Efficient database storage is crucial for managing large volumes of data while ensuring quick access and retrieval. Optimizing storage solutions can improve your system's performance and reduce operational costs. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective strategies for enhancing your database storage.
Table of Comparison
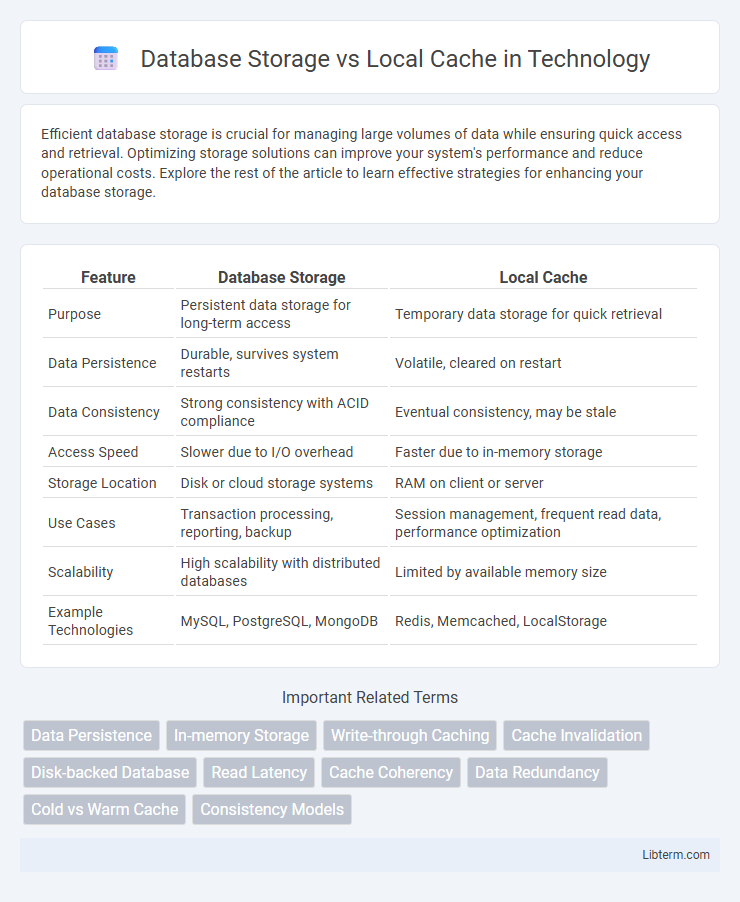
| Feature | Database Storage | Local Cache |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Persistent data storage for long-term access | Temporary data storage for quick retrieval |
| Data Persistence | Durable, survives system restarts | Volatile, cleared on restart |
| Data Consistency | Strong consistency with ACID compliance | Eventual consistency, may be stale |
| Access Speed | Slower due to I/O overhead | Faster due to in-memory storage |
| Storage Location | Disk or cloud storage systems | RAM on client or server |
| Use Cases | Transaction processing, reporting, backup | Session management, frequent read data, performance optimization |
| Scalability | High scalability with distributed databases | Limited by available memory size |
| Example Technologies | MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB | Redis, Memcached, LocalStorage |
Introduction to Database Storage and Local Cache
Database storage provides a scalable and persistent means of organizing and retrieving large volumes of structured data using systems like SQL and NoSQL databases. Local cache stores frequently accessed data temporarily in memory on the client side to reduce latency and improve application performance by minimizing direct database queries. Combining database storage with efficient local caching strategies is essential for optimizing data access speed and maintaining data consistency in modern applications.
Key Differences Between Database Storage and Local Cache
Database storage provides persistent, durable storage optimized for managing large volumes of structured data with ACID compliance, whereas local cache offers temporary, high-speed storage designed to reduce data retrieval latency by storing frequently accessed data closer to the application. Unlike local cache, which is volatile and often limited by client-side memory constraints, database storage ensures consistency and reliability across multiple users and sessions. The key differences lie in persistence, data volatility, scalability, and access speed, with database storage excelling in durability and consistency while local cache excels in performance optimization for read-heavy operations.
How Database Storage Works
Database storage works by organizing data into structured tables with rows and columns, utilizing indexing methods to enable efficient retrieval and management of large datasets. It employs transaction management and concurrency control to ensure data integrity and consistency in multi-user environments. Data is physically stored on hardware such as SSDs or HDDs, and database management systems (DBMS) optimize access speed through buffering and query optimization techniques.
How Local Cache Functions
Local cache functions by temporarily storing frequently accessed data in fast-access memory close to the application, reducing latency and improving retrieval speed compared to database storage. It operates through mechanisms like write-through or write-back policies to maintain consistency between the cache and the main database. By minimizing direct database queries, local cache enhances application performance and scalability under high-demand conditions.
Advantages of Using Database Storage
Database storage offers robust data persistence, ensuring information remains intact and accessible across sessions, which local cache cannot guarantee due to its volatile nature. It supports complex querying and data relationships, enabling scalable and structured data management essential for applications requiring consistency and integrity. Centralized storage in databases facilitates multi-user access and synchronization, improving collaboration and reducing data conflicts compared to isolated local caches.
Benefits of Implementing Local Cache
Implementing local cache significantly reduces data retrieval latency by storing frequently accessed information closer to the application, enhancing overall system performance. It decreases the load on the primary database, leading to improved scalability and reduced operational costs. Local caching also enhances user experience by providing faster access to data during offline scenarios or intermittent network connectivity.
Performance Comparison: Database vs Local Cache
Local cache offers significantly faster data retrieval times compared to database storage due to its in-memory nature, reducing latency from milliseconds to microseconds. Database storage provides durability and consistency, but accessing data often involves disk I/O, query processing, and network overhead, which can slow performance. Leveraging a local cache reduces the load on databases and improves application responsiveness by minimizing repeated database queries and accelerating read operations.
Common Use Cases for Database Storage and Cache
Database storage is commonly used for persistent data management in applications requiring reliable, long-term access to structured data such as user profiles, transaction records, and inventory lists. Local cache is typically employed to enhance performance by temporarily storing frequently accessed data, reducing latency in scenarios like session management, page rendering, and real-time analytics. Combining database storage with local cache optimizes both data durability and application responsiveness in high-traffic environments.
Data Consistency and Reliability Concerns
Database storage ensures high data consistency and reliability through ACID-compliant transactions that prevent data corruption and guarantee durability even during system failures. Local caches improve application performance by storing frequently accessed data closer to the user, but they introduce challenges with stale or inconsistent data due to synchronization delays. Implementing robust cache invalidation strategies and real-time synchronization mechanisms is essential to maintain consistency between the database and local cache layers.
Choosing the Right Solution for Your Application
Database storage provides persistent, centralized data management ideal for applications requiring durability, complex queries, and multi-user access. Local cache offers faster data retrieval by temporarily storing data closer to the application, reducing latency and server load in scenarios with frequent, repeatable reads. Selecting between database storage and local cache depends on data consistency needs, access speed priorities, and scalability requirements specific to the application's usage patterns.
Database Storage Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com