Continuous Data Protection (CDP) ensures that every change made to your data is captured and saved in real-time, minimizing the risk of data loss. By enabling near-instantaneous backups, CDP allows you to restore files to any point in time with precision, enhancing data recovery capabilities. Explore the rest of the article to understand how CDP can safeguard your critical information.
Table of Comparison
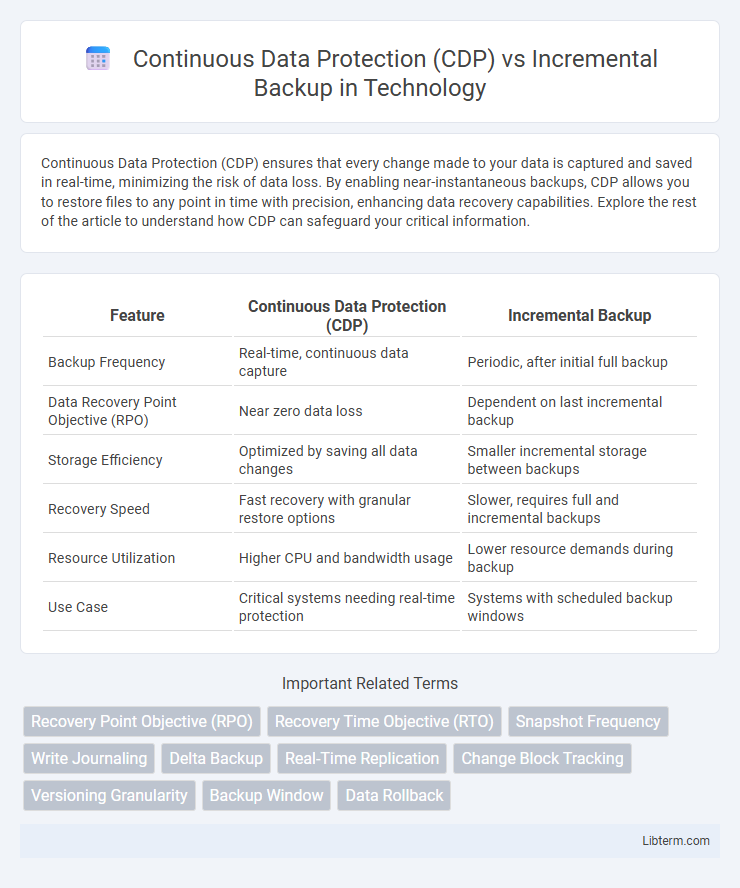
| Feature | Continuous Data Protection (CDP) | Incremental Backup |
|---|---|---|
| Backup Frequency | Real-time, continuous data capture | Periodic, after initial full backup |
| Data Recovery Point Objective (RPO) | Near zero data loss | Dependent on last incremental backup |
| Storage Efficiency | Optimized by saving all data changes | Smaller incremental storage between backups |
| Recovery Speed | Fast recovery with granular restore options | Slower, requires full and incremental backups |
| Resource Utilization | Higher CPU and bandwidth usage | Lower resource demands during backup |
| Use Case | Critical systems needing real-time protection | Systems with scheduled backup windows |
Introduction to Data Protection Strategies
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) captures and saves every change made to data in real-time, ensuring minimal data loss and instant recovery points compared to Incremental Backup, which only saves changes since the last backup session, potentially risking larger data gaps. CDP provides comprehensive data protection by storing every version of data, supporting fast restoration to any specific point in time, whereas Incremental Backup reduces storage requirements and backup time but may require multiple steps during recovery. Selecting between CDP and Incremental Backup depends on the criticality of data, recovery time objectives (RTO), and storage capacity priorities within an organization's data protection strategy.
What is Continuous Data Protection (CDP)?
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) captures and saves data changes automatically and in real-time, ensuring every modification is recorded immediately to minimize data loss. Unlike incremental backups that save changes at set intervals, CDP continuously records updates to provide near-instant recovery points. This technology is essential for businesses requiring stringent data recovery objectives and minimizing recovery time objectives (RTO).
Understanding Incremental Backup
Incremental Backup captures only the changes made since the last backup, minimizing storage usage and reducing backup time compared to full backups. It relies on a chain of backups, where each incremental backup depends on the previous one to restore the data fully. Continuous Data Protection (CDP) differs by continuously saving every data change in real-time, offering granular recovery points but requiring more storage and network resources.
Key Differences Between CDP and Incremental Backup
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) captures every change in real-time, providing near-instant recovery points, whereas incremental backup saves only changes made since the last backup at scheduled intervals, resulting in longer recovery times. CDP minimizes data loss by continuously recording modifications at the byte level, while incremental backup aggregates changes in discrete backup sets, often requiring multiple restores during recovery. The key difference lies in CDP's ability to offer granular, continuous snapshots for precise recovery versus incremental backup's periodic snapshots that optimize storage but may increase recovery complexity.
Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) Comparison
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) offers near-zero Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) by capturing data changes in real-time, ensuring minimal data loss during recovery. Incremental Backup typically has higher RPO values since it backs up only the data changed since the last backup, often on scheduled intervals like daily or hourly. The choice between CDP and Incremental Backup directly impacts the frequency of data snapshots and the potential window of data loss in disaster recovery scenarios.
Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) Comparison
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) offers near-instantaneous Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) by continuously capturing data changes, enabling rapid restoration to any point in time. Incremental Backup involves saving only changes since the last backup, resulting in longer RTOs as restoration requires sequential application of backups before reaching the desired state. Organizations prioritizing minimal downtime often favor CDP for its superior recovery speed compared to incremental backup methodologies.
Performance and Storage Impact
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) captures data changes in real-time, minimizing data loss and enabling faster recovery point objectives, but requires higher storage capacity and more processing power due to constant data capture. Incremental backup only saves changes since the last backup, reducing storage consumption and system load but may extend recovery time due to the need to restore multiple backup sets. While CDP delivers superior performance for critical applications needing near-instant recovery, incremental backup offers a balanced approach with less impact on storage and server performance.
Security and Compliance Considerations
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) offers real-time data capture, minimizing data loss risks and enhancing compliance with stringent regulatory standards like GDPR and HIPAA by ensuring up-to-the-second backup copies. Incremental Backup, while efficient in storage and speed, creates backups at scheduled intervals, potentially exposing organizations to data gaps that can challenge adherence to security policies and regulatory audits. Both methods require encryption and access controls, but CDP's near-instant replication aligns better with continuous compliance monitoring and rapid incident response frameworks.
Use Cases: When to Choose CDP vs Incremental Backup
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) is ideal for environments requiring near real-time data recovery, such as financial institutions and e-commerce platforms, where minimizing data loss is critical. Incremental backup suits businesses with scheduled backup windows and moderate recovery time objectives, like small to medium-sized enterprises managing periodic data changes. Choosing CDP over incremental backup depends on the need for granular restore points and minimal data loss tolerance versus efficient storage use and reduced backup time.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Backup Solution
Choosing between Continuous Data Protection (CDP) and Incremental Backup depends on recovery objectives and data change frequency. CDP offers near-real-time data replication ideal for minimizing data loss in high-transaction environments, while Incremental Backup efficiently saves storage and bandwidth by capturing only changes since the last backup. Organizations must assess their Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO) to determine which solution aligns with their data protection strategy and operational requirements.
Continuous Data Protection (CDP) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com