Serverless computing allows you to run applications without managing the underlying infrastructure, automatically scaling resources based on demand, which reduces operational complexity and costs. It enhances agility by enabling developers to focus solely on writing code, while cloud providers handle server maintenance, fault tolerance, and scaling. Discover how serverless can transform your development process and optimize your cloud strategy by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
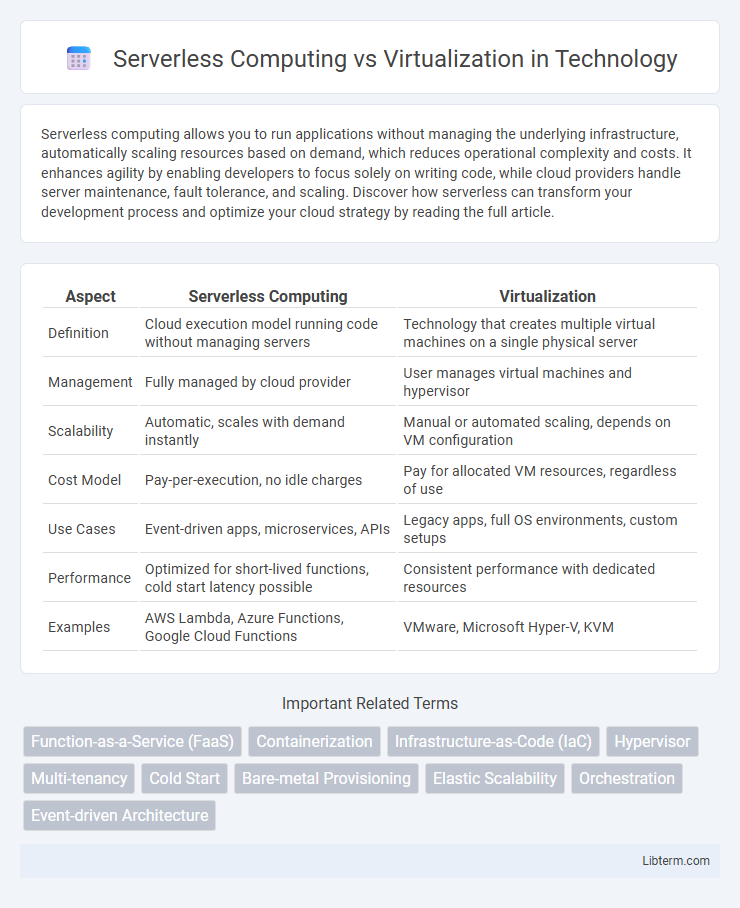
| Aspect | Serverless Computing | Virtualization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cloud execution model running code without managing servers | Technology that creates multiple virtual machines on a single physical server |
| Management | Fully managed by cloud provider | User manages virtual machines and hypervisor |
| Scalability | Automatic, scales with demand instantly | Manual or automated scaling, depends on VM configuration |
| Cost Model | Pay-per-execution, no idle charges | Pay for allocated VM resources, regardless of use |
| Use Cases | Event-driven apps, microservices, APIs | Legacy apps, full OS environments, custom setups |
| Performance | Optimized for short-lived functions, cold start latency possible | Consistent performance with dedicated resources |
| Examples | AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, Google Cloud Functions | VMware, Microsoft Hyper-V, KVM |
Introduction to Serverless Computing and Virtualization
Serverless computing enables developers to build and run applications without managing underlying servers, utilizing cloud providers' on-demand resource allocation to optimize scalability and cost efficiency. Virtualization abstracts physical hardware into multiple virtual machines, allowing better hardware utilization and isolation by running different operating systems on a single physical server. Both technologies enhance cloud infrastructure agility but address different layers: serverless focuses on application-level management, while virtualization concentrates on hardware resource partitioning.
Core Concepts: What Is Serverless? What Is Virtualization?
