Shadow deployment enables seamless software updates by running new versions alongside current systems without disruption. This technique allows you to test functionality and performance in a live environment, minimizing risks before full rollout. Explore the rest of the article to understand how shadow deployment can enhance your development process.
Table of Comparison
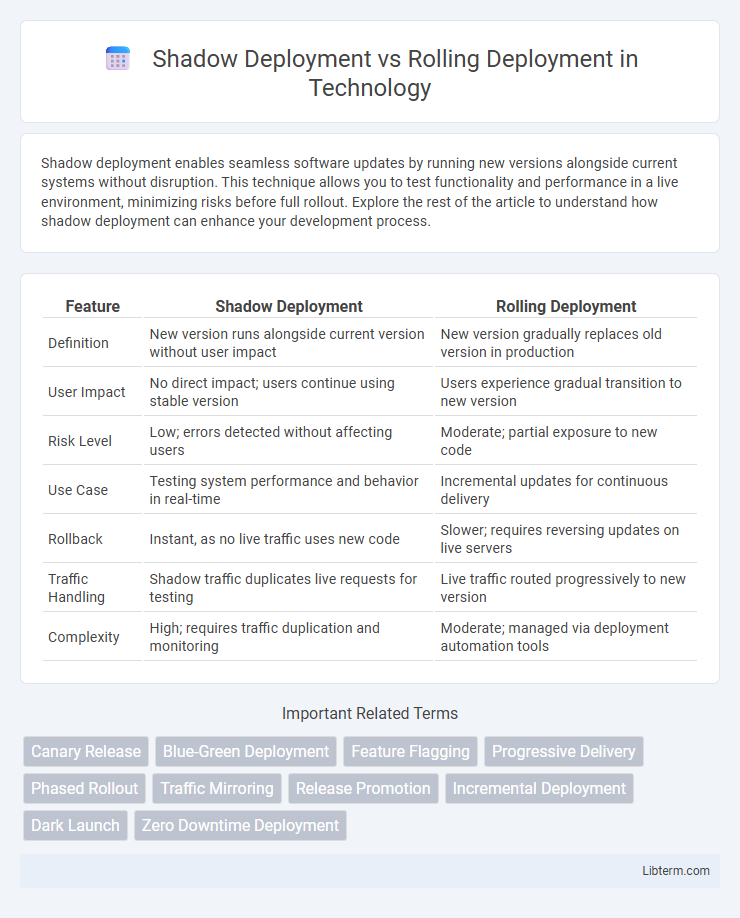
| Feature | Shadow Deployment | Rolling Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | New version runs alongside current version without user impact | New version gradually replaces old version in production |
| User Impact | No direct impact; users continue using stable version | Users experience gradual transition to new version |
| Risk Level | Low; errors detected without affecting users | Moderate; partial exposure to new code |
| Use Case | Testing system performance and behavior in real-time | Incremental updates for continuous delivery |
| Rollback | Instant, as no live traffic uses new code | Slower; requires reversing updates on live servers |
| Traffic Handling | Shadow traffic duplicates live requests for testing | Live traffic routed progressively to new version |
| Complexity | High; requires traffic duplication and monitoring | Moderate; managed via deployment automation tools |
Understanding Shadow Deployment
Shadow deployment involves releasing a new version of software alongside the current production environment without affecting live traffic or user experience, enabling real-time performance comparisons and early detection of issues. This method allows teams to validate changes under actual conditions by mirroring user requests to the new version without impacting end users. It provides a safe way to test updates with minimal risk before fully rolling out, contrasting with rolling deployment's phased traffic shifting across versions.
What Is Rolling Deployment?
Rolling deployment is a software release strategy that gradually updates application instances with new versions without downtime, ensuring continuous service availability. This method replaces old instances incrementally, minimizing risk by allowing immediate rollback if issues occur. Compared to shadow deployment, rolling deployment directly shifts traffic to updated versions rather than running new code alongside existing production environments.
Key Differences Between Shadow and Rolling Deployment
Shadow deployment tests new code by running it alongside the current version without exposing users to changes, ensuring real-time comparison and error detection without user impact. Rolling deployment gradually replaces instances of the old version with the new one across the environment, minimizing downtime and enabling phased rollout. Key differences include user exposure, risk management--shadow deployment avoids user impact, while rolling deployment balances gradual update with limited disruption--and monitoring focus, with shadow emphasizing parallel testing and rolling on sequential release.
Pros and Cons of Shadow Deployment
Shadow deployment allows testing new software versions by running them concurrently with the current production system without impacting live user traffic, ensuring thorough validation under real-world conditions. Its advantages include risk mitigation, as it exposes issues before full release, and the ability to gather valuable performance and error data without affecting customers. However, it requires significant infrastructure resources to run parallel environments and can increase operational complexity due to simultaneous management of multiple system versions.
Advantages and Limitations of Rolling Deployment
Rolling deployment offers continuous updates by gradually replacing instances of an application, minimizing downtime and reducing the risk of system failures. This approach allows for easy rollback if issues arise, ensuring stability and enhanced user experience. However, it may consume more time and resources due to the sequential update process and can complicate troubleshooting when multiple versions run simultaneously.
Use Cases for Shadow Deployment
Shadow deployment is ideal for testing new features or updates in a live environment without affecting the user experience, allowing real-time traffic to be mirrored to the new version. It is commonly used for validating system performance, reliability, and impact on backend services before full release. This strategy helps identify potential issues in complex architectures such as microservices or large-scale cloud environments without risking downtime.
When to Choose Rolling Deployment
Rolling deployment is ideal when minimizing downtime and ensuring system stability during updates is critical, particularly in environments with continuous user interaction such as e-commerce platforms or SaaS applications. This strategy gradually replaces instances with new versions, allowing instant rollback if issues arise, making it suitable for organizations with mature monitoring and quick response capabilities. Choose rolling deployment when maintaining user experience without complete service disruption is a priority and incremental updates align with the operational risk tolerance.
Impact on System Reliability and Performance
Shadow deployment allows new code to run alongside the existing system without impacting live traffic, minimizing risks to system reliability while enabling performance evaluation in real-world conditions. Rolling deployment updates subsets of servers progressively, providing controlled exposure to changes and allowing rapid rollback if performance degradation or failures occur. Both strategies mitigate downtime, but shadow deployment offers safer testing environments, whereas rolling deployment balances continuous availability with incremental updates, directly influencing system stability and user experience.
Best Practices for Deployment Strategies
Shadow deployment enables running new software versions alongside live traffic without impacting users, facilitating real-time monitoring and validation, which minimizes risk during releases. Rolling deployment gradually replaces old instances with new ones in controlled batches, ensuring continuous service availability and quick rollback if problems arise. Combining thorough automated testing, detailed monitoring, and incremental rollout phases establishes best practices for both strategies to enhance reliability and reduce deployment failures.
Selecting the Right Deployment Approach
Choosing the right deployment approach depends on factors like risk tolerance, system complexity, and user impact. Shadow deployment allows for testing new features in a live environment without affecting production traffic, ideal for validating changes with minimal risk. Rolling deployment updates servers incrementally, ensuring continuous service availability and is best suited for systems requiring zero downtime during releases.
Shadow Deployment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com