QR codes offer a fast and efficient way to connect users with information, products, or services by simply scanning with a smartphone. These versatile codes enhance marketing strategies, streamline payments, and improve access to essential details without manual input. Explore the rest of this article to discover how QR codes can elevate your digital interactions and business solutions.
Table of Comparison
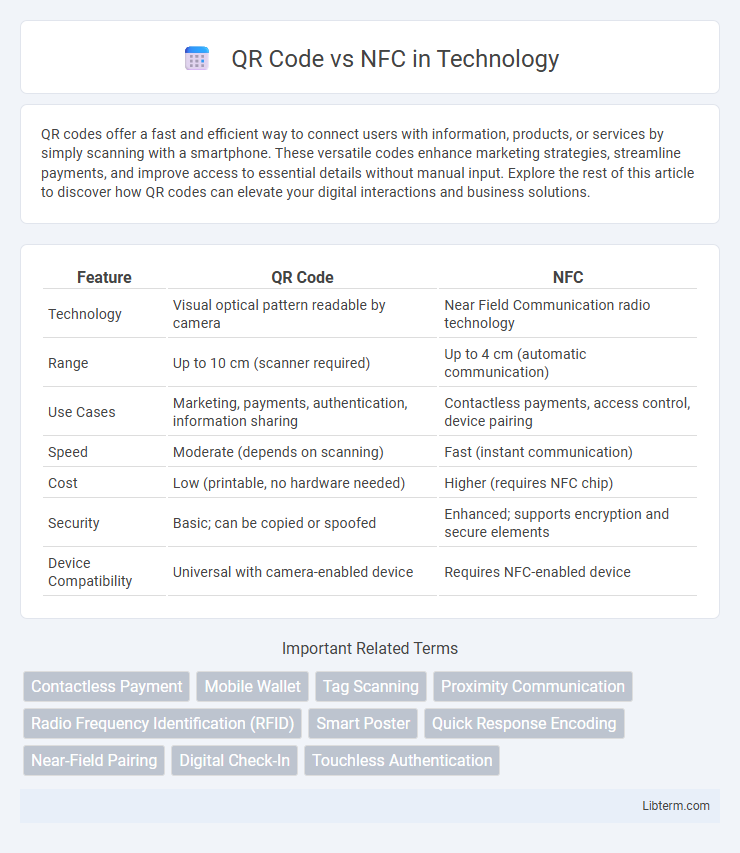
| Feature | QR Code | NFC |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | Visual optical pattern readable by camera | Near Field Communication radio technology |
| Range | Up to 10 cm (scanner required) | Up to 4 cm (automatic communication) |
| Use Cases | Marketing, payments, authentication, information sharing | Contactless payments, access control, device pairing |
| Speed | Moderate (depends on scanning) | Fast (instant communication) |
| Cost | Low (printable, no hardware needed) | Higher (requires NFC chip) |
| Security | Basic; can be copied or spoofed | Enhanced; supports encryption and secure elements |
| Device Compatibility | Universal with camera-enabled device | Requires NFC-enabled device |
Introduction to QR Code and NFC
QR Code technology uses a matrix barcode that can be scanned by smartphones to quickly access information, websites, or perform transactions. NFC (Near Field Communication) enables secure, contactless data exchange between devices within a short range, commonly used for mobile payments and access control. Both technologies enhance user convenience but differ in interaction method and data transmission speed.
How QR Codes Work
QR codes function through a matrix of black and white squares that encode data, which smartphones or QR scanners decode by capturing the image and interpreting the patterns using error correction algorithms. When scanned, the QR code directs the device to specific information, such as URLs, contact details, or payment instructions, making it a versatile tool for quick information transfer. Unlike NFC, which requires close proximity and hardware-enabled communication, QR codes rely solely on optical recognition and can be scanned from a distance or displayed on various surfaces.
How NFC Technology Works
NFC technology operates through electromagnetic fields to enable wireless communication between two devices within a range of a few centimeters. It uses radio frequency identification (RFID) standards to seamlessly exchange data when devices come into close contact, allowing instant pairing and secure transactions. This proximity-based functionality makes NFC ideal for contactless payments, access control, and data sharing without the need for scanning or line-of-sight alignment like QR codes.
Comparison of QR Code vs NFC: Key Differences
QR Code uses optical scanning technology requiring a camera to read printed codes, while NFC relies on radio frequency communication enabling contactless data exchange within a short range. QR Codes are easier and cheaper to implement across various surfaces, but NFC offers faster interactions and enhanced security through encryption. The choice between QR Code and NFC depends on factors like user experience, cost, range, and intended application functionality.
Security Features: QR Code vs NFC
NFC technology offers enhanced security features through encrypted communication and secure elements that protect data during wireless transactions, making it ideal for contactless payments and sensitive information exchange. QR codes, while widely accessible and easy to scan, are vulnerable to phishing attacks and misdirection due to the static nature of the encoded data and lack of built-in encryption. Implementing dynamic QR codes and secure backend verification can mitigate some risks, but NFC inherently provides stronger protection against data interception and fraud.
User Experience and Accessibility
QR codes offer quick access by requiring only a smartphone camera, making them widely accessible across devices without specialized hardware. NFC provides a seamless tap-to-connect experience, eliminating the need to align or scan, which enhances convenience for users familiar with the technology. However, QR codes have broader compatibility, as NFC functionality is limited to devices equipped with specialized NFC chips.
Cost and Implementation
QR codes offer an affordable, low-cost solution requiring only a printed code and a smartphone camera, making implementation simple and accessible for small businesses. NFC technology involves higher initial expenses due to the need for specialized chips and compatible devices, limiting widespread adoption in cost-sensitive environments. Cost-effectiveness of QR codes is enhanced by easy scalability and minimal hardware requirements, whereas NFC delivers faster interactions and enhanced security at a premium.
Popular Use Cases for QR Code and NFC
QR codes are widely used for contactless payments, digital menus in restaurants, and product tracking in retail, leveraging smartphone cameras for quick access. NFC technology powers mobile wallets like Apple Pay and Google Pay, public transit ticketing systems, and access control in secure buildings due to its close-range wireless communication. Both technologies enhance user convenience in marketing campaigns and inventory management through seamless data exchange and authentication.
Future Trends in Contactless Technologies
Future trends in contactless technologies indicate that NFC (Near Field Communication) will expand its role in secure, seamless transactions and smart device interactions due to its encrypted data transfer and user convenience. QR Codes continue to evolve with dynamic and customized solutions, enabling enhanced marketing engagement, contactless payments, and authentication processes through easy integration and smartphone compatibility. Hybrid systems combining QR Code scanning with NFC-enabled devices are emerging, offering versatile, efficient, and user-friendly contactless experiences across retail, transportation, and healthcare sectors.
Choosing the Right Technology: QR Code or NFC?
Choosing between QR Code and NFC depends on factors such as user convenience, cost, and device compatibility. QR Codes are inexpensive, require only a smartphone camera, and work universally across different devices, making them ideal for broad user engagement. NFC offers faster, contactless interactions and enhanced security but requires NFC-enabled devices, limiting accessibility compared to QR Codes.
QR Code Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com