database calls, application code execution, and third-party service integrations.
Essential Capabilities of Real User Monitoring
Real User Monitoring (RUM) captures and analyzes actual user interactions, providing essential capabilities such as detailed session tracking, geographic performance metrics, and real-time user experience insights. Unlike Application Performance Monitoring (APM), which focuses on backend performance and server metrics, RUM offers granular visibility into front-end load times, page responsiveness, and user behavior patterns across different devices and browsers. These insights enable businesses to optimize user journeys, quickly identify bottlenecks, and enhance overall digital experience based on real-world usage data.
Use Cases: When to Use APM vs RUM
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) is ideal for diagnosing backend issues, tracking server performance, and analyzing code-level errors within complex applications. Real User Monitoring (RUM) excels in capturing actual user experiences, measuring front-end load times, and monitoring session behaviors in real-world environments. Use APM during development and troubleshooting phases to identify bottlenecks in application infrastructure, while RUM is best suited for ongoing performance assessment and optimizing user experience based on live data.
Benefits of Combining APM and RUM
Combining Application Performance Monitoring (APM) and Real User Monitoring (RUM) provides a comprehensive view of both backend server health and actual user experience, enabling faster detection and resolution of performance bottlenecks. This integrated approach leverages APM's detailed metrics on application components alongside RUM's real-time user behavior data, enhancing accuracy in diagnosing issues and improving overall application reliability. Organizations benefit from reduced downtime, optimized resource allocation, and increased user satisfaction by correlating system performance with real-world usage patterns.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) faces challenges such as limited visibility into actual user experiences and difficulty in diagnosing issues in complex, distributed environments due to reliance on synthetic transactions and server-side data. Real User Monitoring (RUM) struggles with data privacy concerns, incomplete visibility in low-traffic scenarios, and potential performance overhead from injecting monitoring scripts into client-side applications. Both approaches have limitations in providing a comprehensive performance picture without integration and contextual correlation of their respective data sets.
Choosing the Right Monitoring Solution for Your Business
Application Performance Monitoring (APM) focuses on tracking and diagnosing backend system metrics such as server response times, error rates, and resource utilization to ensure optimal application function. Real User Monitoring (RUM) captures actual user interactions, providing insights into user experience by analyzing page load times, click behavior, and geographic performance variations. Choosing the right monitoring solution depends on your business needs: APM suits organizations prioritizing technical infrastructure health, while RUM benefits those aiming to enhance customer experience through real-world usage data.
Application Performance Monitoring Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com