Serverless computing enables developers to run applications without managing the underlying servers, automatically scaling resources based on demand while billing only for actual usage. Virtualization involves creating multiple simulated environments or virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server, allowing isolated operating systems to run concurrently. Serverless focuses on abstracting infrastructure management, whereas virtualization emphasizes hardware resource partitioning for flexibility and efficiency.
Architecture Differences: Serverless vs Virtual Machines
Serverless computing architecture abstracts server management by executing functions on demand within ephemeral containers, eliminating the need for fixed infrastructure provisioning. In contrast, virtual machines (VMs) rely on hypervisors to run full guest operating systems on allocated physical hardware, requiring continuous resource allocation and maintenance. This fundamental architectural difference results in serverless offering greater scalability and resource efficiency compared to the resource-intensive, persistent environment of VMs.
Deployment and Scalability: Comparative Analysis
Serverless computing enables automatic scaling by abstracting server management, allowing seamless deployment of functions that execute on-demand without pre-provisioned infrastructure, leading to cost efficiency and agility. Virtualization relies on provisioning and managing virtual machines or containers, requiring manual scaling configurations and infrastructure maintenance, which can introduce latency in deployment and scalability adjustments. In terms of deployment speed and scalability, serverless computing offers higher elasticity and fine-grained resource allocation compared to virtualization's fixed resource allocation and slower scaling processes.
Resource Management and Efficiency
Serverless computing optimizes resource management by automatically scaling functions based on demand, eliminating the need for manual provisioning and reducing idle resource usage. Virtualization allocates resources through virtual machines, which may lead to overhead and fixed allocation inefficiencies compared to event-driven serverless models. The efficiency of serverless platforms stems from fine-grained billing and dynamic allocation, whereas virtualization often results in reserved resource capacities regardless of actual consumption.
Cost Implications: Pay-as-You-Go vs Fixed Infrastructure
Serverless computing offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model that charges based on actual usage, significantly reducing costs related to idle infrastructure and over-provisioning common in virtualization's fixed resource allocation. Virtualization requires upfront investment in physical servers and ongoing expenses for maintenance, regardless of workload fluctuations, leading to potentially higher fixed costs. Organizations benefit from serverless architectures by optimizing spending through dynamic scalability, while virtualization suits environments with predictable workloads and constant resource demands.
Security Considerations in Both Models
Serverless computing reduces the attack surface by abstracting infrastructure management, but it introduces risks related to multi-tenancy, function-level vulnerabilities, and limited control over underlying hardware security. Virtualization offers stronger isolation through hypervisor-enforced separation between virtual machines, enabling more granular security policies and better control over network segmentation and resource allocation. However, both models require rigorous patch management, identity and access management, and continuous monitoring to mitigate risks such as privilege escalation, side-channel attacks, and compliance violations.
Use Cases: When to Choose Serverless or Virtualization
Serverless computing is ideal for event-driven applications, microservices, and unpredictable workloads requiring automatic scaling and reduced operational management. Virtualization suits legacy applications, consistent workloads, and environments needing full OS control or customized infrastructure configurations. Organizations choose serverless for rapid development and cost efficiency, while virtualization is preferred for security, compliance, and complex enterprise systems.
Performance and Latency Comparison
Serverless computing offers dynamic resource allocation that reduces latency by scaling functions based on demand, minimizing idle times compared to virtualization's fixed resource allocation. Virtualization introduces overhead from hypervisor management, which can increase latency and reduce performance efficiency relative to serverless environments. Benchmarks indicate serverless architectures excel in event-driven, short-duration workloads, while virtualization provides more consistent performance for long-running, resource-intensive applications.
Future Trends in Serverless Computing and Virtualization
Future trends in serverless computing emphasize enhanced scalability, reduced latency through edge computing integration, and expanded support for diverse programming languages and frameworks. Virtualization continues to evolve with lightweight container technologies and improved resource isolation, enabling seamless hybrid cloud deployments. Both paradigms are converging toward greater automation, security enhancements, and cost efficiency to meet growing demands in distributed application architectures.
Serverless Computing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com