Scripting languages are essential tools designed to automate tasks, manipulate data, and enhance software functionality efficiently. They are often interpreted rather than compiled, making them flexible and easy to write for developers who want rapid results. Discover how mastering scripting languages can elevate your programming skills in the full article.
Table of Comparison
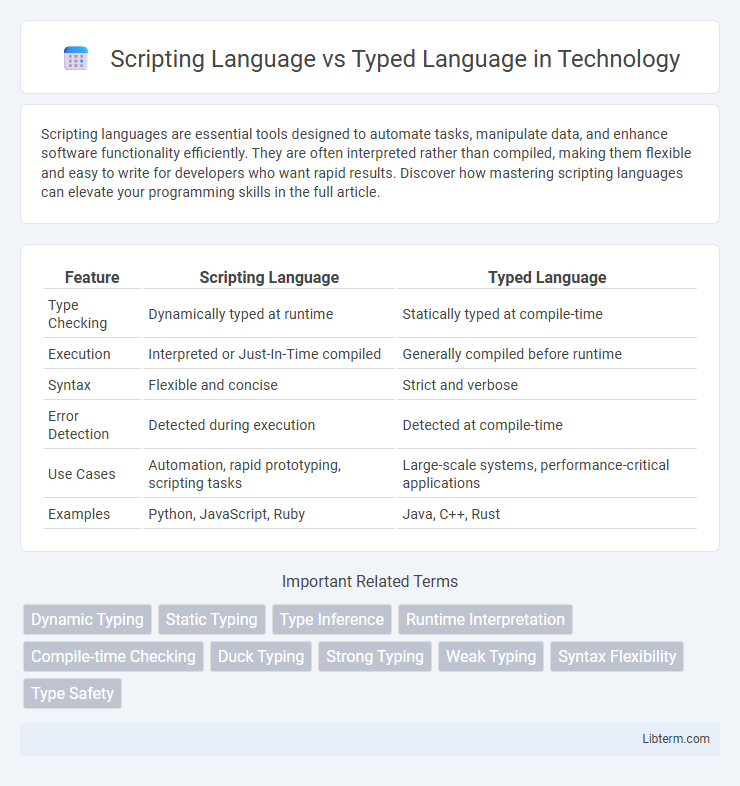
| Feature | Scripting Language | Typed Language |
|---|---|---|
| Type Checking | Dynamically typed at runtime | Statically typed at compile-time |
| Execution | Interpreted or Just-In-Time compiled | Generally compiled before runtime |
| Syntax | Flexible and concise | Strict and verbose |
| Error Detection | Detected during execution | Detected at compile-time |
| Use Cases | Automation, rapid prototyping, scripting tasks | Large-scale systems, performance-critical applications |
| Examples | Python, JavaScript, Ruby | Java, C++, Rust |
Overview of Scripting and Typed Languages
Scripting languages, such as Python, JavaScript, and Ruby, are typically interpreted and dynamically typed, enabling rapid development with flexible syntax that simplifies automation and web development tasks. Typed languages, including Java, C++, and C#, enforce strict type definitions at compile-time, enhancing performance, error detection, and maintainability in large-scale software projects. The choice between these languages depends on project requirements for speed, scalability, and type safety.
Key Differences Between Scripting and Typed Languages
Scripting languages, such as JavaScript and Python, are typically dynamically typed, allowing variable types to be determined at runtime, whereas typed languages like Java and C++ enforce static typing with explicit type declarations at compile time. Scripting languages prioritize ease of use and rapid development, often featuring interpreted execution, while typed languages emphasize performance and type safety through compiled binaries. The key differences lie in type checking, execution methods, and error detection, impacting development speed and application robustness.
Popular Examples of Scripting Languages
Popular scripting languages include JavaScript, Python, and Ruby, known for their dynamic typing and ease of use in rapid development. These languages are commonly used for web development, automation, and prototyping due to their flexibility and extensive libraries. In contrast, typed languages like Java and C++ enforce variable types, providing stronger type safety and performance optimizations.
Popular Examples of Typed Languages
Popular typed languages include Java, C++, and C#, which enforce strict type-checking during compilation to reduce runtime errors and improve code reliability. These statically typed languages provide better performance optimization and enhanced debugging compared to scripting languages like JavaScript or Python. Developers often choose typed languages for large-scale applications requiring maintainable and secure codebases.
Syntax and Structure: Flexibility vs. Rigor
Scripting languages such as Python and JavaScript prioritize flexibility in syntax and structure, allowing developers to write concise and dynamic code with less emphasis on strict type enforcement. Typed languages like Java and C++ enforce rigorous syntax rules and static type checking, which helps catch errors at compile-time and ensures code stability. This strictness in typed languages results in more structured and predictable code, whereas scripting languages offer quicker iteration and ease of use for rapid development.
Performance and Execution Speed Comparison
Typed languages such as C++ and Rust typically offer superior performance and execution speed due to static type checking and ahead-of-time (AOT) compilation, which optimize code before runtime. Scripting languages like Python and JavaScript rely on dynamic typing and just-in-time (JIT) compilation or interpretation, resulting in slower execution but increased flexibility and rapid development cycles. Benchmark tests consistently demonstrate that typed languages provide lower latency and higher throughput in computation-intensive tasks compared to their scripting counterparts.
Use Cases and Application Domains
Scripting languages like Python and JavaScript excel in rapid prototyping, automation, and web development due to their dynamic typing and ease of use, making them ideal for tasks such as data analysis, front-end development, and scripting system operations. Typed languages, including Java and C++, offer robust type-checking and compile-time error detection, which are crucial in large-scale software development, embedded systems, and applications requiring high performance and reliability. Use cases in finance, gaming, and enterprise software often favor typed languages for their stability, while startups and scientific research benefit from scripting languages for flexibility and speed.
Error Handling and Debugging
Scripting languages often feature dynamic typing, which enables rapid error detection during runtime but can lead to runtime errors that are harder to trace early in development. Typed languages enforce static type checking at compile time, reducing the likelihood of certain types of errors and simplifying debugging by catching type mismatches before execution. This static type enforcement improves error handling precision and enhances overall code reliability in complex applications.
Learning Curve and Developer Productivity
Scripting languages like Python and JavaScript offer a gentler learning curve due to their dynamic typing and simpler syntax, enabling rapid prototyping and faster development cycles. Typed languages such as Java and C# enforce strict type checking, which can initially slow learning but improves code reliability and maintainability, boosting long-term developer productivity. Developers often find scripting languages ideal for quick iterations, while typed languages better support large-scale projects where type safety reduces debugging time.
Choosing the Right Language for Your Project
Choosing the right language for your project depends on factors like development speed, type safety, and project complexity. Scripting languages such as Python and JavaScript offer rapid prototyping and flexibility, ideal for startups and smaller projects with frequent changes. Typed languages like Java and C# provide strong type checking and better error detection, making them suitable for large-scale applications requiring robustness and maintainability.
Scripting Language Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com