Load testing evaluates how a system performs under expected and peak user demand by simulating real-world traffic patterns to identify bottlenecks and ensure stability. This process helps optimize application responsiveness, scalability, and reliability to maintain a seamless user experience. Discover how mastering load testing can safeguard Your system's performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
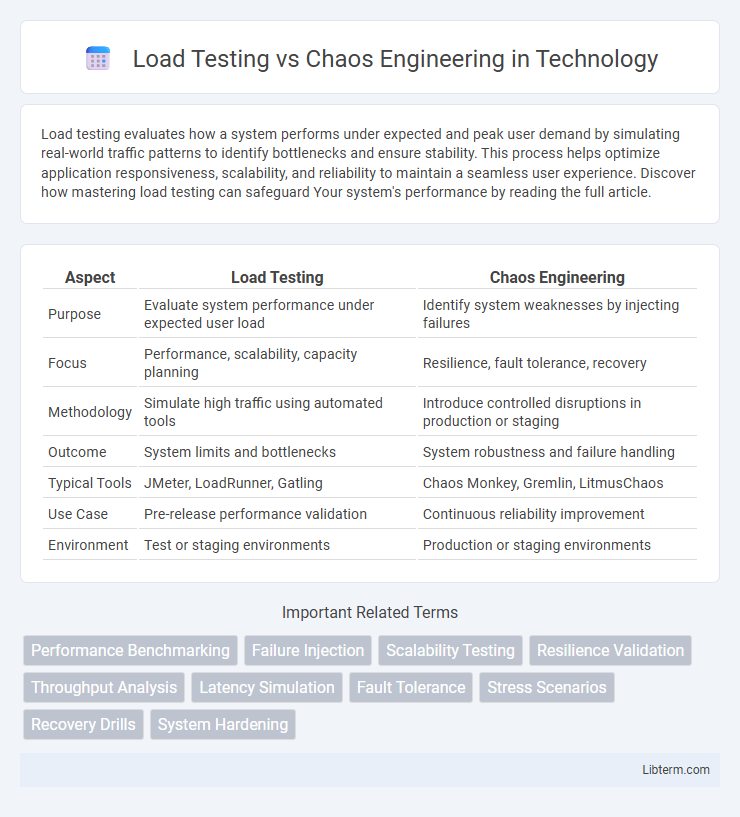
| Aspect | Load Testing | Chaos Engineering |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate system performance under expected user load | Identify system weaknesses by injecting failures |
| Focus | Performance, scalability, capacity planning | Resilience, fault tolerance, recovery |
| Methodology | Simulate high traffic using automated tools | Introduce controlled disruptions in production or staging |
| Outcome | System limits and bottlenecks | System robustness and failure handling |
| Typical Tools | JMeter, LoadRunner, Gatling | Chaos Monkey, Gremlin, LitmusChaos |
| Use Case | Pre-release performance validation | Continuous reliability improvement |
| Environment | Test or staging environments | Production or staging environments |
Introduction to Load Testing and Chaos Engineering
Load testing evaluates system performance by simulating high user traffic to identify bottlenecks and ensure reliability under peak conditions. Chaos engineering deliberately introduces failures into a system to test its resilience and ability to recover from unexpected disruptions. Both practices enhance software robustness but focus on different aspects: load testing targets capacity limits, while chaos engineering emphasizes fault tolerance.
Key Differences Between Load Testing and Chaos Engineering
Load Testing evaluates system performance under expected user demand by simulating high traffic to identify bottlenecks and capacity limits. Chaos Engineering intentionally introduces faults and disruptions in a controlled environment to test system resilience and fault tolerance. While Load Testing focuses on verifying scalability and stability under stress, Chaos Engineering emphasizes uncovering weaknesses through unexpected failure scenarios.
Objectives: What Each Approach Aims to Achieve
Load testing aims to evaluate a system's performance under expected user traffic by simulating high volumes of concurrent requests to identify bottlenecks and ensure scalability. Chaos engineering focuses on improving system resilience by intentionally injecting faults and failures in a controlled environment to observe system behavior and verify fault tolerance. Both approaches enhance system reliability but differ in objectives: load testing targets performance thresholds, while chaos engineering targets robustness under unpredictable disruptions.
Common Tools for Load Testing vs Chaos Engineering
Common tools for load testing include Apache JMeter, LoadRunner, and Gatling, which simulate high user traffic to evaluate system performance under stress. Chaos engineering relies on tools like Gremlin, Chaos Monkey, and LitmusChaos to introduce controlled faults and disruptions, targeting system resilience and fault tolerance. Both approaches utilize specialized software to identify performance bottlenecks and vulnerabilities but differ in methodology and objectives.
When to Use Load Testing vs Chaos Engineering
Load testing is ideal for assessing system performance under expected user loads, helping identify bottlenecks and ensuring scalability during peak traffic periods. Chaos engineering is best employed when validating system resilience and fault tolerance by intentionally injecting failures to reveal weaknesses in production or pre-production environments. Use load testing during development phases for capacity planning, while chaos engineering should be reserved for maturity stages to strengthen reliability and incident response strategies.
Benefits of Load Testing in System Performance
Load testing evaluates system performance under expected user loads, identifying bottlenecks and ensuring scalability before deployment. This method provides concrete metrics on response times, throughput, and resource utilization, enabling proactive optimization. Effective load testing minimizes downtime risk, enhances user experience, and supports capacity planning for robust system reliability.
Advantages of Chaos Engineering for System Resilience
Chaos Engineering enhances system resilience by proactively identifying vulnerabilities through controlled experiments that simulate real-world failures. Unlike traditional Load Testing, which measures performance under expected conditions, Chaos Engineering exposes systems to unexpected disruptions, enabling teams to strengthen fault tolerance and recovery mechanisms. This approach leads to improved reliability, faster incident response, and increased confidence in handling unforeseen system stresses.
Limitations and Challenges of Both Approaches
Load testing primarily struggles with replicating real-world unpredictability and scaling complex user behaviors, often leading to incomplete performance insights. Chaos engineering faces challenges in safely injecting faults without causing service outages and requires extensive monitoring to identify subtle system weaknesses. Both approaches demand significant resource investment and expert knowledge to design effective tests that accurately reflect production environments.
Integrating Load Testing and Chaos Engineering in DevOps
Integrating load testing and chaos engineering in DevOps enhances system resilience by continuously validating performance under expected and unexpected stress conditions. Load testing ensures applications handle peak traffic efficiently, while chaos engineering proactively identifies vulnerabilities by injecting failures and disruptions. This combined approach supports automated pipeline integration, real-time monitoring, and faster incident response to maintain high availability and reliability in production environments.
Best Practices for Effective Testing and Engineering
Load testing requires precise simulation of peak user traffic to identify system bottlenecks, employing realistic usage patterns and gradually increasing load to avoid false negatives. Chaos engineering emphasizes controlled fault injection in production-like environments to uncover latent vulnerabilities, relying on automated monitoring and real-time alerting to promptly detect failures. Combining thorough scenario planning with continuous validation and rollback strategies ensures robust, resilient systems capable of handling unpredictable traffic and failures.
Load Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com