Intrusion detection systems monitor network traffic to identify unauthorized access or malicious activities, enhancing your cybersecurity defenses. These systems analyze patterns and anomalies, providing real-time alerts to prevent potential breaches. Explore the rest of the article to understand how intrusion detection can safeguard your digital environment effectively.
Table of Comparison
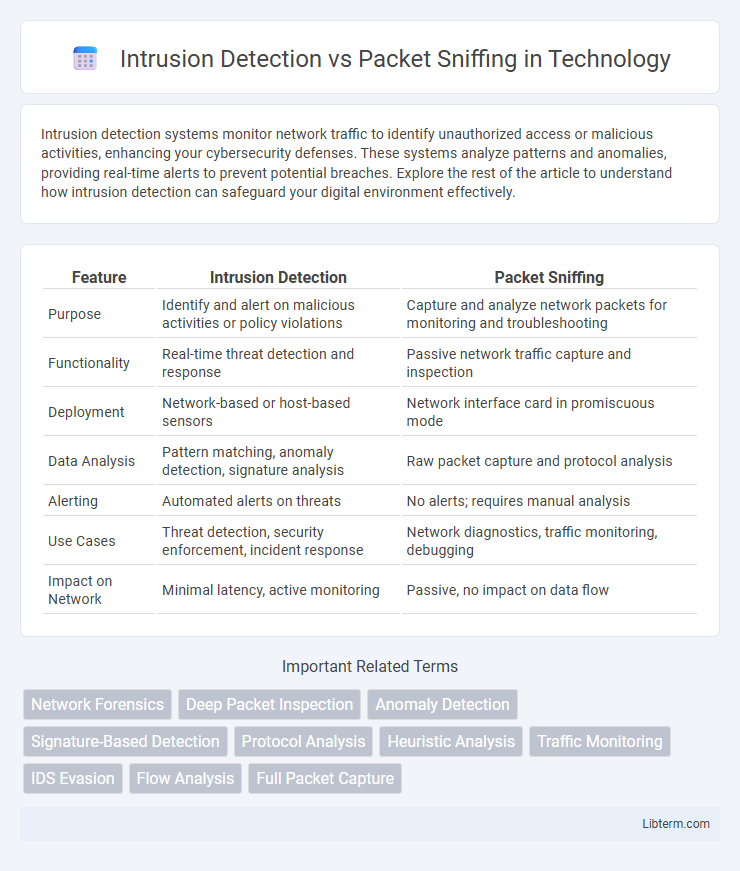
| Feature | Intrusion Detection | Packet Sniffing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify and alert on malicious activities or policy violations | Capture and analyze network packets for monitoring and troubleshooting |
| Functionality | Real-time threat detection and response | Passive network traffic capture and inspection |
| Deployment | Network-based or host-based sensors | Network interface card in promiscuous mode |
| Data Analysis | Pattern matching, anomaly detection, signature analysis | Raw packet capture and protocol analysis |
| Alerting | Automated alerts on threats | No alerts; requires manual analysis |
| Use Cases | Threat detection, security enforcement, incident response | Network diagnostics, traffic monitoring, debugging |
| Impact on Network | Minimal latency, active monitoring | Passive, no impact on data flow |
Introduction to Intrusion Detection and Packet Sniffing
Intrusion detection involves monitoring network traffic and system activities to identify suspicious behavior and potential security breaches using tools like IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems). Packet sniffing captures and analyzes data packets transmitted over a network to monitor and troubleshoot network communication or gather information for security analysis. IDS focuses on detecting and responding to malicious activity, whereas packet sniffing primarily serves as a data collection and analysis method.
Defining Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are specialized security tools designed to monitor network traffic or system activities for malicious actions or policy violations. Unlike packet sniffing, which captures and analyzes raw data packets without inherent threat identification, IDS employ signature-based or anomaly-based techniques to detect unauthorized intrusions in real time. IDS play a crucial role in proactive cybersecurity by alerting administrators to potential threats and enabling prompt incident response.
