Service discovery enables automated detection of devices and services within a network, improving efficiency and reducing manual configuration. By leveraging protocols like DNS-SD or mDNS, it ensures seamless connectivity and dynamic resource allocation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how service discovery can optimize your network management.
Table of Comparison
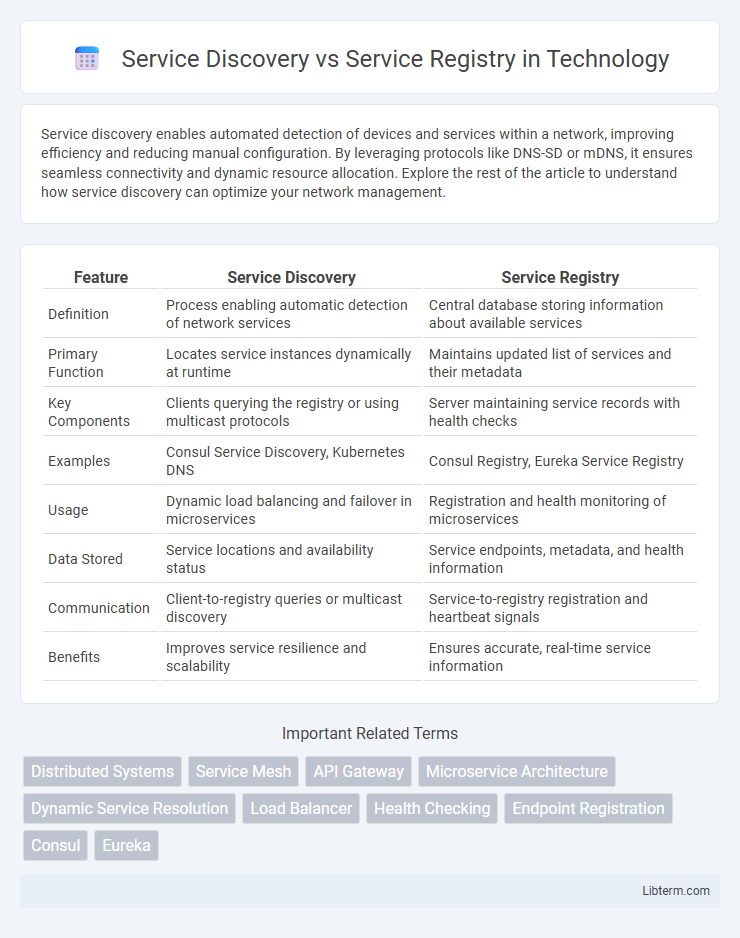
| Feature | Service Discovery | Service Registry |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Process enabling automatic detection of network services | Central database storing information about available services |
| Primary Function | Locates service instances dynamically at runtime | Maintains updated list of services and their metadata |
| Key Components | Clients querying the registry or using multicast protocols | Server maintaining service records with health checks |
| Examples | Consul Service Discovery, Kubernetes DNS | Consul Registry, Eureka Service Registry |
| Usage | Dynamic load balancing and failover in microservices | Registration and health monitoring of microservices |
| Data Stored | Service locations and availability status | Service endpoints, metadata, and health information |
| Communication | Client-to-registry queries or multicast discovery | Service-to-registry registration and heartbeat signals |
| Benefits | Improves service resilience and scalability | Ensures accurate, real-time service information |
Introduction to Service Discovery and Service Registry
Service Discovery enables dynamic detection and interaction between microservices by automatically identifying service instances and their network locations in real-time. Service Registry acts as the authoritative database where service instances register, providing updated metadata, health status, and endpoints to facilitate efficient discovery. Together, Service Discovery and Service Registry simplify service communication, load balancing, and fault tolerance in distributed systems.
Understanding Service Discovery: Definition and Purpose
Service Discovery enables dynamic detection and connection of microservices within a distributed system, improving scalability and fault tolerance. It functions by using a Service Registry, a centralized database that stores information about service instances and their network locations. The primary purpose of Service Discovery is to ensure seamless communication between services without hard-coded addresses, facilitating efficient load balancing and service availability.
What is a Service Registry?
A Service Registry is a centralized database that stores information about available services, including their network locations and metadata, enabling dynamic service discovery in microservices architecture. It maintains real-time service instance health and status, allowing clients to efficiently locate and connect to the appropriate service endpoints. Common Service Registry implementations include Consul, Eureka, and ZooKeeper, which facilitate seamless service communication and load balancing.
Key Differences Between Service Discovery and Service Registry
Service discovery automates the process of locating services within a network, enabling dynamic communication between microservices by resolving service instances at runtime. Service registry acts as a centralized database that maintains a continuously updated list of available service instances and their network locations, serving as a reference point for service discovery. The key difference lies in service discovery performing the active lookup and routing, while the service registry provides the authoritative source of service metadata that supports this dynamic resolution.
How Service Discovery Works in Microservices Architecture
Service discovery in microservices architecture automatically detects and manages service instances, enabling efficient communication between distributed services. It operates by querying a centralized service registry, where each microservice periodically registers its location, status, and metadata to ensure accurate and up-to-date routing information. This dynamic lookup mechanism facilitates load balancing, fault tolerance, and seamless scaling in complex, containerized environments like Kubernetes or Docker Swarm.
The Role of Service Registry in Modern Systems
Service Registry acts as a dynamic database that maintains the locations and statuses of microservices, enabling efficient service discovery in modern distributed architectures. It allows services to register themselves on startup and deregister upon shutdown, ensuring real-time updates on available service instances. This mechanism is crucial for load balancing, fault tolerance, and seamless service-to-service communication in microservices ecosystems.
Centralized vs Decentralized Service Discovery
Centralized service discovery relies on a service registry where all instances register their locations, enabling clients to query a single authoritative source for service information, which simplifies management but may create a single point of failure. Decentralized service discovery distributes the responsibility across multiple nodes, often using peer-to-peer protocols or gossip mechanisms, enhancing fault tolerance and scalability while increasing system complexity. Choosing between centralized and decentralized approaches depends on factors like system size, fault tolerance requirements, and network topology.
Popular Tools for Service Discovery and Registry
Service discovery and service registry are critical components in microservices architecture, with popular tools like Consul, Eureka, and ZooKeeper leading the space. Consul provides both service registry and discovery with health checking features, while Netflix Eureka specializes in REST-based service registration and discovery optimized for AWS environments. Apache ZooKeeper offers a robust, distributed coordination service often used for maintaining configuration and naming in service registries to ensure high availability and consistency.
Best Practices for Implementing Service Discovery and Registry
Service Discovery relies on dynamic routing mechanisms to locate services, while a Service Registry acts as a central repository maintaining real-time service metadata. Best practices include implementing health checks in the Service Registry to ensure accurate service availability, using consistent naming conventions for services, and leveraging automated updates to reduce manual errors. Ensuring scalability and fault tolerance through distributed registries and client-side caching enhances performance and reliability in microservices environments.
Choosing Between Service Discovery and Service Registry: Key Considerations
Choosing between service discovery and service registry requires evaluating system architecture, scalability, and operational complexity. Service registries act as centralized databases for service metadata, essential for environments with dynamic service instances and frequent changes. Service discovery mechanisms, often integrated with registries, enable clients to locate services in real-time, supporting high availability and load balancing in microservices ecosystems.
Service Discovery Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com