A/B testing compares two versions of a web page or app to determine which performs better based on user interactions and conversion rates. This method enables data-driven decisions that enhance user experience and increase overall efficiency. Discover actionable insights and strategies by reading the full article on optimizing your A/B testing process.
Table of Comparison
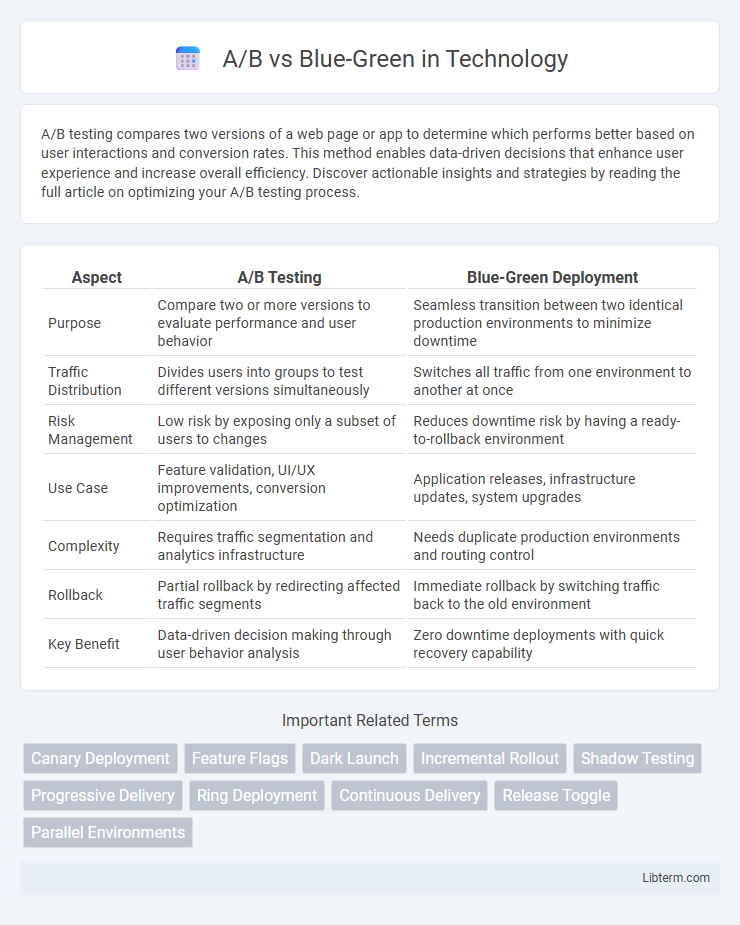
| Aspect | A/B Testing | Blue-Green Deployment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Compare two or more versions to evaluate performance and user behavior | Seamless transition between two identical production environments to minimize downtime |
| Traffic Distribution | Divides users into groups to test different versions simultaneously | Switches all traffic from one environment to another at once |
| Risk Management | Low risk by exposing only a subset of users to changes | Reduces downtime risk by having a ready-to-rollback environment |
| Use Case | Feature validation, UI/UX improvements, conversion optimization | Application releases, infrastructure updates, system upgrades |
| Complexity | Requires traffic segmentation and analytics infrastructure | Needs duplicate production environments and routing control |
| Rollback | Partial rollback by redirecting affected traffic segments | Immediate rollback by switching traffic back to the old environment |
| Key Benefit | Data-driven decision making through user behavior analysis | Zero downtime deployments with quick recovery capability |
Introduction to A/B and Blue-Green Deployment
A/B deployment involves running two versions of an application simultaneously to test user responses and performance, enabling data-driven decision-making for feature rollout. Blue-Green deployment maintains two identical production environments, switching traffic between them to achieve zero-downtime releases and streamlined rollback capabilities. Both techniques optimize software delivery, with A/B emphasizing experimentation and Blue-Green focusing on seamless production updates.
