Identity and Access Management (IAM) ensures secure and efficient control over user identities and their access to systems and data, protecting organizations from unauthorized access and data breaches. Implementing robust IAM strategies helps streamline authentication, authorization, and compliance processes, reducing security risks while improving user experience. Explore the rest of the article to understand how IAM can safeguard your organization's digital assets and enhance operational security.
Table of Comparison
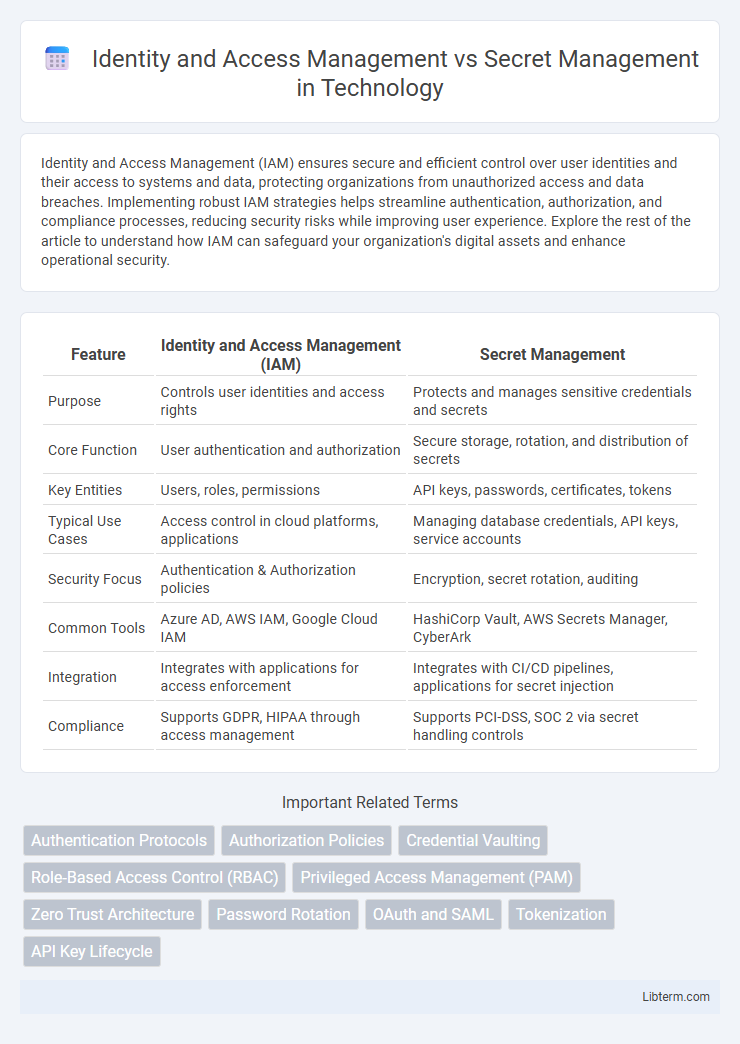
| Feature | Identity and Access Management (IAM) | Secret Management |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Controls user identities and access rights | Protects and manages sensitive credentials and secrets |
| Core Function | User authentication and authorization | Secure storage, rotation, and distribution of secrets |
| Key Entities | Users, roles, permissions | API keys, passwords, certificates, tokens |
| Typical Use Cases | Access control in cloud platforms, applications | Managing database credentials, API keys, service accounts |
| Security Focus | Authentication & Authorization policies | Encryption, secret rotation, auditing |
| Common Tools | Azure AD, AWS IAM, Google Cloud IAM | HashiCorp Vault, AWS Secrets Manager, CyberArk |
| Integration | Integrates with applications for access enforcement | Integrates with CI/CD pipelines, applications for secret injection |
| Compliance | Supports GDPR, HIPAA through access management | Supports PCI-DSS, SOC 2 via secret handling controls |
Introduction to Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) is a framework that ensures the right individuals access the appropriate resources at the right times for the right reasons, central to securing organizational assets. IAM involves managing user identities, authentication, authorization, and enforcing policies to restrict access based on roles and permissions. Unlike Secret Management, which focuses on safeguarding credentials, API keys, and sensitive information, IAM provides a broader governance layer for overseeing user access and identity lifecycle management.
