Digital Asset Management (DAM) streamlines the organization, storage, and retrieval of digital content, boosting efficiency and consistency across your marketing and creative projects. By centralizing assets like images, videos, and documents, DAM solutions enable faster collaboration and ensure brand compliance. Discover how implementing a DAM system can transform your workflow and elevate your brand presence in the full article.
Table of Comparison
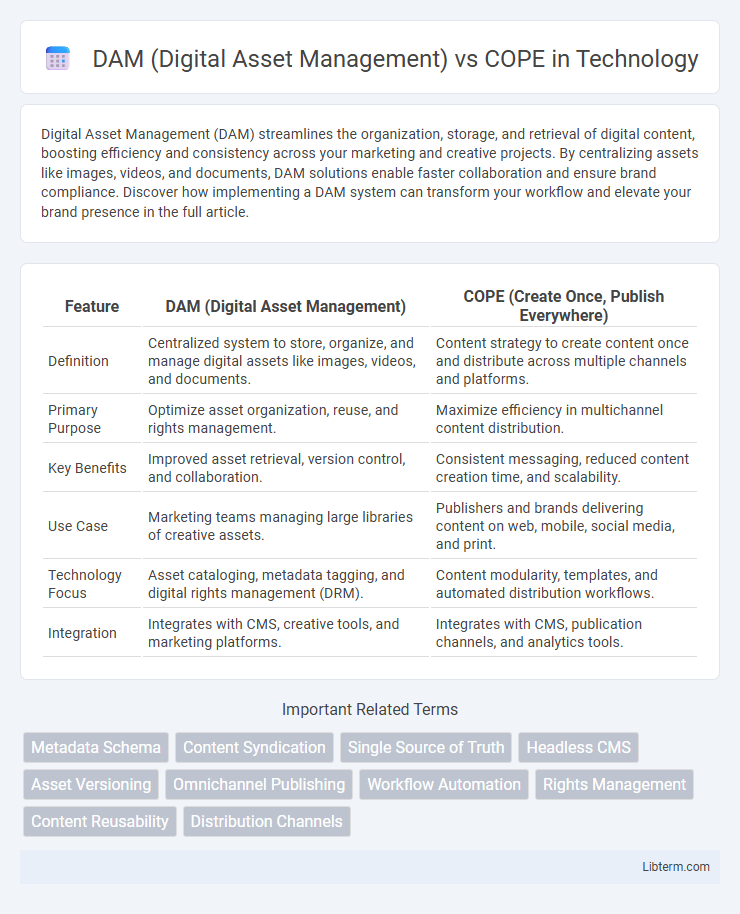
| Feature | DAM (Digital Asset Management) | COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Centralized system to store, organize, and manage digital assets like images, videos, and documents. | Content strategy to create content once and distribute across multiple channels and platforms. |
| Primary Purpose | Optimize asset organization, reuse, and rights management. | Maximize efficiency in multichannel content distribution. |
| Key Benefits | Improved asset retrieval, version control, and collaboration. | Consistent messaging, reduced content creation time, and scalability. |
| Use Case | Marketing teams managing large libraries of creative assets. | Publishers and brands delivering content on web, mobile, social media, and print. |
| Technology Focus | Asset cataloging, metadata tagging, and digital rights management (DRM). | Content modularity, templates, and automated distribution workflows. |
| Integration | Integrates with CMS, creative tools, and marketing platforms. | Integrates with CMS, publication channels, and analytics tools. |
Introduction to DAM and COPE
Digital Asset Management (DAM) is a system designed to store, organize, and retrieve rich media assets such as images, videos, and documents, ensuring efficient workflow and brand consistency. Create Once, Publish Everywhere (COPE) is a content strategy that emphasizes producing content a single time and distributing it across multiple channels and formats to maximize reach and streamline publishing. Integrating DAM with COPE enhances content scalability, enabling seamless asset reuse and multi-platform content delivery.
What is Digital Asset Management (DAM)?