Defining A/B Deployment
A/B deployment involves releasing two distinct versions of an application simultaneously to different user segments to test variations and measure performance, user engagement, or conversion rates. This method contrasts with blue-green deployment, which switches traffic between two identical production environments to enable zero-downtime updates and rollback capabilities. A/B testing emphasizes experimentation and data-driven decisions, while blue-green deployment prioritizes stability and seamless transitions.
Understanding Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-Green Deployment involves maintaining two identical production environments, where one (Blue) serves live traffic while the other (Green) is updated and tested before switching traffic to it, minimizing downtime and risk. This strategy enhances release reliability by enabling instant rollback to the previous environment if issues arise, contrasting with A/B testing that splits traffic for feature comparison rather than deployment safety. Understanding Blue-Green Deployment is essential for seamless continuous delivery, ensuring zero-downtime releases and efficient risk management in software development.
Key Differences Between A/B and Blue-Green
A/B testing involves comparing two or more variants simultaneously to determine which performs better based on user interactions, while Blue-Green deployment focuses on reducing downtime by running two identical production environments where one is active and the other is idle. A/B testing prioritizes user experience and data-driven decision-making, whereas Blue-Green deployment emphasizes seamless releases and rollback capabilities. The key difference lies in A/B testing's role in experimentation and conversion optimization compared to Blue-Green's strategy for safe and reliable software deployment.
Benefits of A/B Deployment
A/B deployment enables precise measurement of user behavior by splitting traffic between multiple versions, facilitating data-driven decisions to optimize features and UI elements. It reduces risk by gradually rolling out changes and quickly identifying underperforming variants without impacting the entire user base. This approach enhances conversion rates and user satisfaction by providing direct insight into preferences and performance metrics.
Advantages of Blue-Green Deployment
Blue-Green Deployment minimizes downtime and risk by maintaining two identical production environments, allowing instant switching between them during updates. It enables thorough testing of new releases in a live environment without affecting users, ensuring smoother rollbacks if issues arise. This approach enhances deployment reliability and user experience compared to traditional A/B testing, which splits traffic and may expose users to unstable features.
Use Cases: When to Choose A/B or Blue-Green
A/B testing excels in scenarios requiring experimentation with multiple variations to optimize user experience, such as website design or marketing campaigns, providing granular insights into user preferences. Blue-Green deployment is ideal for seamless, low-risk production updates in applications demanding high availability, like database migrations or critical service upgrades, by maintaining two identical environments to minimize downtime. Organizations should choose A/B testing for iterative feature validation and Blue-Green for safe, immediate version switching in live systems.
Technical Requirements and Best Practices
A/B testing requires consistent traffic segmentation, precise feature flagging, and robust analytics tracking to compare variations effectively, while Blue-Green deployment demands synchronized environments, database schema compatibility, and seamless traffic switching mechanisms to minimize downtime. Use feature toggles to control experiment exposure in A/B tests, and implement automated deployment pipelines with health checks for Blue-Green releases to ensure reliability. Monitoring performance metrics and rollback strategies are critical in both approaches to maintain service stability and optimize user experience.
Common Challenges and Solutions
A/B and Blue-Green deployment strategies often face common challenges such as traffic routing complexities, data consistency issues, and rollback difficulties. Implementing feature flags and automated monitoring tools helps streamline traffic segmentation and detect failures early, while robust database versioning ensures data integrity across deployments. Leveraging infrastructure as code (IaC) and continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines provides efficient rollback mechanisms and reduces human error during transitions.
Conclusion: Which Deployment Strategy Is Right for You?
Choosing between A/B and Blue-Green deployment depends on your application's complexity and risk tolerance; A/B testing excels in user experience optimization by gradually rolling out features to distinct user groups, while Blue-Green deployment ensures near-zero downtime and rapid rollback by maintaining two identical production environments. For high-availability systems requiring minimal disruption, Blue-Green deployment is optimal, whereas A/B testing suits scenarios demanding detailed user behavior analysis and iterative feature validation. Evaluating factors like infrastructure costs, deployment frequency, and error tolerance guides the decision toward the most effective continuous delivery strategy.
A/B Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com