Extreme Programming (XP) is a software development methodology focused on improving software quality and responsiveness to changing customer requirements through frequent releases and collaborative practices. Key practices include pair programming, test-driven development, continuous integration, and close customer involvement to ensure your project adapts swiftly. Discover how XP can transform your development process by exploring the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
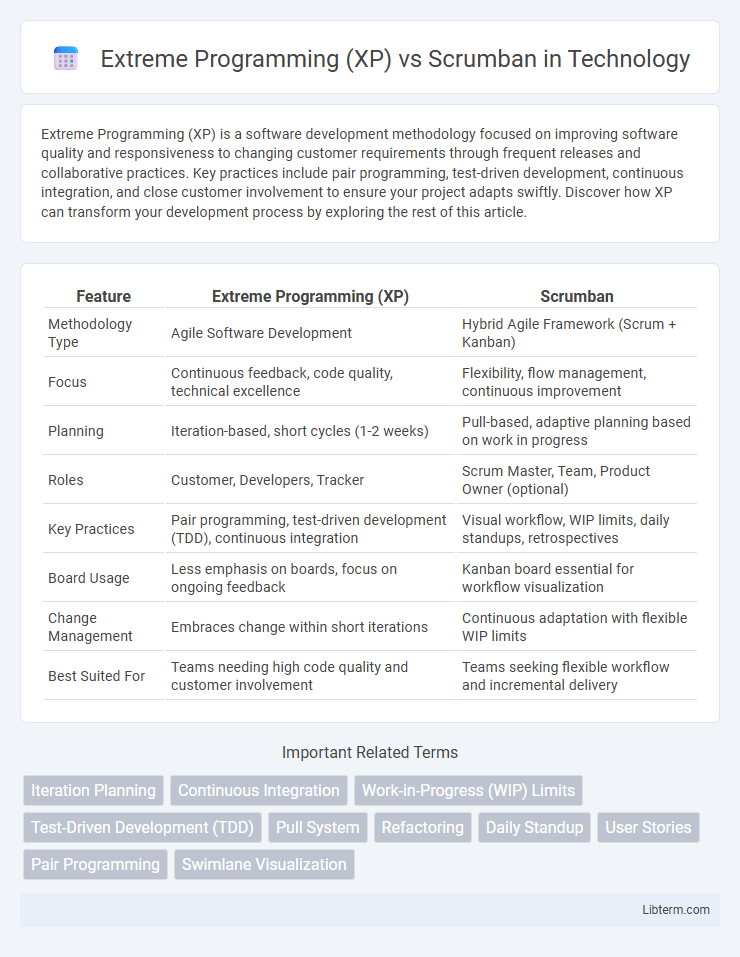
| Feature | Extreme Programming (XP) | Scrumban |
|---|---|---|
| Methodology Type | Agile Software Development | Hybrid Agile Framework (Scrum + Kanban) |
| Focus | Continuous feedback, code quality, technical excellence | Flexibility, flow management, continuous improvement |
| Planning | Iteration-based, short cycles (1-2 weeks) | Pull-based, adaptive planning based on work in progress |
| Roles | Customer, Developers, Tracker | Scrum Master, Team, Product Owner (optional) |
| Key Practices | Pair programming, test-driven development (TDD), continuous integration | Visual workflow, WIP limits, daily standups, retrospectives |
| Board Usage | Less emphasis on boards, focus on ongoing feedback | Kanban board essential for workflow visualization |
| Change Management | Embraces change within short iterations | Continuous adaptation with flexible WIP limits |
| Best Suited For | Teams needing high code quality and customer involvement | Teams seeking flexible workflow and incremental delivery |
Introduction to Extreme Programming (XP) and Scrumban
Extreme Programming (XP) emphasizes frequent releases in short development cycles, promoting high customer involvement and adaptive planning to improve software quality and responsiveness to changing requirements. Scrumban combines Scrum's structured sprint framework with Kanban's continuous workflow visualization, offering flexibility in managing work-in-progress and enhancing team productivity. Both methodologies prioritize collaboration and iterative progress but differ in workflow control and scheduling approaches for software development.
