Continuous Deployment automates the release of code changes directly to production, ensuring faster delivery of new features and bug fixes. By integrating rigorous testing and monitoring, it reduces human error and enhances software reliability. Discover how implementing continuous deployment can transform your development workflow in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
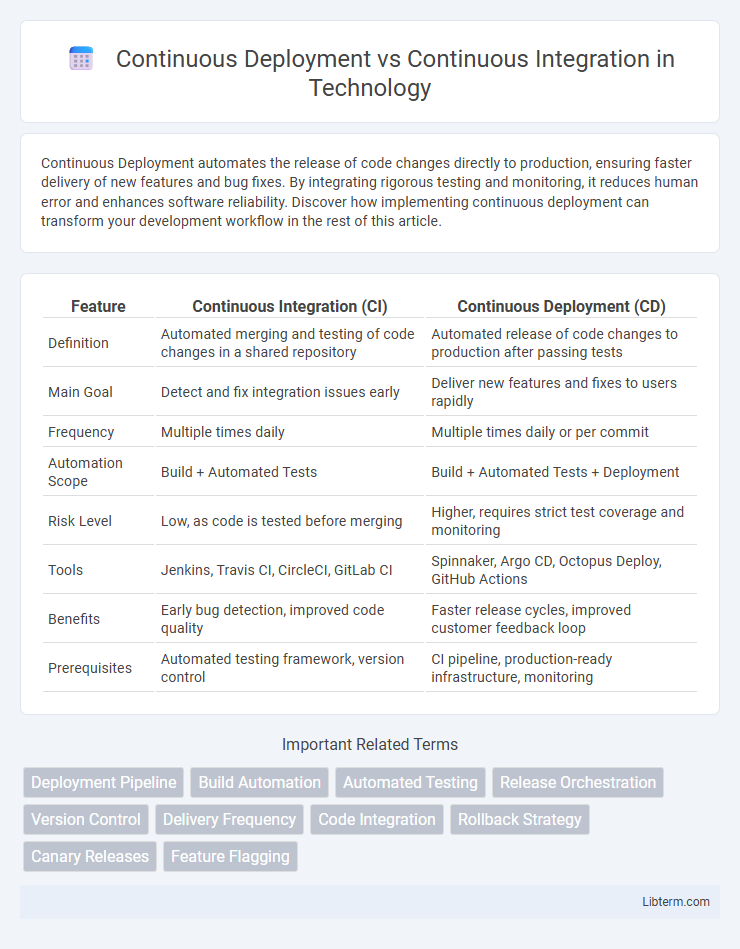
| Feature | Continuous Integration (CI) | Continuous Deployment (CD) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated merging and testing of code changes in a shared repository | Automated release of code changes to production after passing tests |
| Main Goal | Detect and fix integration issues early | Deliver new features and fixes to users rapidly |
| Frequency | Multiple times daily | Multiple times daily or per commit |
| Automation Scope | Build + Automated Tests | Build + Automated Tests + Deployment |
| Risk Level | Low, as code is tested before merging | Higher, requires strict test coverage and monitoring |
| Tools | Jenkins, Travis CI, CircleCI, GitLab CI | Spinnaker, Argo CD, Octopus Deploy, GitHub Actions |
| Benefits | Early bug detection, improved code quality | Faster release cycles, improved customer feedback loop |
| Prerequisites | Automated testing framework, version control | CI pipeline, production-ready infrastructure, monitoring |
Introduction to Continuous Deployment and Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) is a software development practice where developers frequently merge code changes into a shared repository, triggering automated builds and tests to detect issues early. Continuous Deployment (CD) extends CI by automatically releasing validated code changes to production environments, ensuring faster delivery and reducing manual intervention. Both practices enhance software quality and accelerate development cycles through automation and consistent feedback loops.
Defining Continuous Integration (CI)
Continuous Integration (CI) is a software development practice where developers frequently merge code changes into a shared repository, typically multiple times per day, enabling automated builds and testing. This process aims to detect integration issues early, improve code quality, and streamline collaboration across development teams. CI serves as the foundation for Continuous Deployment by ensuring that code changes are continuously validated before automatic release.
Understanding Continuous Deployment (CD)
Continuous Deployment (CD) automates the release of code changes directly into production environments after passing automated tests, ensuring rapid delivery and reducing manual intervention. Unlike Continuous Integration (CI), which focuses on integrating code changes frequently and verifying them through builds and tests, CD extends this process by automatically deploying validated changes to users. This practice enhances software development efficiency, minimizes deployment risks, and supports continuous feedback through real-time updates.
Core Differences Between CI and CD
Continuous Integration (CI) primarily focuses on automating the process of merging code changes into a shared repository, ensuring immediate testing and validation to detect integration issues early. Continuous Deployment (CD) extends CI by automating the release of validated code into production environments, enabling faster delivery of features and bug fixes directly to end users. Core differences lie in CI's emphasis on code integration and testing, while CD concentrates on deployment automation and release management within the software development lifecycle.
Benefits of Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) enhances software quality by frequently merging code changes into a shared repository, enabling early detection and resolution of defects. Automated testing during CI accelerates feedback loops, reducing integration issues and minimizing deployment risks. Teams practicing CI benefit from improved collaboration, streamlined workflows, and faster delivery cycles, laying a strong foundation for Continuous Deployment.
Advantages of Continuous Deployment
Continuous Deployment accelerates software delivery by automatically releasing every code change that passes automated tests, significantly reducing time to market. This approach enhances product quality through frequent, smaller updates that simplify debugging and improve feedback loops with end users. Continuous Deployment also boosts developer productivity by eliminating manual release processes, enabling faster innovation cycles and greater responsiveness to customer needs.
Key Challenges and Common Pitfalls
Continuous Deployment faces key challenges such as ensuring automated testing reliability and managing rollback mechanisms to avoid production outages, while Continuous Integration struggles with maintaining code quality and handling merge conflicts efficiently. Common pitfalls in Continuous Deployment include insufficient monitoring and lack of environment consistency, whereas Continuous Integration often suffers from slow build times and inadequate test coverage. Both practices require robust infrastructure and stringent process adherence to minimize risks and maximize delivery speed.
Best Practices for Implementing CI and CD
Implementing Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) requires best practices such as automating build and test processes to ensure code quality and reduce integration issues. Maintaining a robust version control system and using feature flags help manage code changes safely during deployment. Monitoring pipelines with real-time feedback and incorporating rollback mechanisms minimize downtime and enhance release reliability.
Selecting the Right Tools for CI/CD
Selecting the right tools for Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) involves evaluating platforms like Jenkins, GitLab CI, and CircleCI for their automation capabilities, scalability, and integration with version control systems such as Git. Tool choice should align with the project's technology stack, team expertise, and the need for real-time monitoring and rollback features in deployment pipelines. Prioritizing tools that support automated testing, seamless code merging, and efficient artifact management ensures streamlined workflows and faster delivery cycles.
Conclusion: Choosing Between CI and CD
Choosing between Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) depends on an organization's delivery goals and risk tolerance. CI emphasizes automated code integration and testing to ensure code quality, while CD extends automation to deployment, enabling faster, frequent releases to production. Teams aiming for rapid feedback and higher deployment frequency should implement both CI and CD for an optimized DevOps pipeline.
Continuous Deployment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com