A gateway device acts as a critical link between different networks, enabling seamless communication and data transfer. It translates protocols and manages traffic to ensure your systems stay interconnected and efficient. Explore the rest of the article to understand how gateway devices enhance network functionality and security.
Table of Comparison
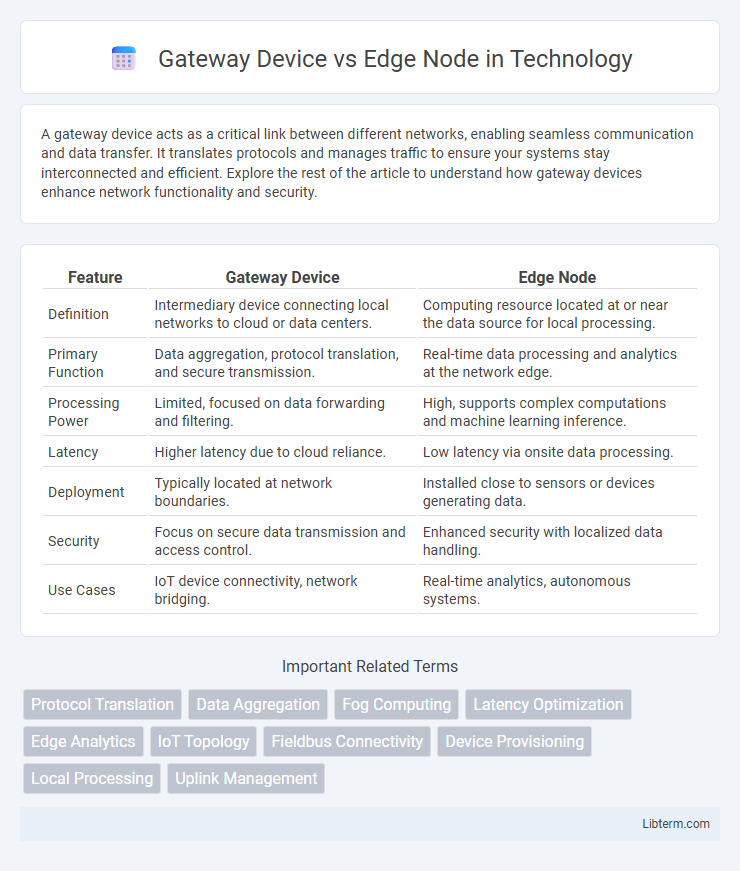
| Feature | Gateway Device | Edge Node |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Intermediary device connecting local networks to cloud or data centers. | Computing resource located at or near the data source for local processing. |
| Primary Function | Data aggregation, protocol translation, and secure transmission. | Real-time data processing and analytics at the network edge. |
| Processing Power | Limited, focused on data forwarding and filtering. | High, supports complex computations and machine learning inference. |
| Latency | Higher latency due to cloud reliance. | Low latency via onsite data processing. |
| Deployment | Typically located at network boundaries. | Installed close to sensors or devices generating data. |
| Security | Focus on secure data transmission and access control. | Enhanced security with localized data handling. |
| Use Cases | IoT device connectivity, network bridging. | Real-time analytics, autonomous systems. |
Introduction to Gateway Devices and Edge Nodes
Gateway devices serve as critical intermediaries that connect local networks to external systems, facilitating data transfer and protocol translation for IoT and industrial applications. Edge nodes function as decentralized computing units positioned near data sources to process information locally, reducing latency and bandwidth usage. Both gateway devices and edge nodes enhance network efficiency but differ in their roles, with gateways primarily managing communication and edge nodes focusing on real-time data analytics and processing.
Key Differences Between Gateway Devices and Edge Nodes
Gateway devices serve as centralized conduits that aggregate data from multiple edge nodes, enabling protocol translation and forwarding information between local networks and cloud services. Edge nodes perform localized data processing and analytics closer to the source of data generation, reducing latency and bandwidth usage by filtering or summarizing information before transmission. Key differences include gateway devices primarily managing communication and network integration, while edge nodes focus on computational tasks at the network periphery.
Core Functions of Gateway Devices
Gateway devices primarily perform protocol translation, data aggregation, and security enforcement to connect heterogeneous IoT devices with cloud platforms. They manage data preprocessing and filtering, reducing bandwidth usage and ensuring efficient communication between edge devices and central systems. Core functions include device management, network connectivity, and real-time analytics, enabling robust and scalable IoT architectures.
Essential Roles of Edge Nodes
Edge nodes serve as critical intermediaries in IoT architectures by processing data locally to reduce latency and bandwidth usage, enabling real-time decision-making closer to data sources. Unlike gateway devices that primarily facilitate connectivity and protocol translation, edge nodes execute analytics, data filtering, and device management at the network's periphery. This local intelligence optimizes network efficiency, enhances security by minimizing data transmission, and supports scalable, robust IoT deployments.
Data Processing: Gateway Device vs Edge Node
Gateway devices primarily perform data aggregation, protocol translation, and preliminary filtering to reduce the volume of data sent to the cloud, enabling efficient data transmission. Edge nodes execute real-time data processing, analytics, and decision-making closer to the data source, minimizing latency and enhancing responsiveness. The key distinction lies in that gateway devices focus on connectivity and data routing, while edge nodes emphasize localized computation and autonomous control.
Network Architecture and Connectivity
Gateway devices serve as centralized hubs connecting multiple edge nodes to broader networks, managing data aggregation, protocol translation, and secure communication. Edge nodes operate at the network periphery, collecting and processing data locally to reduce latency and bandwidth usage before transmitting to the gateway. This hierarchical network architecture enhances scalability and efficiency by distributing processing tasks between edge nodes and gateways.
Security Features Comparison
Gateway devices offer robust security features such as built-in firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption to protect centralized data flow between IoT devices and cloud services. Edge nodes emphasize decentralized security by enabling localized data processing, reducing attack surfaces, and supporting endpoint authentication and secure boot mechanisms. Comparing security, gateway devices provide comprehensive perimeter defense, while edge nodes enhance protection through distributed, real-time anomaly detection and minimized data exposure.
Scalability and Deployment Scenarios
Gateway devices offer centralized data processing and protocol translation, making them ideal for small to medium IoT deployments where managing device connectivity and security is critical. Edge nodes provide decentralized computing power closer to data sources, enhancing scalability by distributing workloads across numerous devices in large-scale, latency-sensitive industrial or smart city applications. Deployment scenarios for gateway devices typically involve controlled environments with fewer sensors, while edge nodes are preferred in expansive networks requiring real-time analytics and high fault tolerance.
Use Cases: When to Choose Gateway Devices or Edge Nodes
Gateway devices are ideal for aggregating data from multiple sensors in industrial IoT settings where real-time data preprocessing and protocol translation are required to reduce cloud dependency. Edge nodes suit scenarios needing advanced analytics and AI inference directly on-site, such as autonomous vehicles or smart surveillance systems, enabling low-latency decision-making. Choose gateway devices when connectivity management and data filtering dominate, while edge nodes are preferable for computationally intensive tasks at the network edge.
Future Trends in IoT: Gateways and Edge Nodes
Future trends in IoT emphasize the increasing convergence of gateway devices and edge nodes, driven by advancements in AI, 5G connectivity, and real-time data processing capabilities. Gateway devices are evolving to support enhanced security protocols and multi-protocol communication, enabling seamless integration between cloud platforms and diverse IoT sensors. Edge nodes are becoming more autonomous with improved computational power and machine learning algorithms, facilitating faster decision-making and reducing latency for critical applications in smart cities, industrial automation, and autonomous vehicles.
Gateway Device Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com