What is Packet Sniffing?
Packet sniffing is the process of capturing and analyzing data packets transmitted over a network to monitor and troubleshoot network traffic. Unlike intrusion detection systems that identify and respond to malicious activities, packet sniffers passively collect data for inspection without actively blocking threats. Common tools like Wireshark enable detailed examination of packet headers and payloads, aiding in diagnosing network issues and detecting unauthorized communication.
Key Differences Between IDS and Packet Sniffing
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) analyze network traffic to identify potential security threats by detecting malicious activities or policy violations, whereas packet sniffing passively captures and monitors data packets without inherently identifying threats. IDS uses signature-based or anomaly-based detection techniques to provide real-time alerts, while packet sniffing tools primarily facilitate traffic analysis or troubleshooting without automated threat detection. The key difference lies in IDS's proactive threat identification and response capabilities compared to the passive data collection function of packet sniffers.
Common Use Cases and Applications
Intrusion detection systems (IDS) primarily monitor network traffic for suspicious activities and known attack patterns, making them essential for real-time threat prevention in enterprise security environments. Packet sniffing is commonly used for network performance analysis, troubleshooting, and capturing data packets to diagnose connectivity issues or understand traffic flow. IDS applications include compliance monitoring and incident response, while packet sniffers are vital tools for network administrators and cybersecurity analysts conducting deep packet inspection and protocol analysis.
Detection Techniques and Methodologies
Intrusion Detection systems rely on signature-based and anomaly-based techniques to analyze network traffic for patterns indicative of malicious activity, using methods such as deep packet inspection and behavioral analysis to detect threats. Packet sniffing captures and inspects raw data packets on a network but does not inherently analyze or identify threats, serving primarily as a data collection method. Intrusion detection methodologies integrate real-time monitoring, correlation of events, and automated alerting to proactively identify and respond to security incidents.
Security Implications and Risks
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) actively analyze network traffic to identify and respond to malicious activities, offering real-time threat detection and mitigation, whereas packet sniffing passively captures data packets without direct threat response capabilities. IDS can detect anomalies and signature-based attacks, reducing the risk of security breaches, while packet sniffers, if misused, pose privacy risks by exposing sensitive data and enabling potential unauthorized monitoring. Effective network security requires combining IDS for proactive defense with controlled packet sniffing to monitor and troubleshoot network traffic safely.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
Intrusion Detection systems offer real-time monitoring and alerting capabilities, enabling proactive identification of malicious activities, but they can generate false positives and require significant computational resources. Packet Sniffing provides detailed packet-level analysis useful for troubleshooting and forensic investigations, though it lacks automated threat detection and can be overwhelmed by high network traffic volumes. Combining both approaches enhances network security by leveraging the comprehensive visibility of packet sniffing alongside the active defense mechanisms of intrusion detection.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Network
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) proactively monitor network traffic for suspicious activities, providing real-time alerts to prevent cyber threats, while packet sniffing tools capture and analyze raw data packets for detailed inspection and troubleshooting. Selecting the right tool depends on your network security needs: IDS is essential for detecting and responding to potential intrusions, whereas packet sniffers are best suited for in-depth traffic analysis and debugging. Understanding your network's vulnerability profile and traffic complexity ensures optimal deployment of IDS or packet sniffing to maintain robust security and performance.
Future Trends in Network Security Monitoring
Intrusion Detection systems leverage advanced machine learning algorithms and behavioral analytics for proactive threat identification, surpassing traditional Packet Sniffing techniques that primarily capture and analyze raw network traffic. Future trends emphasize the integration of AI-driven anomaly detection and real-time threat intelligence sharing to enhance the accuracy and speed of network security monitoring. The evolution towards automated, adaptive security frameworks will significantly reduce false positives and improve response times in dynamic network environments.
Intrusion Detection Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com