Dynamic typing allows variables to be assigned different data types throughout a program, enabling flexible and rapid development. This feature reduces the need for explicit type declarations, making it easier to write and modify code on the fly. Explore the rest of this article to understand how dynamic typing impacts programming efficiency and error handling.
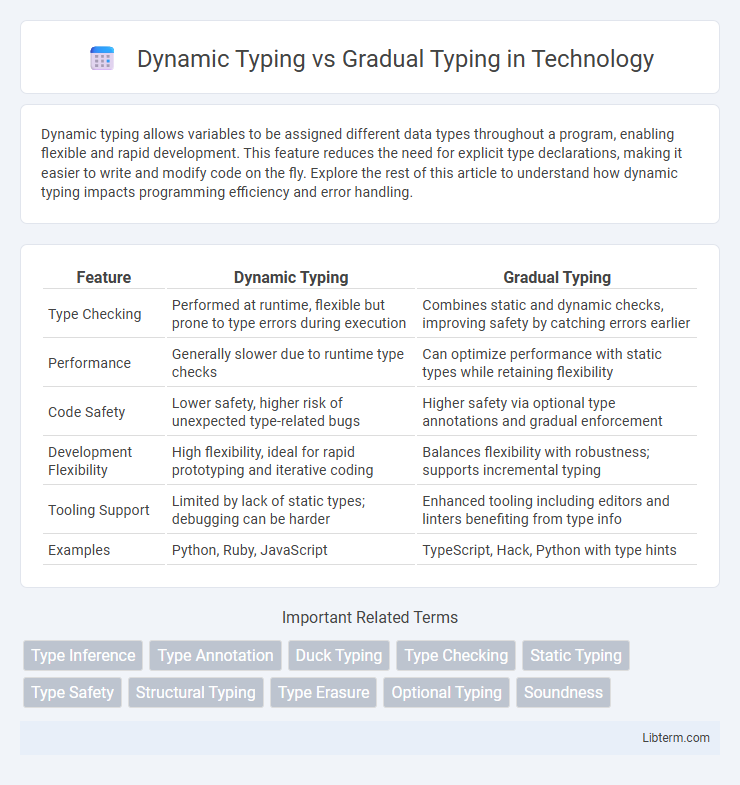
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Dynamic Typing | Gradual Typing |
|---|---|---|
| Type Checking | Performed at runtime, flexible but prone to type errors during execution | Combines static and dynamic checks, improving safety by catching errors earlier |
| Performance | Generally slower due to runtime type checks | Can optimize performance with static types while retaining flexibility |
| Code Safety | Lower safety, higher risk of unexpected type-related bugs | Higher safety via optional type annotations and gradual enforcement |
| Development Flexibility | High flexibility, ideal for rapid prototyping and iterative coding | Balances flexibility with robustness; supports incremental typing |
| Tooling Support | Limited by lack of static types; debugging can be harder | Enhanced tooling including editors and linters benefiting from type info |
| Examples | Python, Ruby, JavaScript | TypeScript, Hack, Python with type hints |
Understanding Dynamic Typing
Dynamic typing allows variables to hold values of any type without explicit type annotations, enabling rapid development and flexibility in coding. This typing approach performs type checking at runtime, which can lead to runtime errors but facilitates easier prototyping and iteration. Languages like Python, Ruby, and JavaScript exemplify dynamic typing, prioritizing developer speed over compile-time type safety.
Exploring Gradual Typing
Gradual typing combines static and dynamic type systems, enabling developers to add type annotations incrementally in languages like TypeScript or Python with type hints. This approach improves code reliability and maintainability while preserving the flexibility of dynamic typing, allowing for runtime checks where static types are absent. Tools such as Flow and mypy facilitate gradual typing by enforcing type correctness without sacrificing development speed or expressiveness.
Key Differences Between Dynamic and Gradual Typing
Dynamic typing assigns types to variables at runtime, allowing greater flexibility but increasing the risk of type errors during execution. Gradual typing integrates static and dynamic typing by enabling developers to specify types incrementally, improving code safety and tooling support while maintaining flexibility. Key differences include error detection timing, with dynamic typing catching errors only when code runs, and gradual typing providing early error detection through optional type annotations.
Benefits of Dynamic Typing
Dynamic typing enhances development speed by allowing variables to change types at runtime, leading to more flexible and concise code. This approach reduces the need for explicit type declarations, facilitating rapid prototyping and iteration in languages like Python and JavaScript. The inherent flexibility of dynamic typing supports dynamic and interactive applications where type constraints could hinder quick modifications and experimentation.
Advantages of Gradual Typing
Gradual typing combines the flexibility of dynamic typing with the safety of static typing, enabling developers to catch type errors early while maintaining runtime adaptability. It improves code maintainability and readability by allowing optional type annotations that facilitate better tooling support and error detection. This hybrid approach enhances developer productivity by supporting incremental typing adoption in large codebases, reducing debugging time and increasing overall code reliability.
Common Use Cases for Each Typing System
Dynamic typing excels in rapid prototyping and scripting where flexibility and speed outweigh strict type constraints, commonly seen in languages like Python and JavaScript. Gradual typing bridges the gap by allowing developers to incrementally add static types to dynamic languages, improving maintainability in large-scale applications exemplified by TypeScript and Python's optional type hints. Use cases for gradual typing often involve complex, evolving codebases requiring both runtime flexibility and compile-time type safety for bug reduction and refactoring ease.
Performance Implications in Dynamic vs Gradual Typing
Dynamic typing allows variables to hold any type at runtime, enabling flexible code but often leading to slower execution due to constant type checks and potential runtime errors. Gradual typing integrates static type annotations incrementally, allowing parts of the code to be type-checked at compile time, which can reduce runtime overhead and improve performance by catching errors earlier. Performance gains in gradual typing depend on the extent of static annotations applied, with more static code resulting in optimizations similar to statically typed languages.
Developer Productivity and Code Maintenance
Dynamic typing accelerates development speed by allowing developers to write code without explicit type annotations, enhancing flexibility and rapid prototyping. Gradual typing improves code maintainability by enabling incremental addition of static types, which helps catch type errors early and facilitates easier refactoring in large codebases. Combining dynamic typing's agility with gradual typing's safety boosts overall developer productivity while ensuring scalable and robust software maintenance.
Popular Languages That Use Dynamic or Gradual Typing
Dynamic typing is prevalent in popular languages like Python, Ruby, and JavaScript, enabling rapid development by allowing variable types to be determined at runtime without explicit annotations. Gradual typing is adopted by languages such as TypeScript, Dart, and Python (through type hints), combining dynamic typing flexibility with optional static type checks to enhance code reliability and maintainability. These typing paradigms influence language ecosystem preferences, where dynamic typing supports quick prototyping, and gradual typing balances flexibility with increased type safety.
Choosing the Right Typing System for Your Project
Choosing the right typing system depends on your project's requirements for flexibility and safety. Dynamic typing, found in languages like Python, allows rapid development with fewer type constraints but can lead to runtime errors. Gradual typing, as implemented in TypeScript, offers a balance by enabling optional static type checks that improve code maintainability and reduce bugs while preserving some of the flexibility found in dynamic languages.
Dynamic Typing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com