Digital Asset Management (DAM) is a centralized system designed to store, organize, retrieve, and distribute digital assets such as images, videos, documents, and audio files. It enhances content workflow efficiency by enabling easy access, version control, and secure sharing across teams and platforms. DAM integrates metadata tagging and advanced search capabilities to streamline asset management and ensure brand consistency.
Understanding COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere)
COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) streamlines digital content distribution by enabling assets to be created a single time and automatically adapted for multiple platforms, enhancing efficiency and consistency. Unlike traditional Digital Asset Management (DAM) systems that primarily focus on storing and organizing digital files, COPE emphasizes content repurposing and omnichannel publishing. This approach reduces redundancy, accelerates time-to-market, and ensures uniform brand messaging across websites, social media, mobile apps, and other digital channels.
Key Features of DAM Solutions
Digital Asset Management (DAM) solutions centralize the storage, organization, and retrieval of rich media assets, enabling efficient metadata tagging, version control, and rights management. Key features include advanced search capabilities, automated workflows for asset approval and distribution, and integration with creative tools such as Adobe Creative Cloud, enhancing collaboration and content reuse. Unlike COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere), which focuses on content repurposing across channels, DAM emphasizes asset governance and seamless access to high-quality digital content within enterprise ecosystems.
Core Principles of the COPE Strategy
COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) centers on content reuse by producing modular, structured assets that can be efficiently distributed across multiple channels, ensuring consistency and scalability. Digital Asset Management (DAM) systems focus on storing, organizing, and retrieving digital files but lack the inherent capability for content repurposing emphasized in COPE. The core principle of COPE lies in decoupling content creation from delivery, enabling seamless, omnichannel publishing without redundant efforts.
Comparing DAM and COPE: Similarities and Differences
Digital Asset Management (DAM) and Create Once Publish Everywhere (COPE) both streamline content distribution but serve distinct purposes; DAM centralizes, organizes, and manages digital assets for easy retrieval, whereas COPE emphasizes content creation flexibility for multi-channel publishing. Both enhance workflow efficiency and ensure content consistency, yet DAM focuses on asset storage and metadata management, while COPE prioritizes content modularity and repurposing across platforms. Integrating DAM with COPE strategies leverages centralized asset control alongside adaptive publishing, improving overall content lifecycle management.
Use Cases: When to Implement DAM vs. COPE
Implement DAM when organizations need centralized storage, easy retrieval, and efficient management of digital assets like images, videos, and documents to ensure brand consistency and streamline marketing workflows. Implement COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) when content must be authored once and distributed seamlessly across multiple platforms and channels, optimizing content scalability and reducing duplication efforts. Use DAM to control and organize assets, while COPE focuses on content distribution strategies to maximize reach and engagement.
Benefits and Challenges of DAM Systems
Digital Asset Management (DAM) systems centralize the storage, organization, and retrieval of digital content, enhancing collaboration and ensuring brand consistency across channels. Benefits include improved metadata management, faster content delivery, and streamlined workflows, but challenges arise from high implementation costs, complex integration with existing tools, and the need for ongoing user training. Unlike Content Optimization for Production Efficiency (COPE), which focuses on repurposing content for multiple platforms, DAM emphasizes secure asset control and long-term digital preservation.
Advantages and Limitations of COPE
COPE (Create Once, Publish Everywhere) streamlines content distribution by enabling a single piece of digital content to be repurposed across multiple platforms, enhancing efficiency and consistency. Advantages of COPE include reducing duplication of effort, maintaining brand cohesion, and accelerating time-to-market for digital assets. Limitations involve potential challenges in customizing content for diverse audiences and platforms, as well as the initial setup complexity compared to traditional Digital Asset Management (DAM) systems.
Choosing Between DAM and COPE for Your Organization
Choosing between Digital Asset Management (DAM) and Create Once Publish Everywhere (COPE) depends on an organization's content strategy and workflow needs. DAM systems excel at storing, organizing, and retrieving rich media assets, ensuring efficient digital asset lifecycle management and brand consistency. COPE frameworks prioritize content reusability and multi-channel distribution, enhancing scalability and reducing redundant content creation across platforms.
DAM (Digital Asset Management) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com