Overview of Secret Management
Secret Management involves the secure storage, distribution, and rotation of sensitive information such as API keys, passwords, certificates, and tokens to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. It ensures that secrets are encrypted at rest and in transit, with access strictly controlled through automated policies and audit trails. Effective Secret Management integrates with Identity and Access Management systems to enforce least privilege access and streamline credential lifecycle management across distributed environments.
Key Differences Between IAM and Secret Management
Identity and Access Management (IAM) focuses on defining, managing, and enforcing user identities and their access permissions within an organization, ensuring that only authorized users can access specific resources. Secret Management specializes in securely storing, distributing, and rotating sensitive information such as passwords, API keys, and certificates to prevent unauthorized disclosure. The key difference lies in IAM managing user identities and access rights, while Secret Management is dedicated to protecting and controlling sensitive credentials and secrets.
Core Functions of Identity and Access Management
Identity and Access Management (IAM) primarily focuses on core functions such as user authentication, authorization, and role-based access control to ensure that only legitimate users gain appropriate access to resources. Secret Management, by contrast, handles the secure storage, distribution, and rotation of sensitive credentials like API keys and passwords. IAM establishes the foundational policies and identities, while Secret Management safeguards the secrets that enable secure communication and operations within those access frameworks.
Essential Features of Secret Management Solutions
Secret management solutions prioritize secure storage, automated rotation, and fine-grained access control of sensitive credentials such as API keys, passwords, and encryption keys. Key features include encryption-at-rest and in-transit, audit logging for compliance tracking, and seamless integration with cloud services and DevOps pipelines. These capabilities reduce the risk of credential exposure and enable dynamic, centralized management of secrets across distributed environments.
Use Cases for IAM and Secret Management
Identity and Access Management (IAM) primarily governs user authentication and authorization, enabling organizations to control who has access to specific resources and systems based on roles and policies, essential for managing employee access to cloud services and enterprise applications. Secret Management focuses on securely storing, distributing, and rotating sensitive credentials such as API keys, passwords, and encryption keys, critical for protecting application secrets and service-to-service authentication in DevOps pipelines. Use cases for IAM include enforcing least privilege access and policy compliance across cloud environments, while Secret Management is vital for safeguarding secrets in microservices architectures and automated workflows.
Security Challenges in Managing Identities and Secrets
Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Secret Management both address critical security challenges, such as unauthorized access and data breaches, but differ in scope: IAM focuses on controlling user identities and permissions, while Secret Management secures sensitive credentials like API keys and passwords. Managing identities involves complexities of role-based access control, multi-factor authentication, and continuous verification to prevent identity theft and insider threats. Secret Management challenges include secure storage, automated rotation, and strict access policies to reduce the risk of secret leakage and unauthorized use.
Integrating IAM and Secret Management Systems
Integrating Identity and Access Management (IAM) with Secret Management systems enhances security by ensuring that access to sensitive credentials is tightly controlled based on verified identities and roles. This integration allows automated credential rotation, audit trails, and dynamic access provisioning, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or leaked secrets. Leveraging IAM policies alongside secret management tools streamlines centralized governance and enforces compliance across cloud environments and enterprise applications.
Best Practices for IAM and Secret Management
Effective Identity and Access Management (IAM) requires implementing the principle of least privilege, enforcing multifactor authentication, and regularly reviewing access rights to minimize security risks. Secret Management best practices involve storing credentials in encrypted vaults, rotating secrets frequently, and automating secret delivery to reduce human error and exposure. Organizations should integrate IAM and Secret Management processes to ensure comprehensive security controls across user identities and sensitive data access.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Organization
Choosing the right solution between Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Secret Management hinges on your organization's security priorities and infrastructure complexity. IAM focuses on managing user identities, roles, and permissions to ensure appropriate access control across systems, while Secret Management securely handles sensitive credentials, API keys, and tokens essential for application-to-application communication. Evaluating factors such as compliance requirements, scalability needs, and integration capabilities helps determine whether a comprehensive IAM system, a specialized Secret Management tool, or a combination of both best supports your security strategy.
Identity and Access Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com