Core Principles of Extreme Programming
Extreme Programming (XP) emphasizes core principles such as continuous feedback, simplicity, and paired programming to enhance software quality and team collaboration. Its practices include test-driven development, frequent releases, and collective code ownership, reinforcing agility and responsiveness. In contrast, Scrumban blends Scrum's iterative planning with Kanban's workflow visualization, focusing more on flexible task management than XP's rigorous coding discipline.
Fundamental Concepts of Scrumban
Scrumban combines Scrum's structured sprints and roles with Kanban's continuous workflow and visual task management, emphasizing flexibility and efficiency in project delivery. It prioritizes work-in-progress limits, pull-based task management, and routine planning to reduce bottlenecks and enhance team productivity. This hybrid approach supports iterative development while allowing dynamic adjustment to changing priorities, making it ideal for teams seeking balance between predictability and adaptability.
Key Differences Between XP and Scrumban
Extreme Programming (XP) emphasizes engineering practices such as pair programming, test-driven development (TDD), continuous integration, and frequent releases to improve software quality and responsiveness. Scrumban combines Scrum's structured sprint planning and roles with Kanban's visual workflow and pull-based system, focusing on flexibility, continuous flow, and limiting work in progress (WIP). The key difference lies in XP's strong focus on engineering excellence and coding practices, whereas Scrumban prioritizes process adaptability and managing work items visually without fixed iteration lengths.
Team Roles and Responsibilities
Extreme Programming (XP) emphasizes distinct team roles including developers, a Customer (who provides continuous feedback), and a Coach to ensure adherence to XP practices, promoting collaborative ownership of code and pair programming. Scrumban merges Scrum's defined roles such as Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team with Kanban's flexible workflow, encouraging self-managed teams and fluid role responsibilities based on work-in-progress limits. Both methodologies prioritize team communication and adaptability, but XP focuses more on technical excellence with specific responsibilities while Scrumban adapts role duties to optimize flow and continuous delivery.
Workflow Management and Iteration Cycles
Extreme Programming (XP) emphasizes short, fixed iteration cycles typically lasting one to two weeks, promoting continuous feedback and iterative development through practices like pair programming and test-driven development. Scrumban combines Scrum's structured sprint planning with Kanban's flexible, continuous workflow, enabling teams to manage tasks on a visual board with WIP (Work In Progress) limits and adapt iteration lengths based on demand. Workflow management in XP is highly disciplined with clearly defined roles and prescribed practices, whereas Scrumban allows dynamic prioritization and flow control, facilitating smoother handling of changing requirements and varying team workloads.
Practices for Continuous Improvement
Extreme Programming (XP) practices for continuous improvement emphasize frequent iterations, pair programming, and continuous feedback loops to enhance software quality and team collaboration. Scrumban integrates Scrum's structured sprint reviews with Kanban's flexible workflow, enabling teams to adapt processes dynamically through visualized work and real-time metrics. Both methodologies prioritize iterative reflection and adaptation, but XP leans heavily on technical practices while Scrumban focuses on workflow optimization and gradual process evolution.
Suitability for Different Project Types
Extreme Programming (XP) excels in projects requiring rapid development cycles and frequent customer feedback, making it ideal for small to medium-sized software projects with evolving requirements. Scrumban combines Scrum's structure and Kanban's flexibility, suited for teams managing continuous workflows or projects with variable priorities and mixed workload. XP's emphasis on engineering practices like pair programming suits high-quality software development, whereas Scrumban adapts well to operational environments needing both predictability and adaptability.
Benefits and Challenges of XP and Scrumban
Extreme Programming (XP) enhances software quality and responsiveness through continuous feedback, pair programming, and test-driven development, but it faces challenges in strict adherence to practices and scalability in larger teams. Scrumban combines Scrum's structured sprint planning with Kanban's flexibility, improving workflow visualization and adaptability, though it may struggle with role clarity and less defined deadlines. Both methodologies offer distinct benefits for iterative development but require careful customization to team dynamics and project complexity.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Team
Extreme Programming (XP) emphasizes technical excellence with practices like pair programming and continuous integration, ideal for teams requiring high code quality and rapid feedback. Scrumban blends Scrum's structured sprint planning with Kanban's flexibility, making it suitable for teams needing adaptable workflows and continuous delivery. Selecting the right approach depends on your team's maturity, project complexity, and collaboration style, with XP favoring disciplined engineering and Scrumban supporting evolving project demands.
Extreme Programming (XP) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com